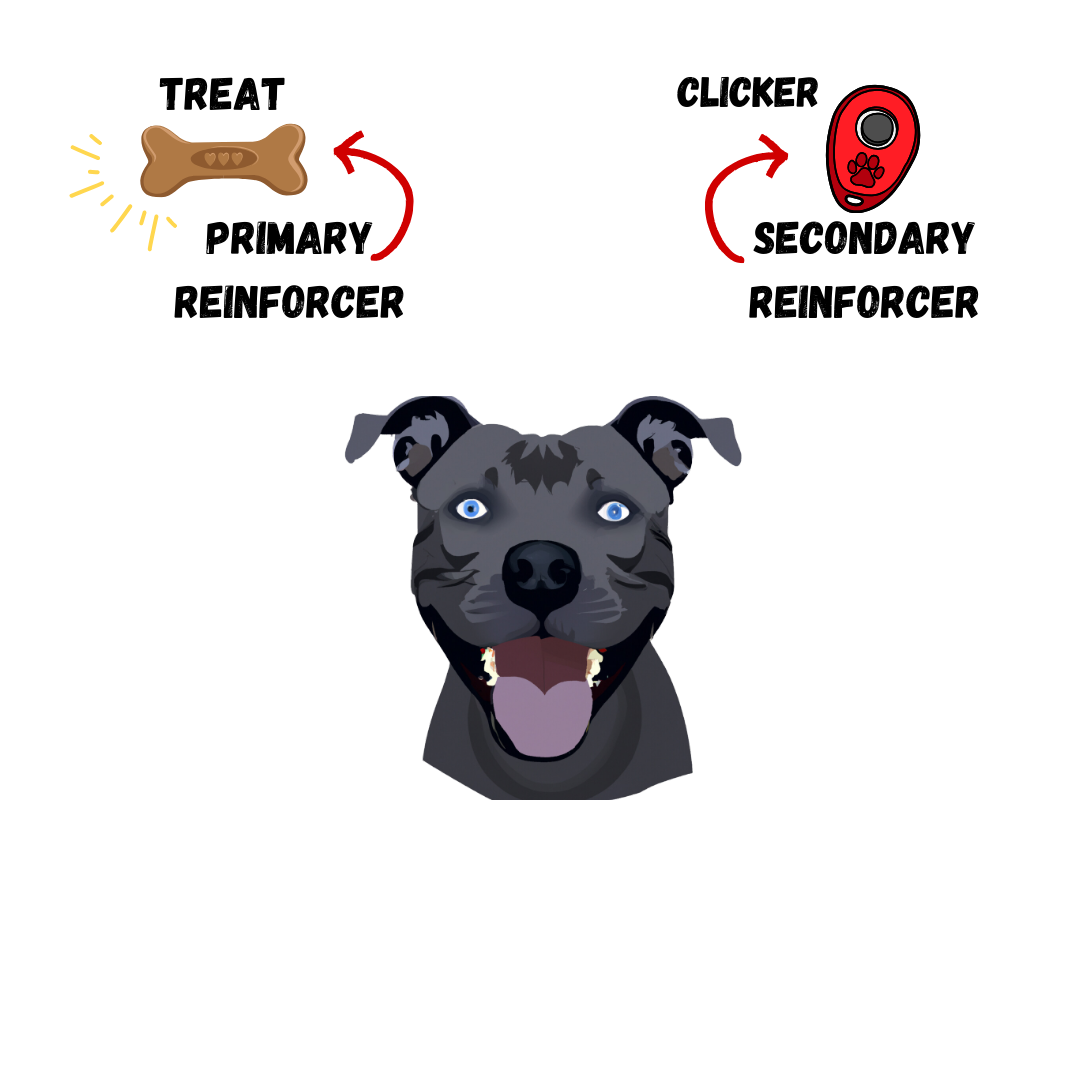
PRIMARY & SECONDARY REINFORCERS

PSYC 181 – Intro to Psych
August 1, 2024
![]()
Learning Objectives
![]()
Reflexes motor or neural reactions to a specific stimulus
Instincts behaviors triggered by a broader range of events (e.g., aging, change of seasons)
Learning relatively permanent change in behavior or knowledge that results from experience
