| Algorithm Type | Process Description | Type of Data Used | Legal Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-Based Decision Making | If condition fulfilled then activity 1 else activity 2 | Boolean data (yes or no) | Court Scheduling |
| Statistical Reasoning | Simple regression | Numerical data allowing for curve fitting | Risk Assessment |
| Machine Learning | Classification tasks | Arbitrary data that needs to be abstracted into numbers | Facial recognition |
| Artificial Intelligence | Dynamic adaptation to novelty | Autonomous selection of best methodology | Intelligent digital assistant |
A.I. and Legal Decision Making
Guest Lecture: Psychology & Law
Emma Marshall, JD, MA
University of Nebraska-Lincoln
November 22, 2024
What is AI?

Understanding of AI-systems

Kennedy, Tyson, and Saks (2023)
Your Class

Types of Algorithms in Decision Making

Code & Math (NOT biology)

AI is just a (powerful) TOOL!
Good at: Document review (TAR)

Bad at: Writing Police Reports?

Ferguson (2024)
AI makes predictions based on past

Bender et al. (2021)
What can go wrong?


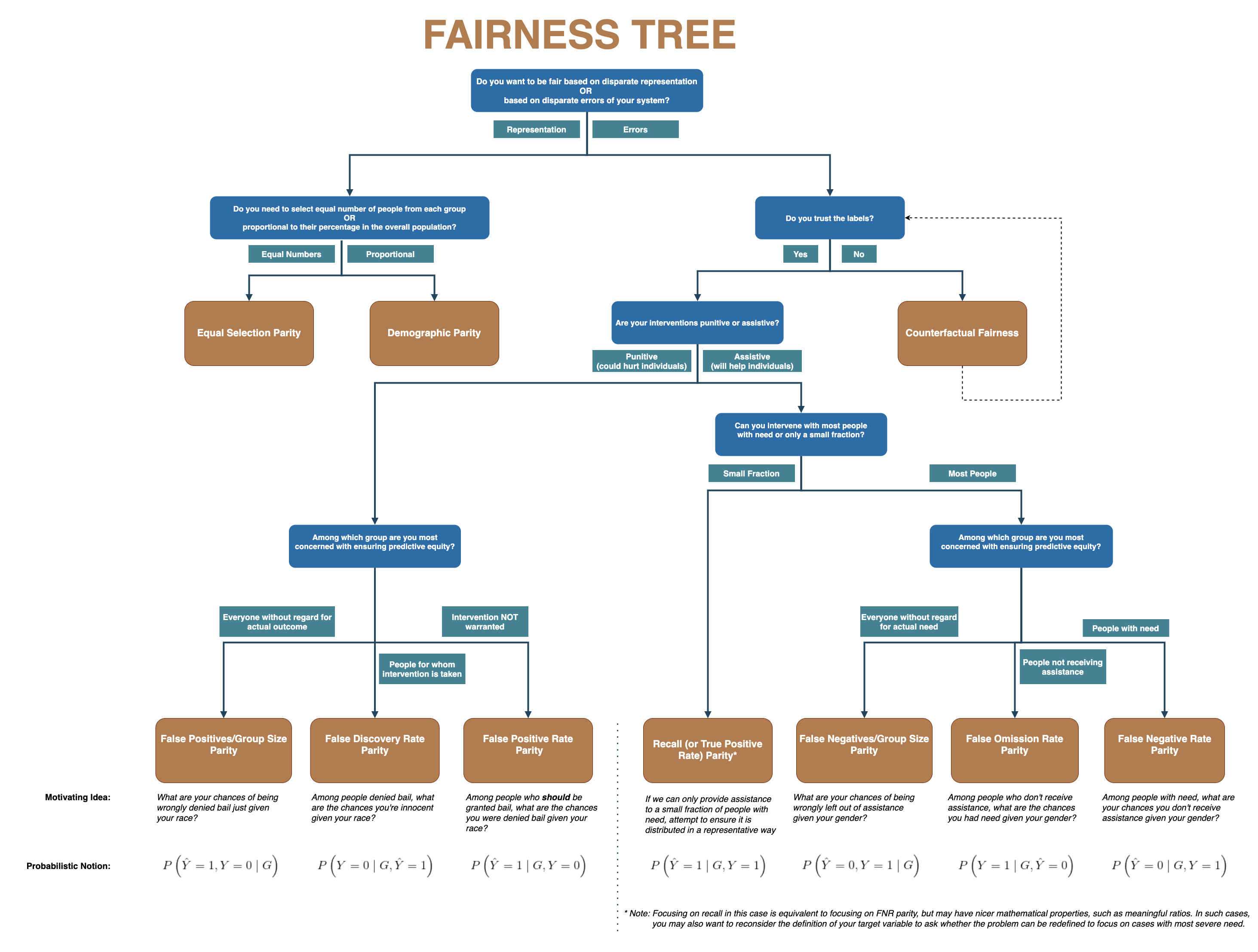
Fairness
- Historical data bias
- Proxy variables (zip codes, arrest records)
- Definitional challenge (what is fair?)

