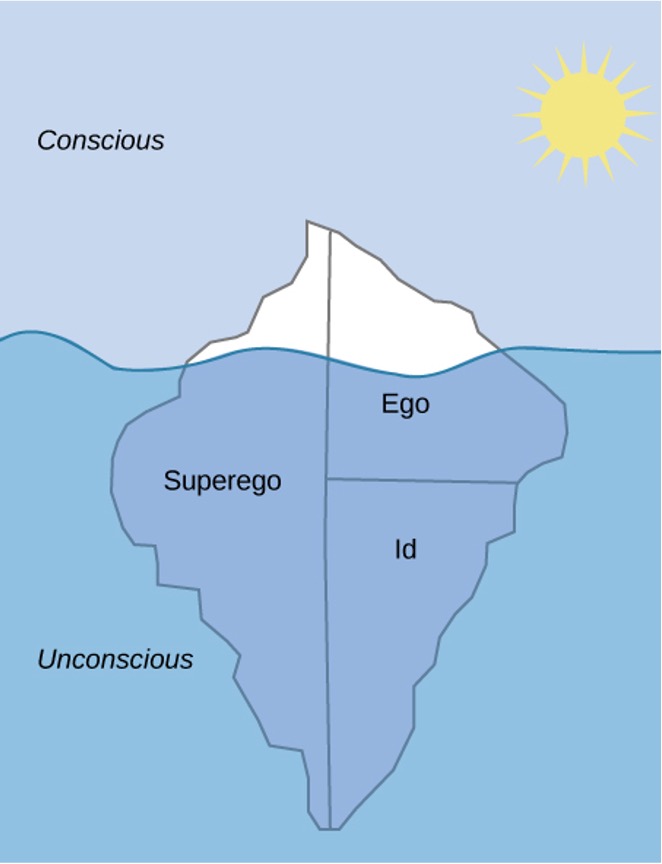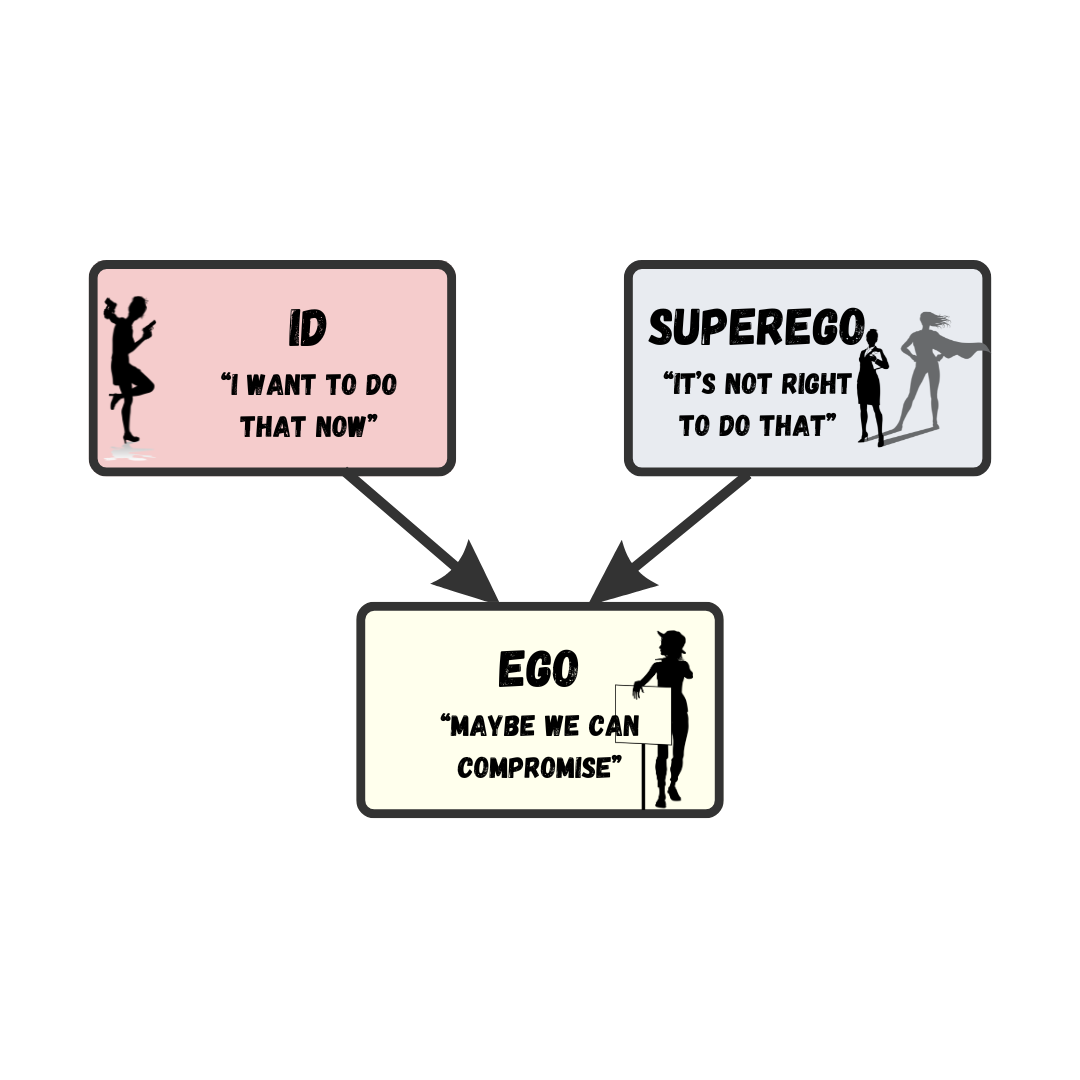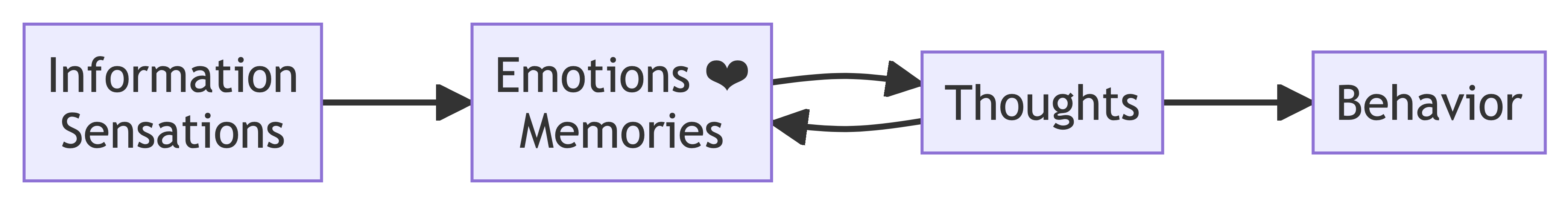
Sensations and information are received by our brains, filtered through emotions and memories, and processed to become thoughts.
PSYC 181 – Intro to Psych
August 14, 2024
![]()
Will cover information from Units 7-11
Exam will include two-phases:
Your final grade will be a weighted average of your score on Phase 1 (75%) and Phase 2 (25%) of each exam.
![]()