Associative learning when an organism makes connections between stimuli or events that occur together in the environment
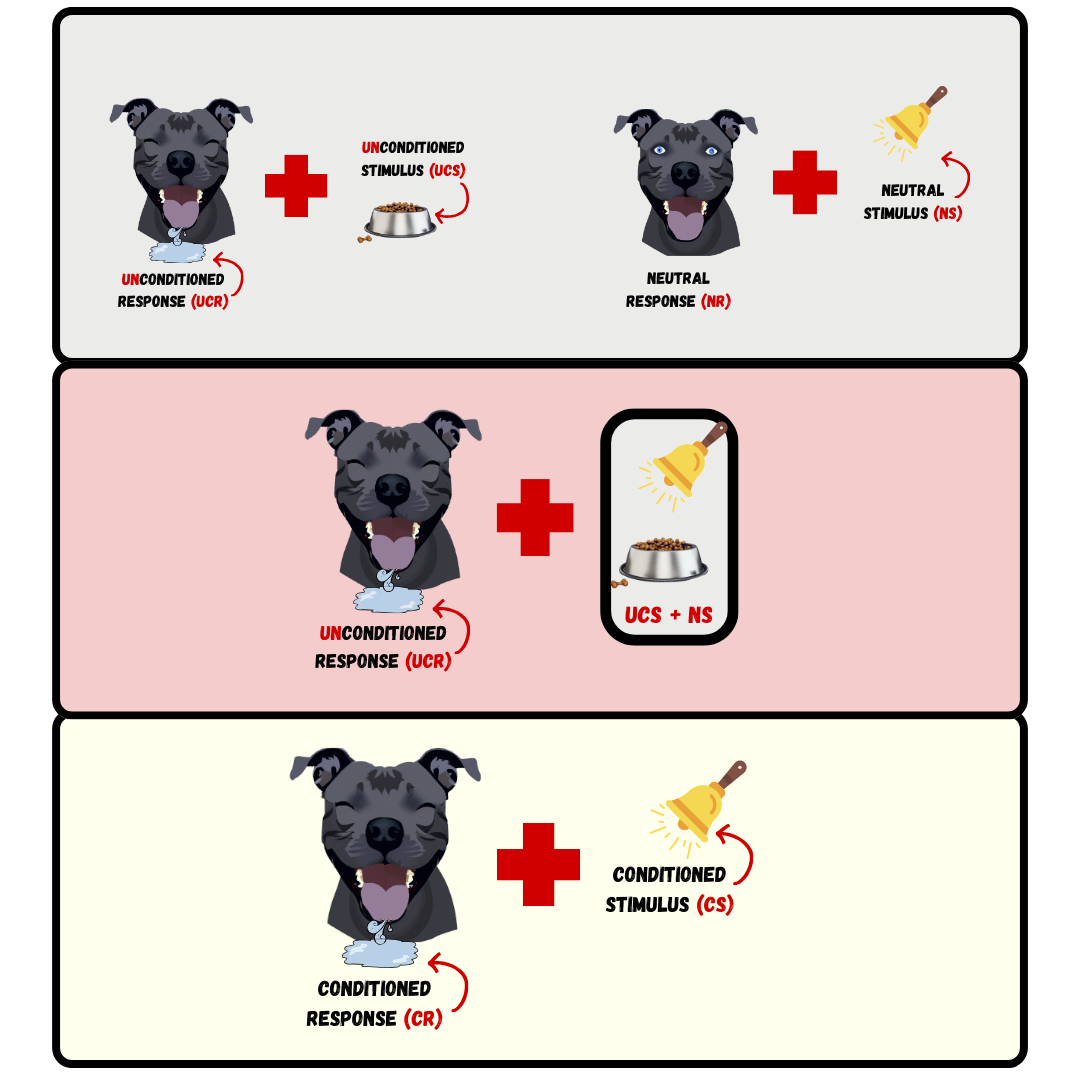
Classical conditioning process by which we learn to associate stimuli and, consequently, to anticipate events

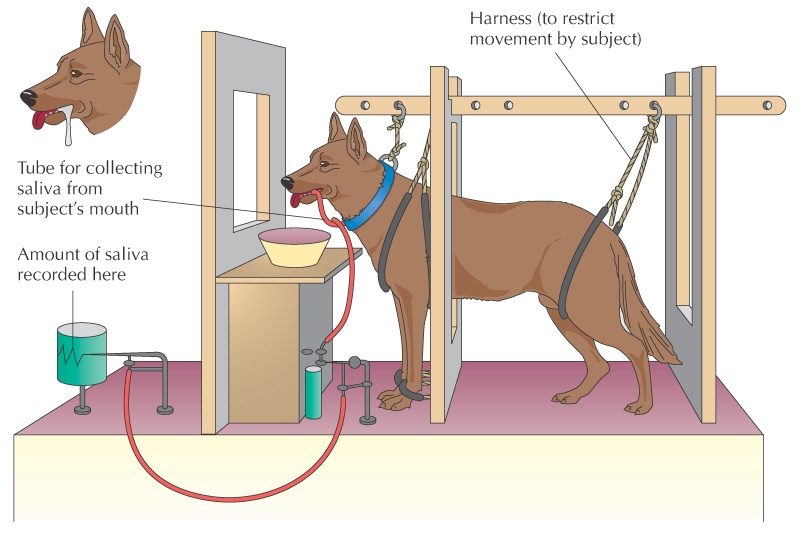
Before

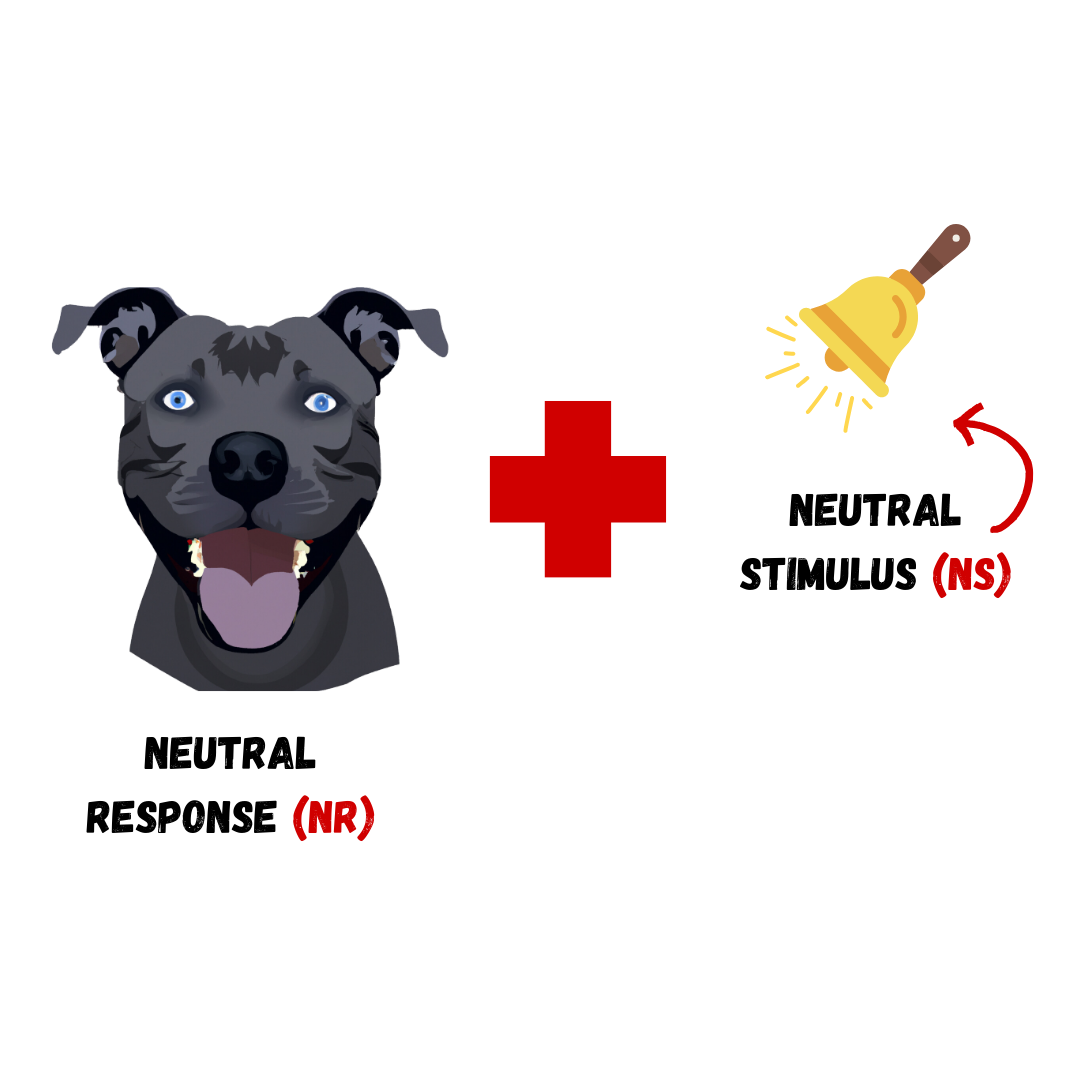
During
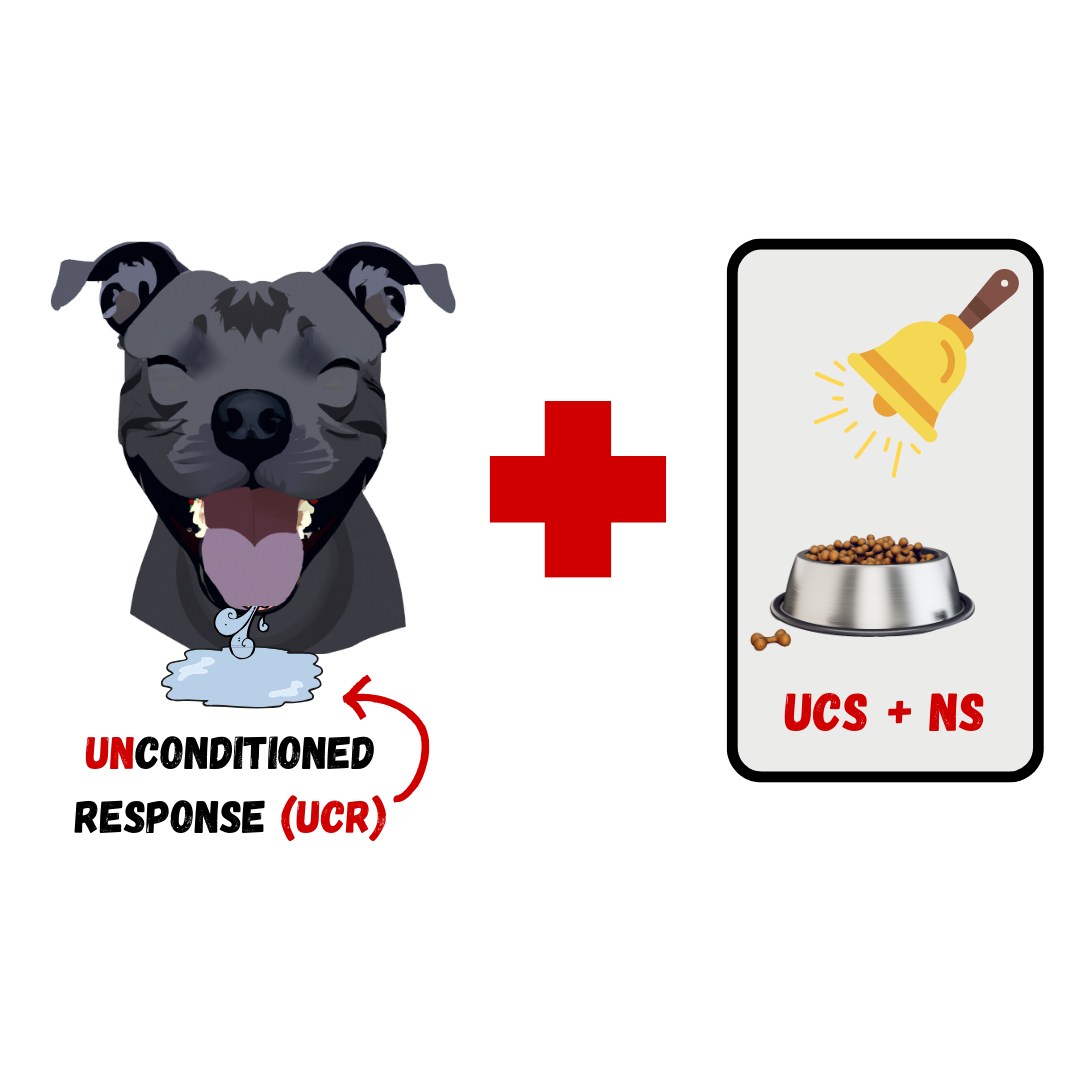
After
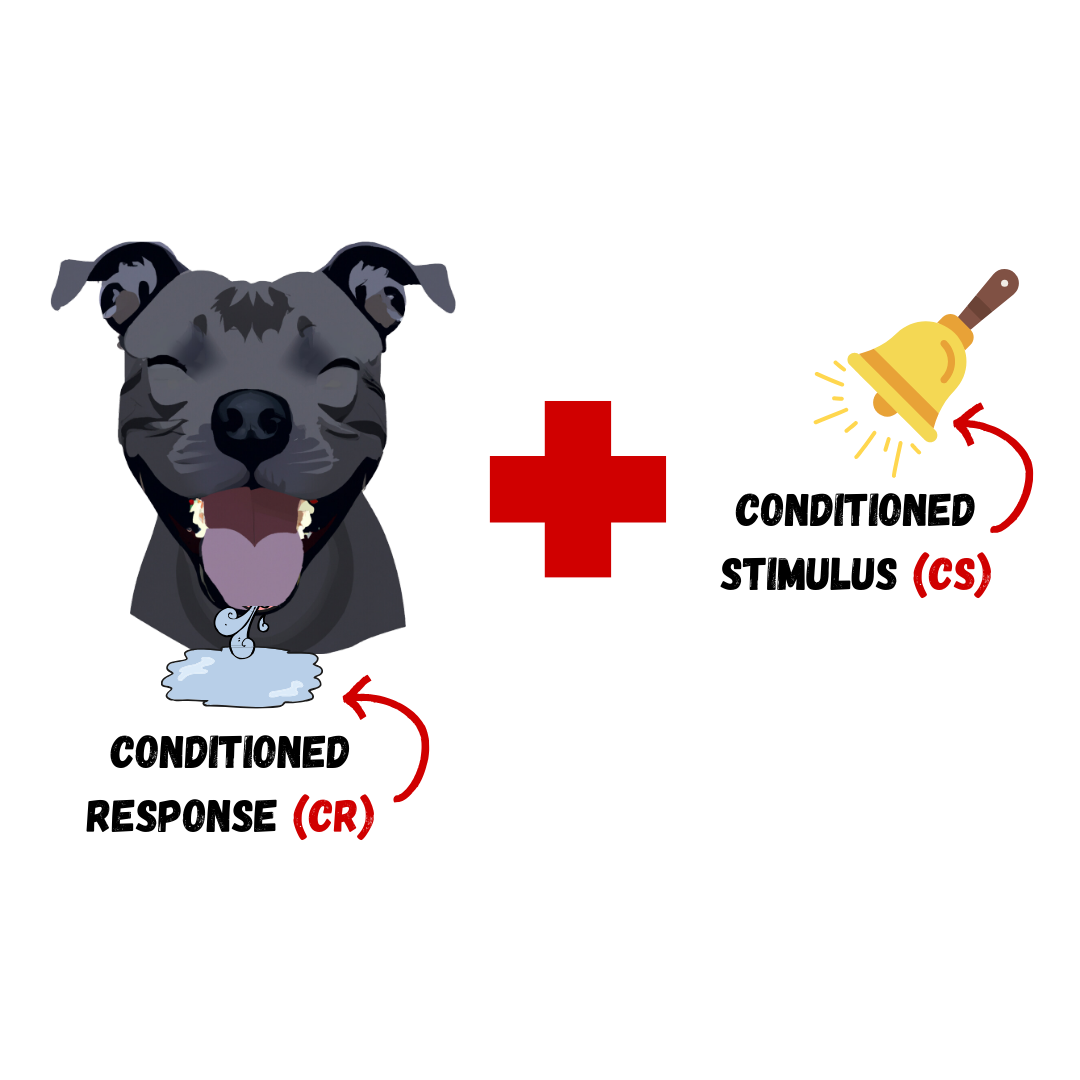