COMPASS: Correctional Offender Management Profiling for Alternative Sanctions



(prop?)
Accuracy
- Performance Metrics:
- Accuracy (overall population)
- Precision (individual cases)
- Recall (detection rate)
- Data quality issues
- Training data limitations
- Hallucinations!

Accountability
- “Black box” systems
- Proprietary software
- Distributed widely
- Responsibility gaps

Transparency
- Propriety algorithms
- Limited public access to:
- Source code
- Training data
- Testing methods
- BUT need for contestability

When is AI Used to Make Legal Decisions?
…all the time!

Law means many things


Example: AI & Deepfake Pornography
What are Deepfakes?


Technical Background
- Uses AI/machine learning to produce/alter images, audio & videos
- Can create realistic content with minimal source material
How They Work

How are they used?
- Entertainment (e.g., make Harrison Ford look young)
- Political manipulation
- Advertising
- Pornography (96% of all deepfakes)
Problem with Deepfake Porn
- Devastating personal and professional consequences
- Difficulty removing content once posted (copywrite)
- Limited legal recourse

What is new about Deepfakes?



Pre-existing Criminal Statutes
- Identity theft (limited application)
- Cyberstalking (18 U.S.C. §2261A)
- Federal legislation (NDAA 2020)
Copyright Law
- Generally ineffective for deepfakes (except for DCMA)
- Faces/voices not always copyrightable
- Fair use/transformative work defenses
Right of Publicity
- Limited to commercial use
- Only ~30 states recognize it
- New York’s digital replica protection
- Section 230 immunity challenges
Defamation
Public Figures
- Must prove actual malice
- Higher burden of proof
- First Amendment considerations
Private Individuals
- Lower standard than public figures
- State law variations
- Must show actual harm
Legal Barriers
- Platform Immunity
- Section 230 protections
- Limited ISP liability
- First Amendment Issues
- Prior restraint doctrine
- Free speech protections
- Parody defenses
Parody Defense
- Hustler Magazine v. Falwell
- “Reasonable person” standard
- Disclaimer effectiveness
- Quality considerations
Practical Issues
- Anonymous creators
- Jurisdiction on internet
- Rapid spread of content & accumulated harm
So what has been done?
Current Legislative Approaches

What role should Psychology & Social Science play?
Psychology and Law

Automation Bias

When might automation bias matter in the deepfake pornography context?
What other psychological factors might influence legal actors decisions?

Questions?
Contact Me
Anslow, Louis. 2024. “The 1912 War on Fake Photos.” Pessimists Archive. https://newsletter.pessimistsarchive.org/p/the-1912-war-on-fake-photos.
Bender, Emily M., Timnit Gebru, Angelina McMillan-Major, and Shmargaret Shmitchell. 2021. “On the Dangers of Stochastic Parrots: Can Language Models Be Too Big? 🦜.” In Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, 610–23. Virtual Event Canada: ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3442188.3445922.
Dolata, Mateusz, and Gerhard Schwabe. 2024. “Towards the Socio-Algorithmic Construction of Fairness: The Case of Automatic Price-Surging in Ride-Hailing.” International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction 40 (1): 55–65. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2023.2210887.
Ferguson, Andrew Guthrie. 2024. “Generative Suspicion and the Risks of AI-Assisted Police Reports.”
“Inescapable AI: The Ways AI Decides How Low Income People Work, Live, Learn, and Survive.” 2024. Techtonic Justice.
Kennedy, Brian, Alec Tyson, and Emily Saks. 2023. “What Americans Know About Everyday Uses of Artificial Intelligence Pew Research Center.” Pew Research. https://www.pewresearch.org/science/2023/02/15/public-awareness-of-artificial-intelligence-in-everyday-activities/.
Mania, Karolina. 2020. “The Legal Implications and Remedies Concerning Revenge Porn and Fake Porn: A Common Law Perspective.” Sexuality & Culture 24 (6): 2079–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12119-020-09738-0.
Starke, Christopher, Janine Baleis, Birte Keller, and Frank Marcinkowski. 2022. “Fairness Perceptions of Algorithmic Decision-Making: A Systematic Review of the Empirical Literature.” Big Data & Society 9 (2): 20539517221115189. https://doi.org/10.1177/20539517221115189.
Suslavich, Benjamin T. 2023. “Nonconsensual Deepfakes: A "Deep Problem" for Victims.” Journal of Science and Technology 33: 160–88. https://towardsdatascience.com/multi-layer-neural-networks-with-sigmoidfunction-deep-learning-for-rookies-2-bf464f09eb7f.