Sensations and information are received by our brains, filtered through emotions and memories, and processed to become thoughts.
Concepts categories of linguistic information, images, ideas or memories
Prototypes the best example or representation of a concept
Natural Created through either direct or indirect experience

Artificial defined by a specific set of characteristics

Anchoring bias Tendency to focus on one piece of information and adjust

Confirmation bias Tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs

Representative bias Tendency to unintentionally stereotype someone or something

Availability heuristic Tendency to make a decision based on readily available example, information, or recent experience
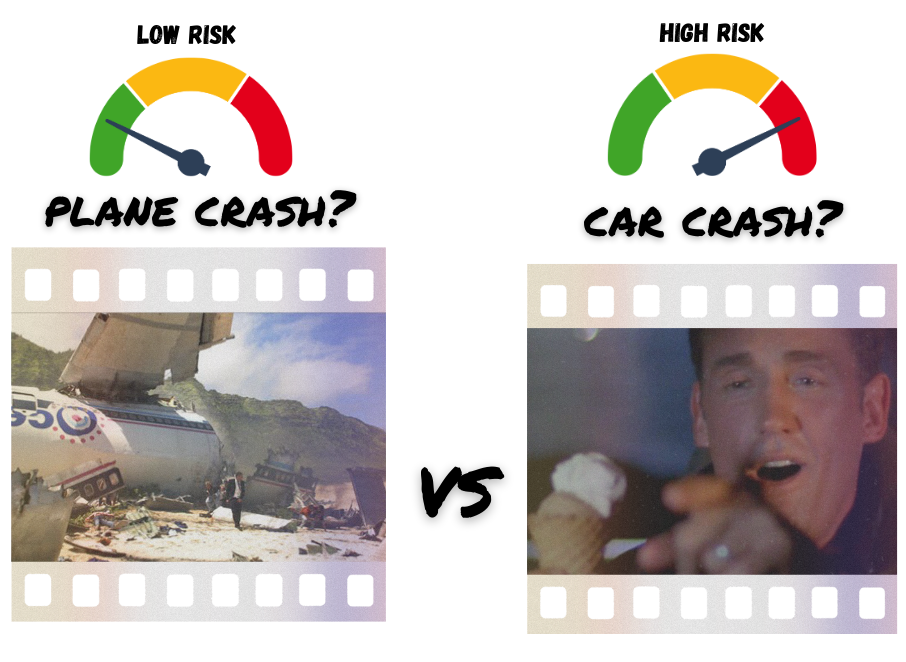
Hindsight biasKnowledge of an outcome makes that outcome appear more inevitable or foreseeable than it would have been beforehand