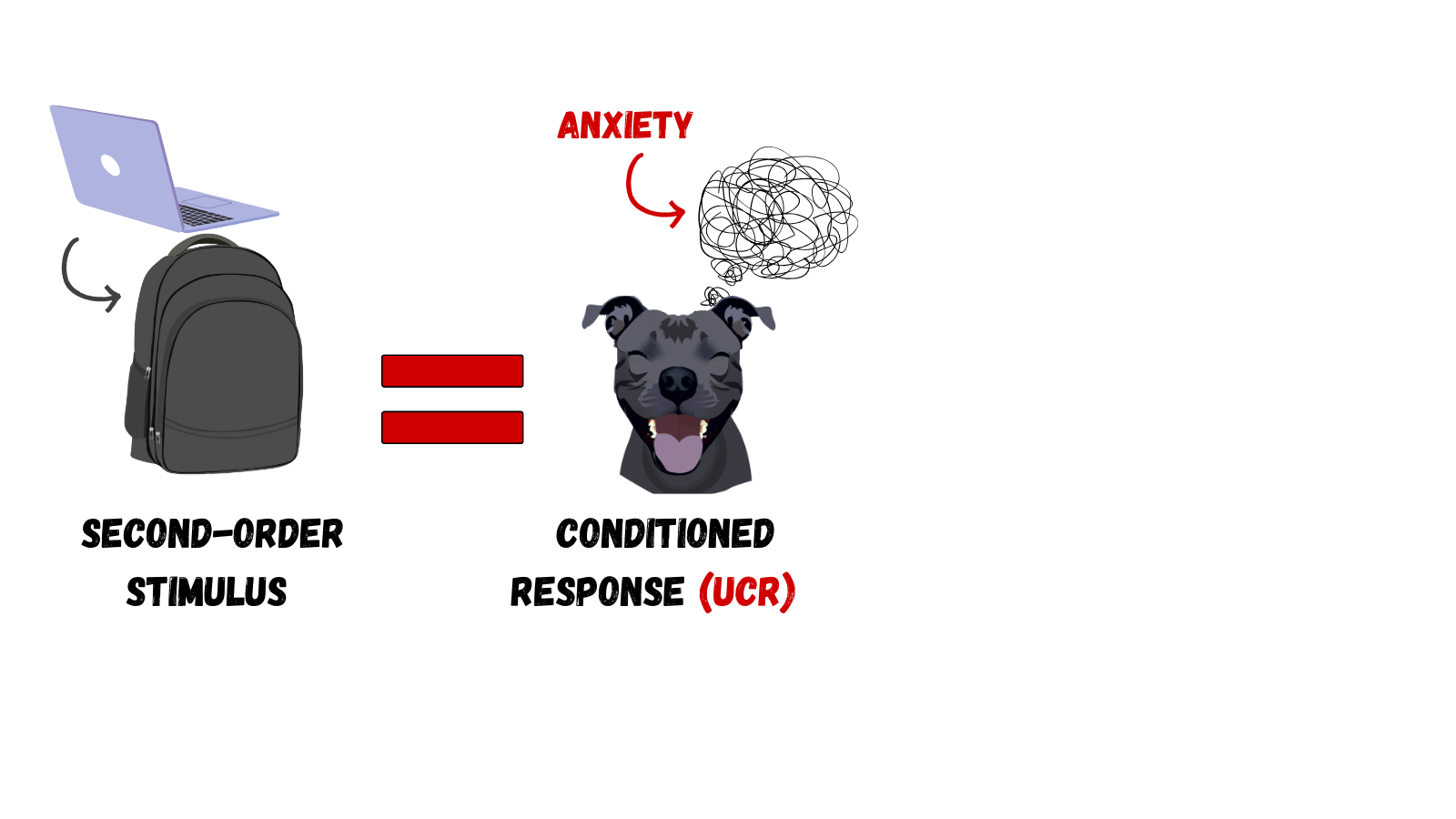
Higher-order conditioning an established conditioned stimulus is paired with a new neutral stimulus (the second-order stimulus)
Before
During
After
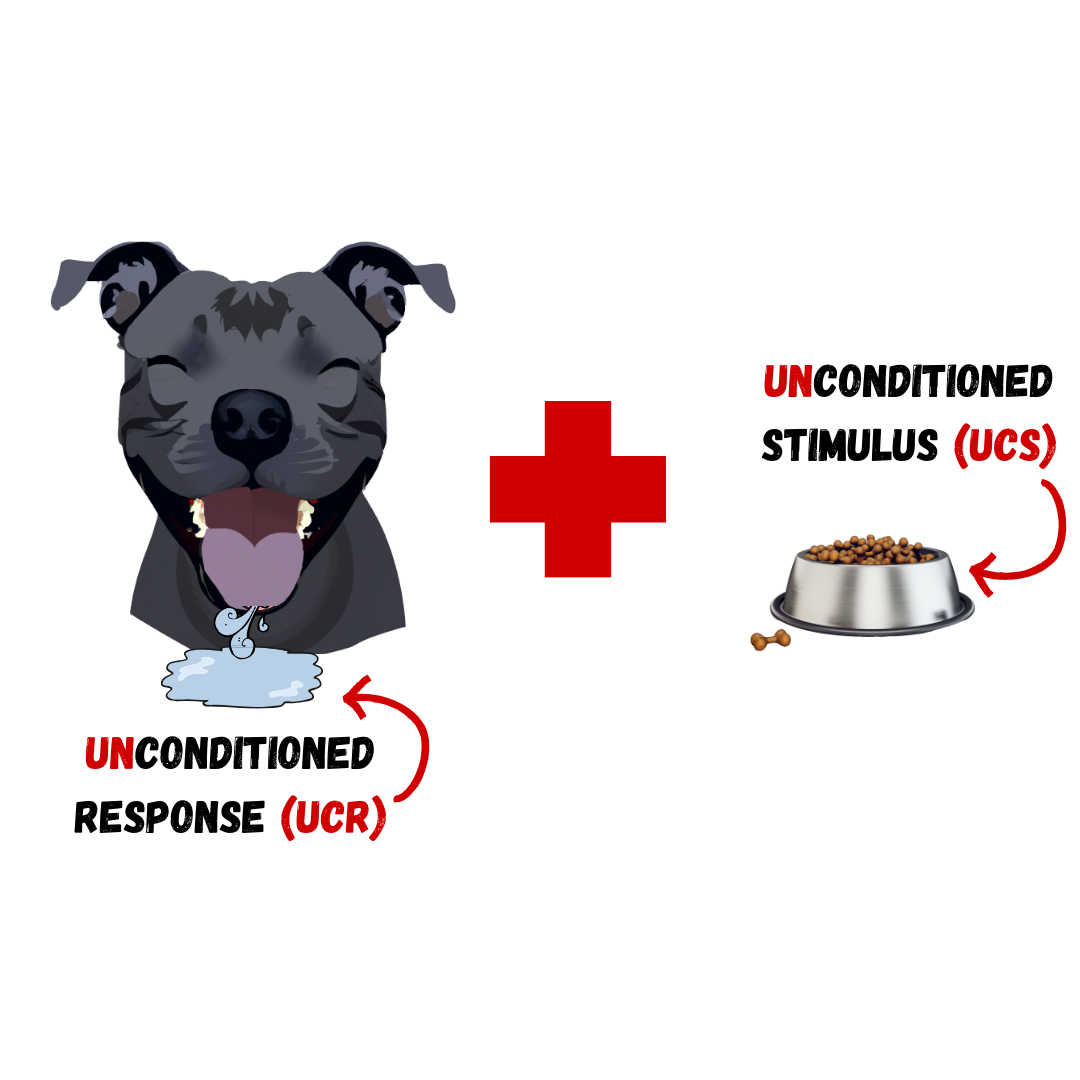
Acquisition the initial period of learning when an organism learns to connect a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus
Typically need short time interval between the NS and the UCS and repeated pairings
But can occur when interval several hours and the pairing occurs only once (e.g. taste aversion).
Extinction decrease in conditioned response when UCS no longer presented with CS
Spontaneous recovery the return of a previously extinguished conditioned response following a rest period
Stimulus discrimination when an organism learns to respond differently to various stimuli that are similar
Stimulus generalization when an organism demonstrates the conditioned response to stimuli that are similar to the conditioned stimulus
Habituation learning not to respond to a stimulus that is presented repeatedly without change

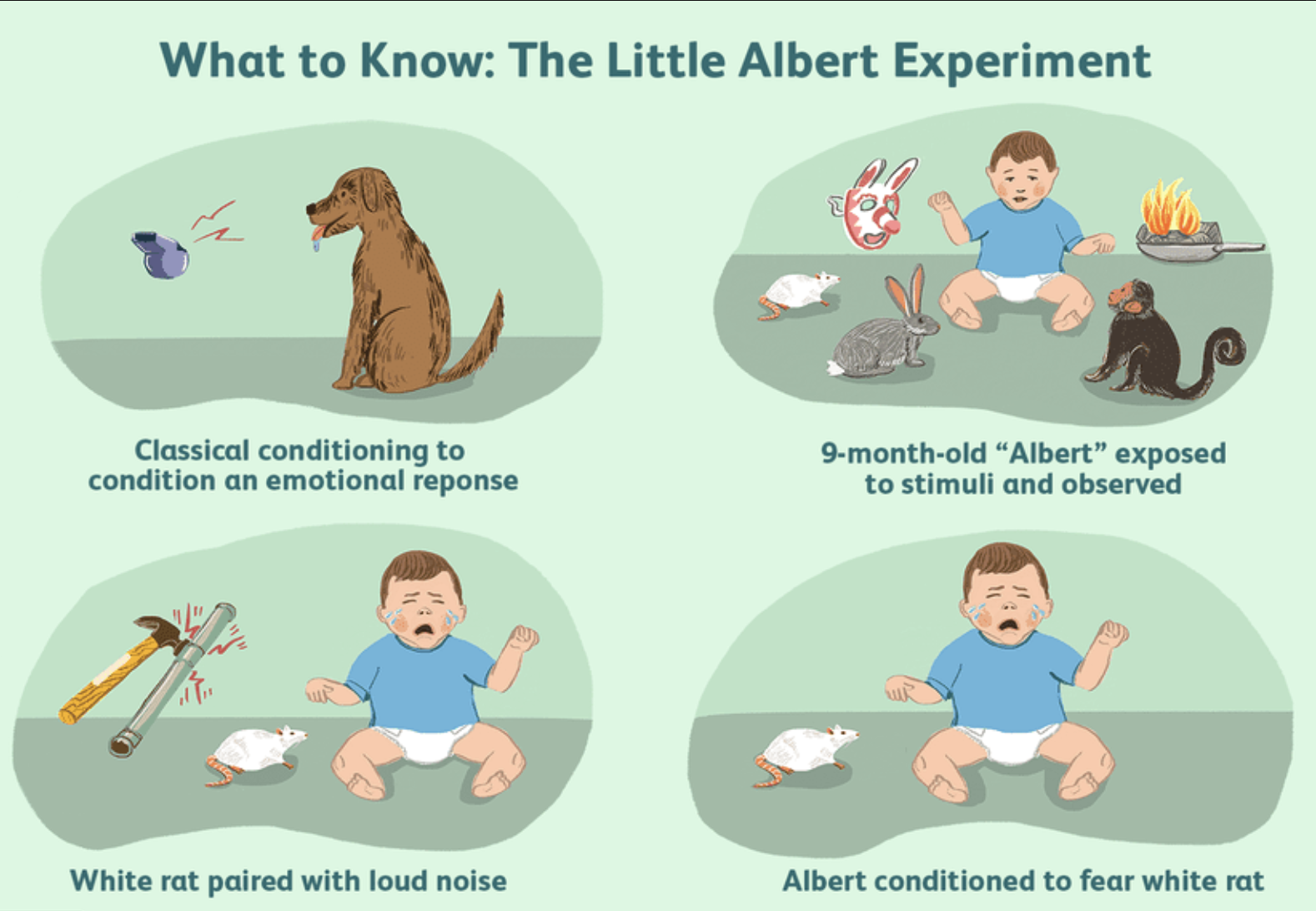
Law of effect:
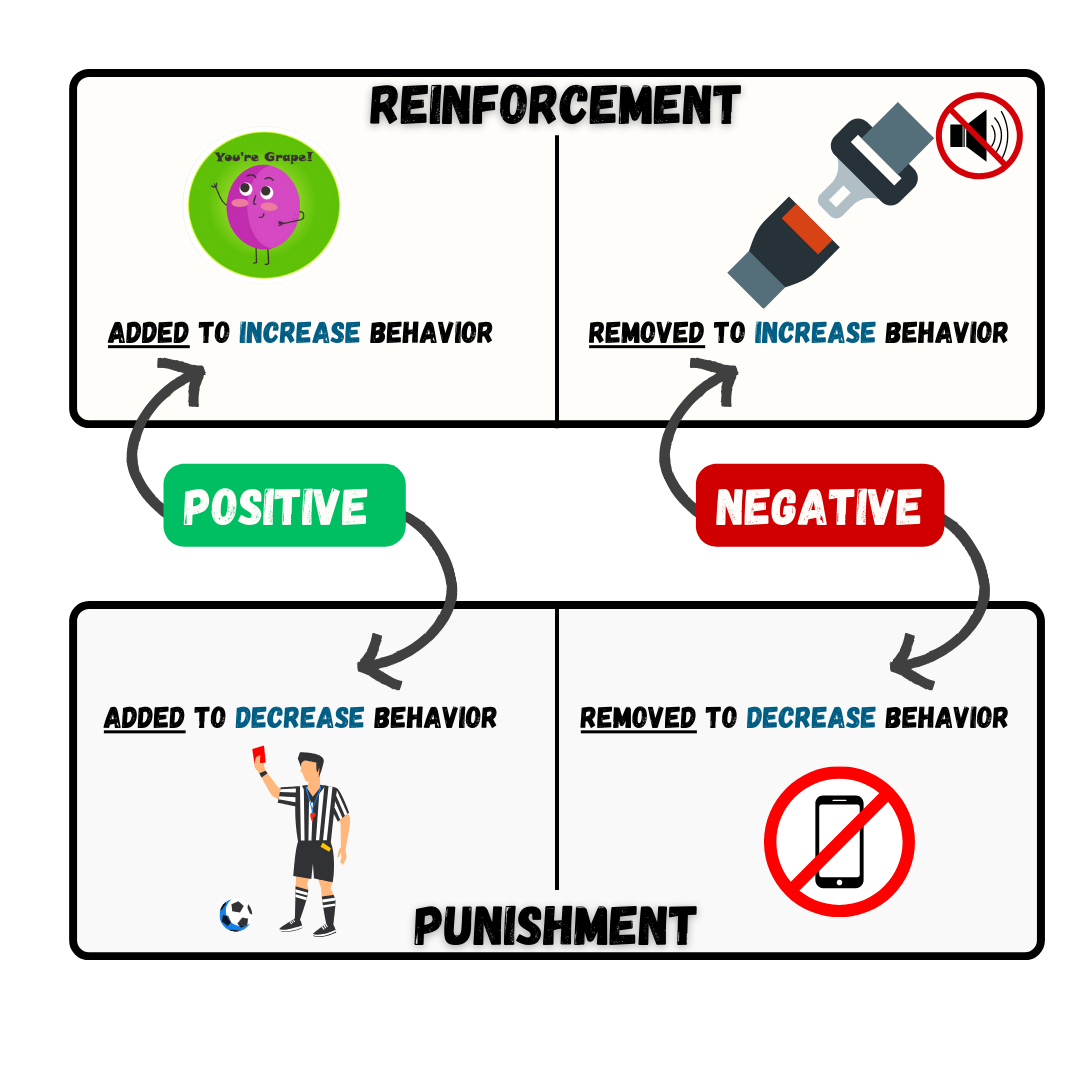
Positive to add something
Negative to take something away
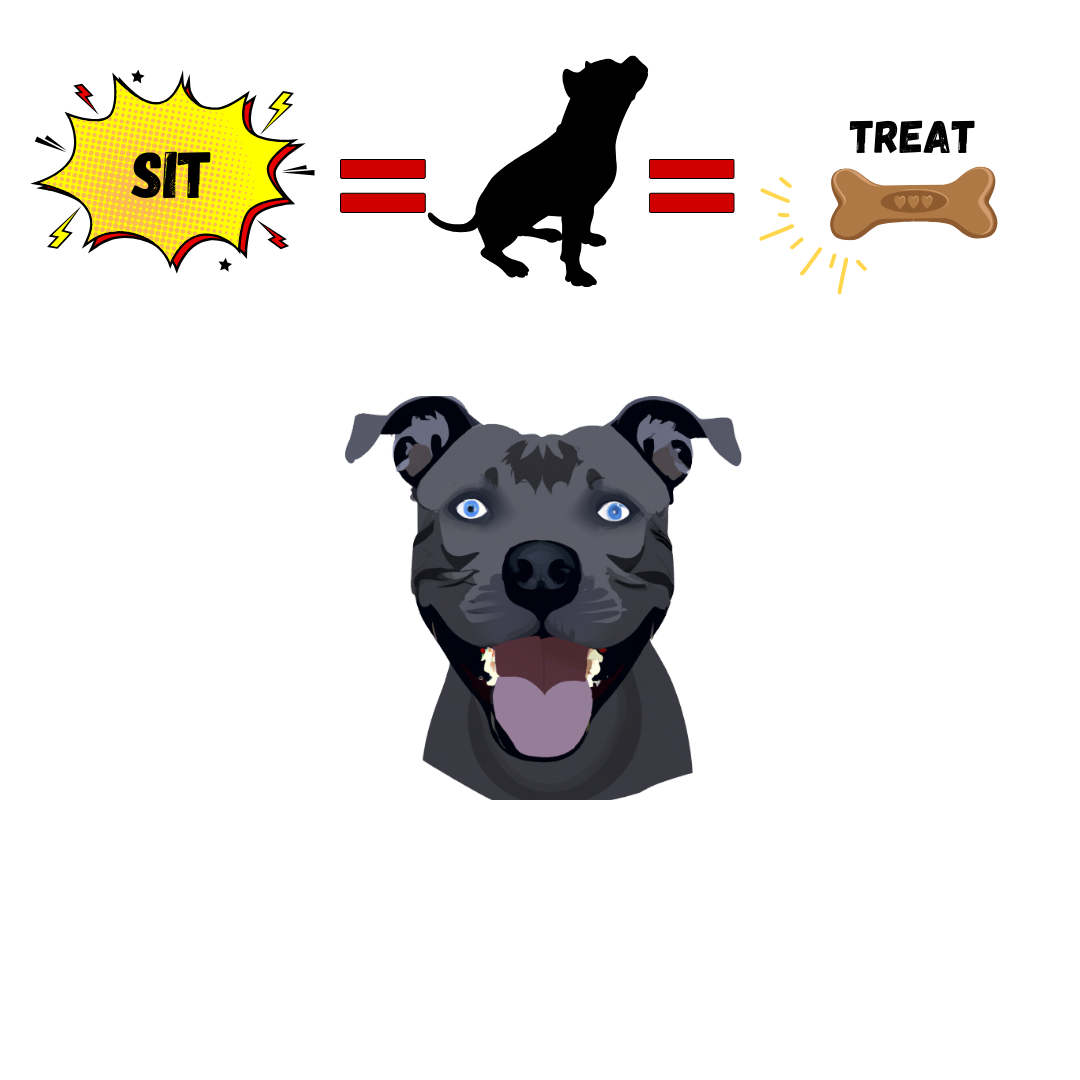