Language a communication system that involves using words and systematic rules to transmit information from one individual to another
Phoneme short, sound units (ah, eh)
Morphemes the smallest units that convey meaning
Lexicon the words of a given language
Grammar the set of rules that are used to convey meaning through the use of the lexicon.
Semanticsthe meaning we derive from morphemes and words
Syntax the way words are organized into sentences

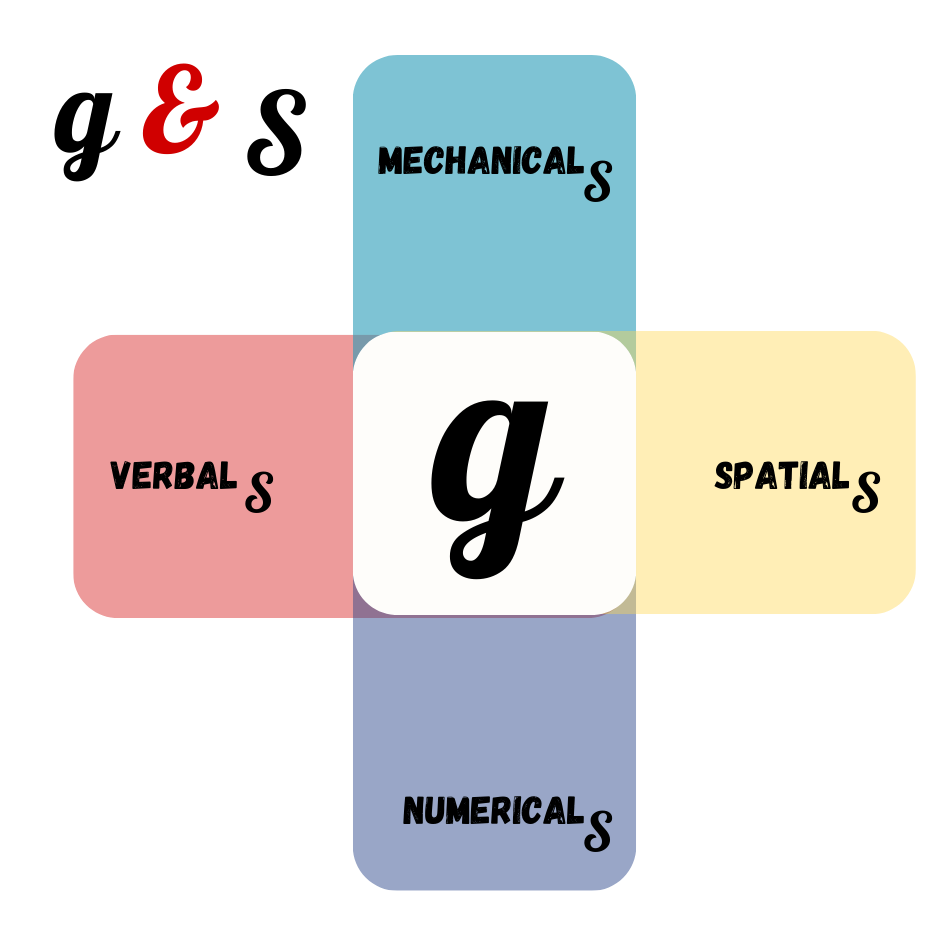
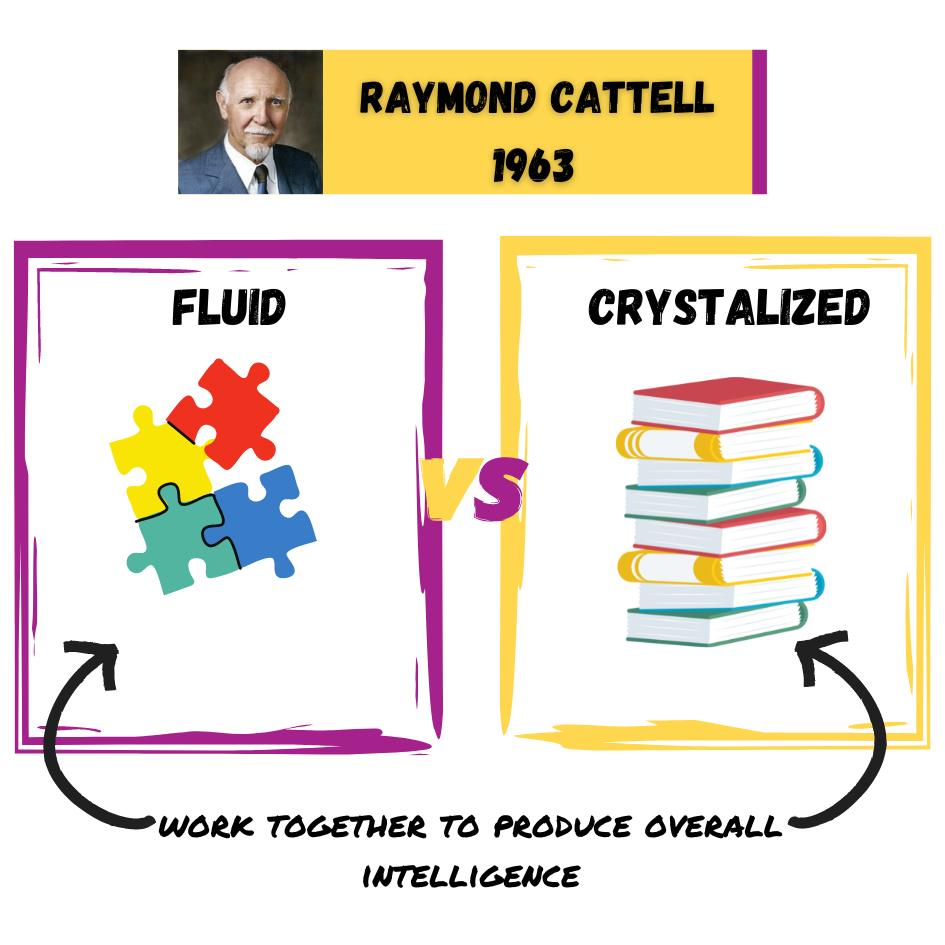
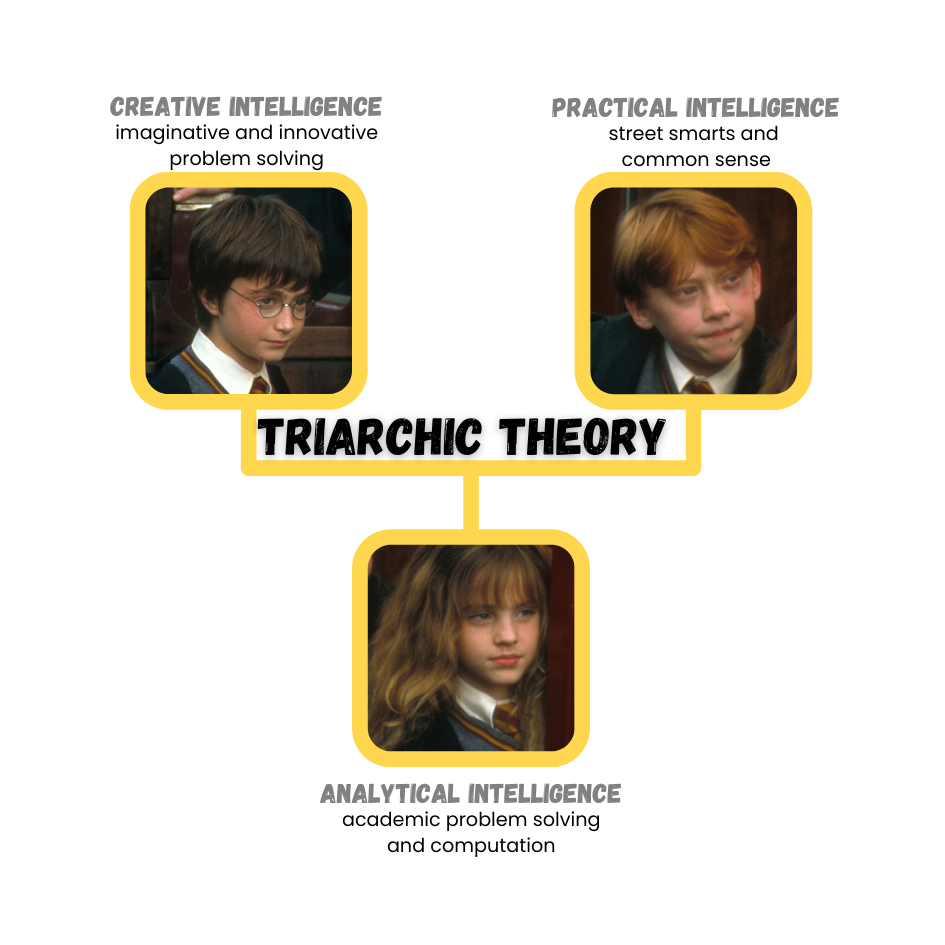
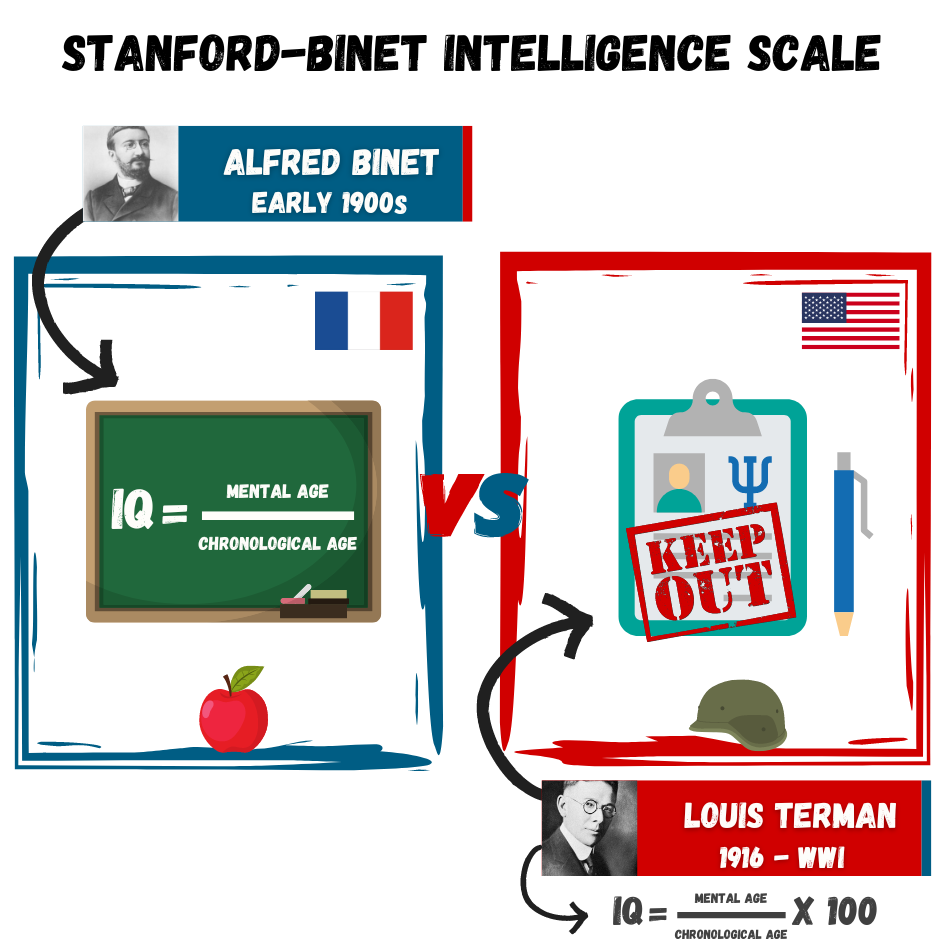
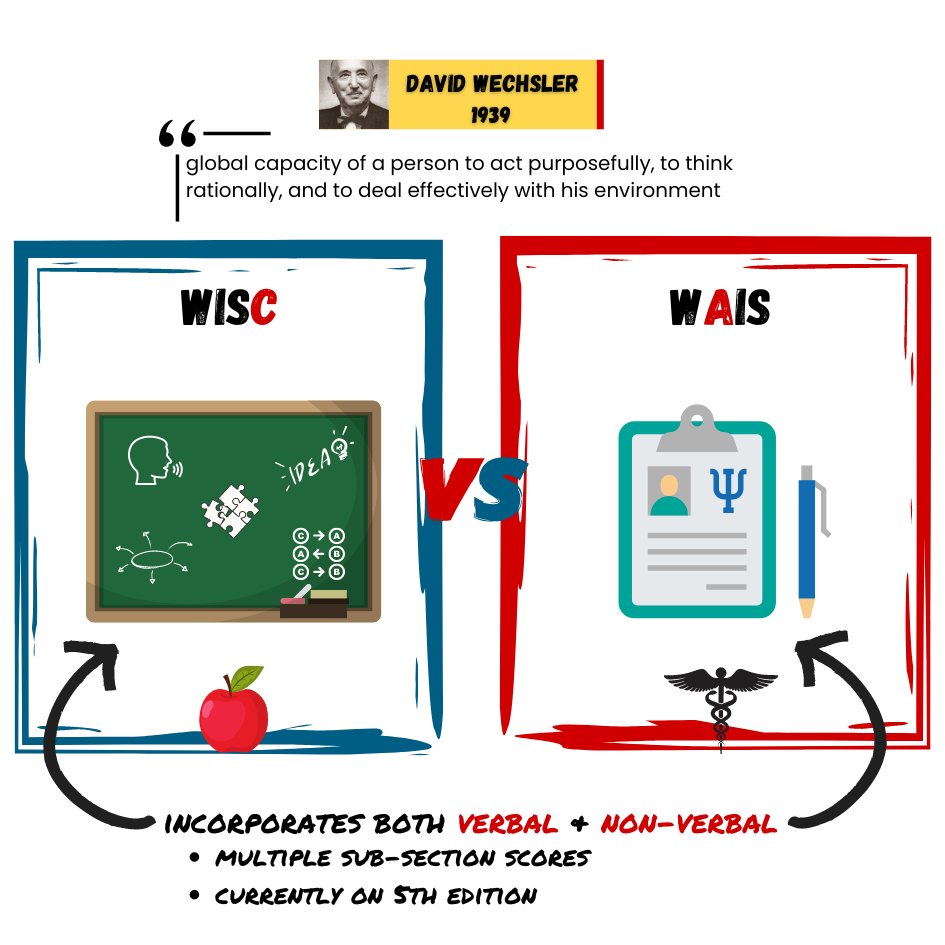
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) score earned on a test designed to measure intelligence
Flynn Effect each generation has a significantly higher IQ than the last
Learning relatively permanent change in behavior or knowledge that results from experience
Associative learning when an organism makes connections between stimuli or events that occur together in the environment
Reflexes motor or neural reactions to
a specific stimulus
Instincts behaviors triggered by a broader
range of events (e.g., aging,
change of seasons)
Situationism the view that our behavior and actions are determined by our immediate environment and surroundings
Dispositionism the view that our behavior is determined by internal factors (i.e., personality traits and temperament)
Fundamental attribution error tendency to overemphasize internal factors as explanations/attributions for the behavior of other people and underestimate the power of the situation
Actor-observer bias phenomenon of explaining other people’s behaviors as due to internal factors and our own behaviors as due to situational factors


Self-serving bias tendency of an individual to take credit by making dispositional or internal attributions for positive outcomes but situational or external attributions for negative outcomes
Just-world hypothesis belief that people get the outcomes they deserve

Groupthink the modification of the opinions of members of a group to align with what they believe is the group consensus

Group Polarization the strengthening of an original group attitude after the discussion of views within a group
 .
.
Social Facilitation occurs when an individual performs better when an audience is watching than when the individual performs the behavior alone

Social Loafing the exertion of less effort by a person working together with a group
In-groups a group that we identify with or see ourselves as belonging to
In-group bias prejudice and discrimination because the out-group is perceived as different and is less preferred than our in-group
Out-groups a group that we view as fundamentally different from us
What influences who we form platonic and romantic relationships with?
proximity people with whom you have
the most contact
similarity people who are similar to us
in background, attitude, and lifestyle
homophily tendency for people to
form social networks with similar others
1Choleric
2Melancholic
3Sanguine
4Phlegmatic