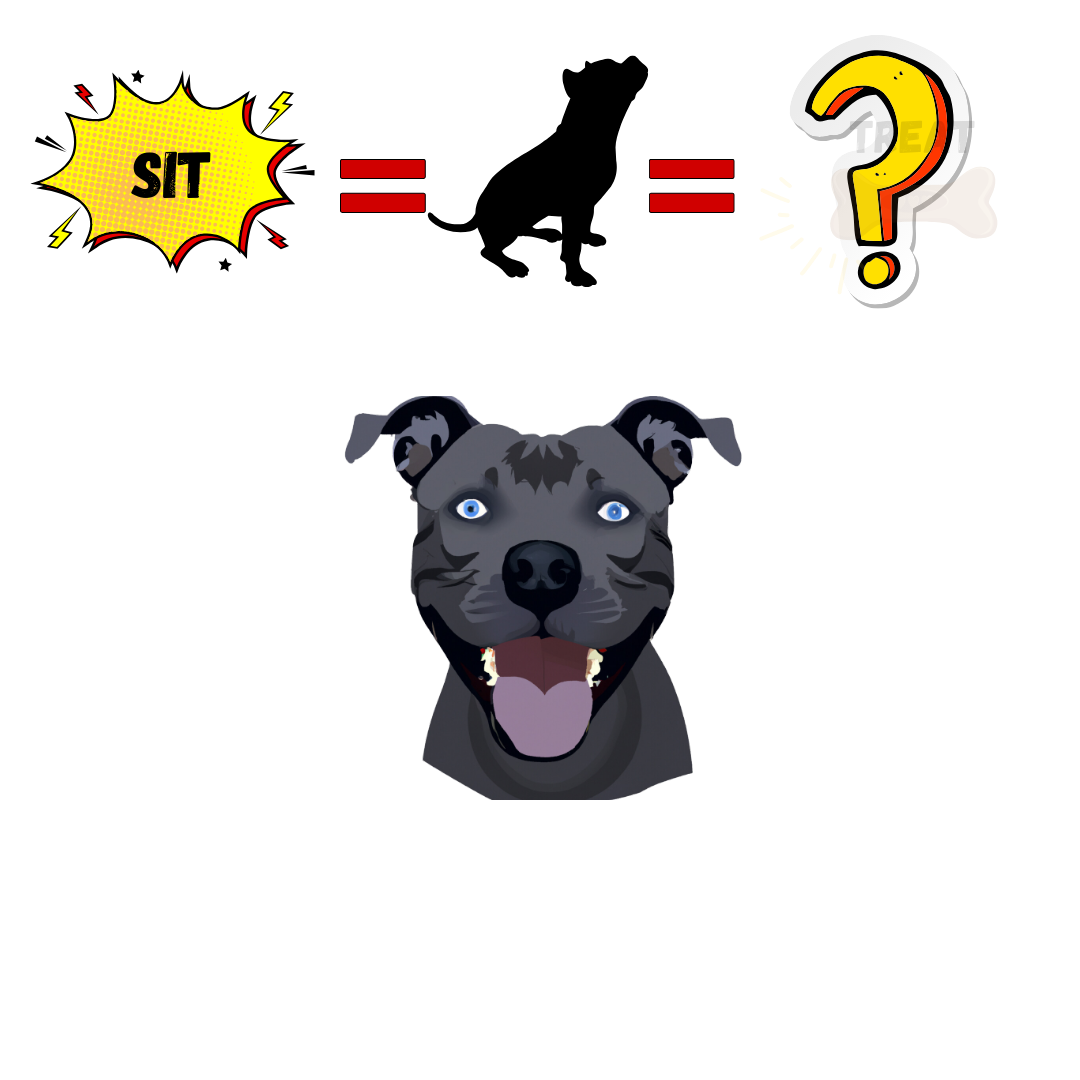
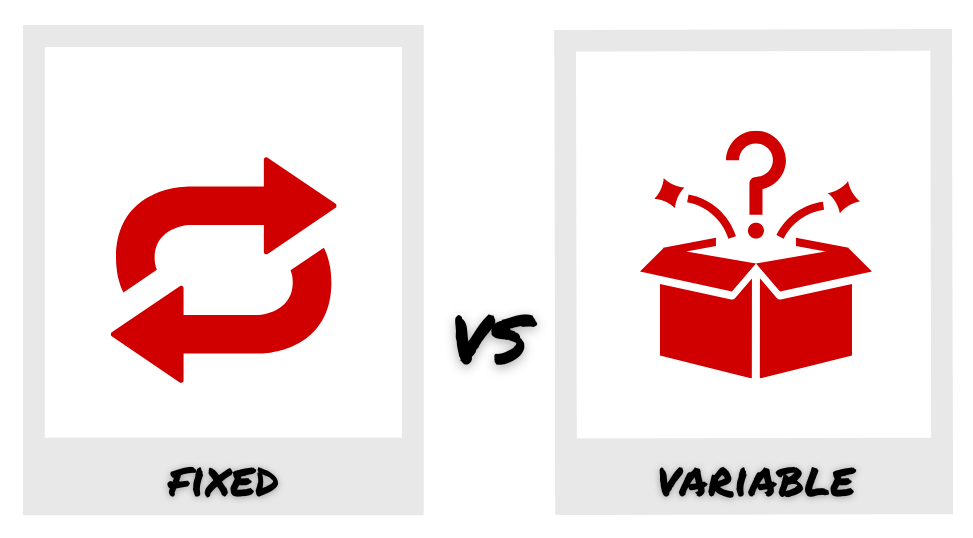
Reinforcement increasing a behavior
Punishment decreasing a behavior
| Classical Conditioning | Operant Conditioning | |
|---|---|---|
| Stimulus timing | Immediately BEFORE | Soon AFTER |
| Conditioning approach |  |
 |
1 Reinforce any response that resembles the desired behavior
2 Reinforce the response that more closely resembles the desired behavior
3 Begin to reinforce the response that even more closely resembles the desired behavior
4 continue to do this until only the desired behavior is reinforced


Cognitive map a mental picture of the layout an environment
Latent learning learning that occurs but is not observable in behavior until there is a reason to demonstrate it


Vicarious reinforcement where observer sees model rewarded making the observer more likely to imitate model
Vicarious punishment where observer sees model punished making observer less likely to imitate model
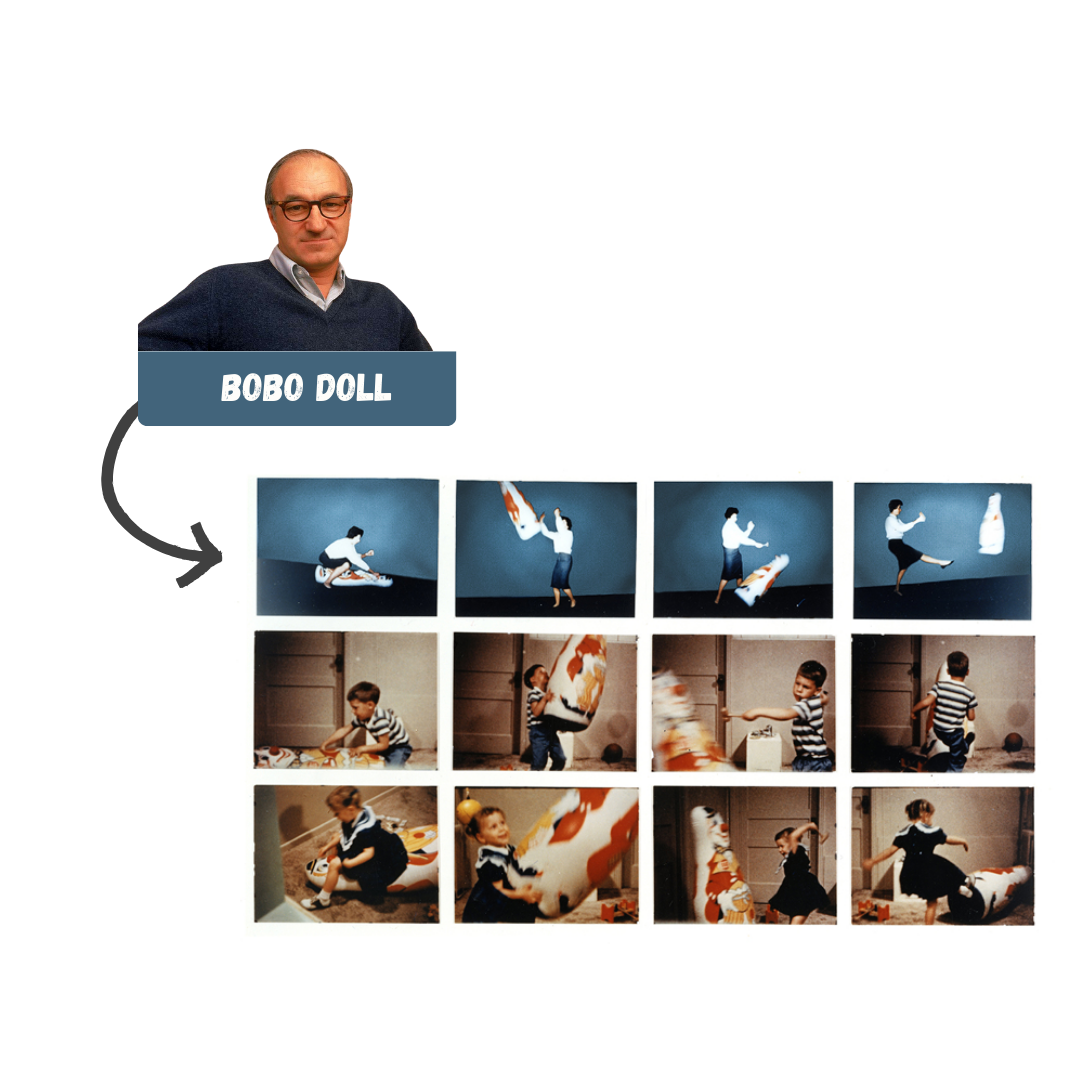

SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY
Modeling Process 1 Attention: focus on the behavior
2 Retention: remember what you observed
3 Reproduction: be able to perform the behavior
4 Motivation: must want to copy the behavior