🗓 Unit 8
Memory
PSYC 181 – Intro to Psych
July 31, 2024
What you will learn
![]()
Learning Objectives
- Define and describe the three phases of memory
- Explain how we encode new information
- Describe how we store memories over time
- Recognize memory failures and discuss the underlying mechanisms and processes
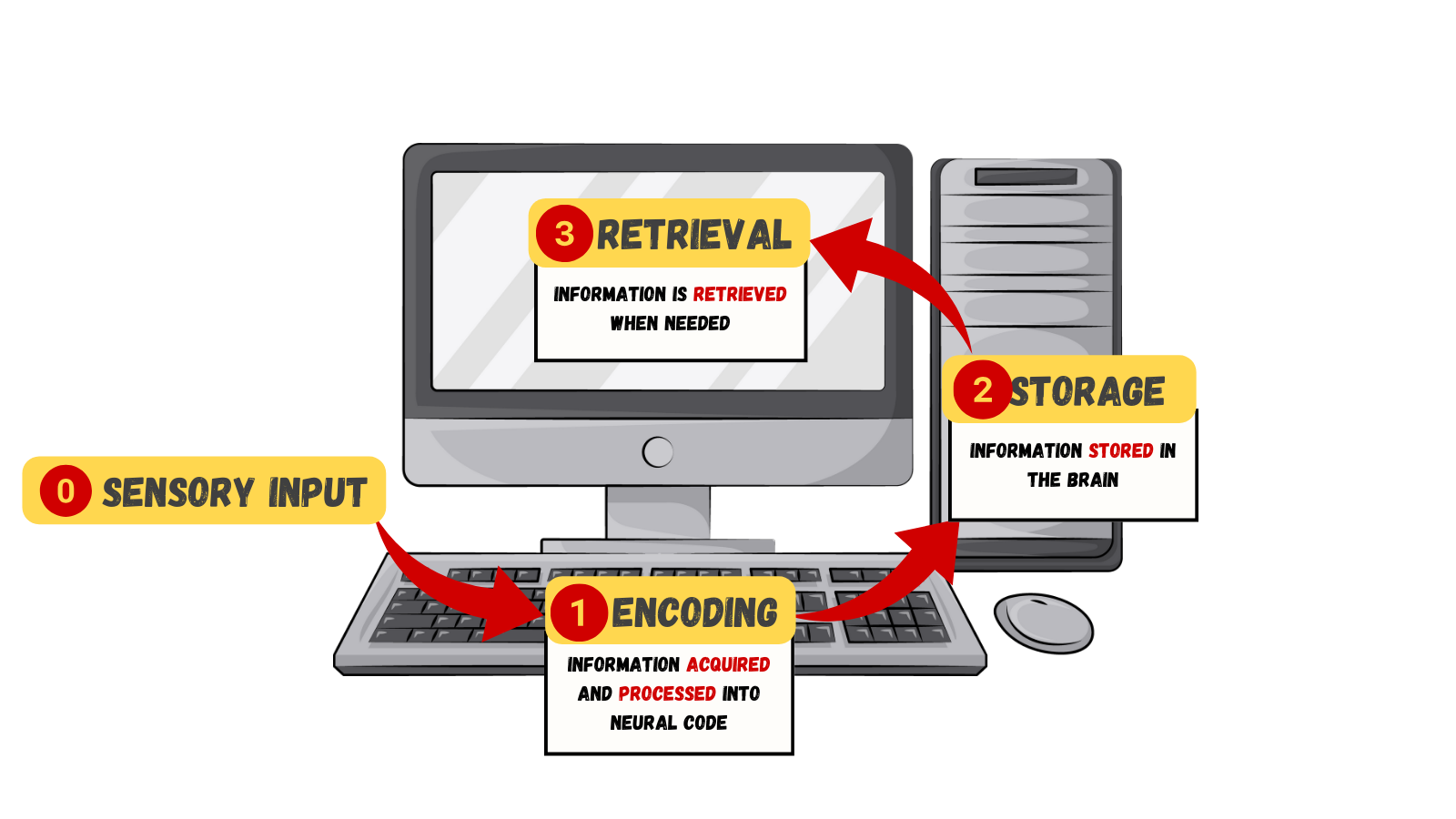
What is memory?
Capacity to retain and retrieve skills and knowledge
![]()
Experience
Process
System
Neural
Flawed
HOW MEMORY FUNCTIONS
PARTS OF THE BRAIN INVOLVED IN MEMORY
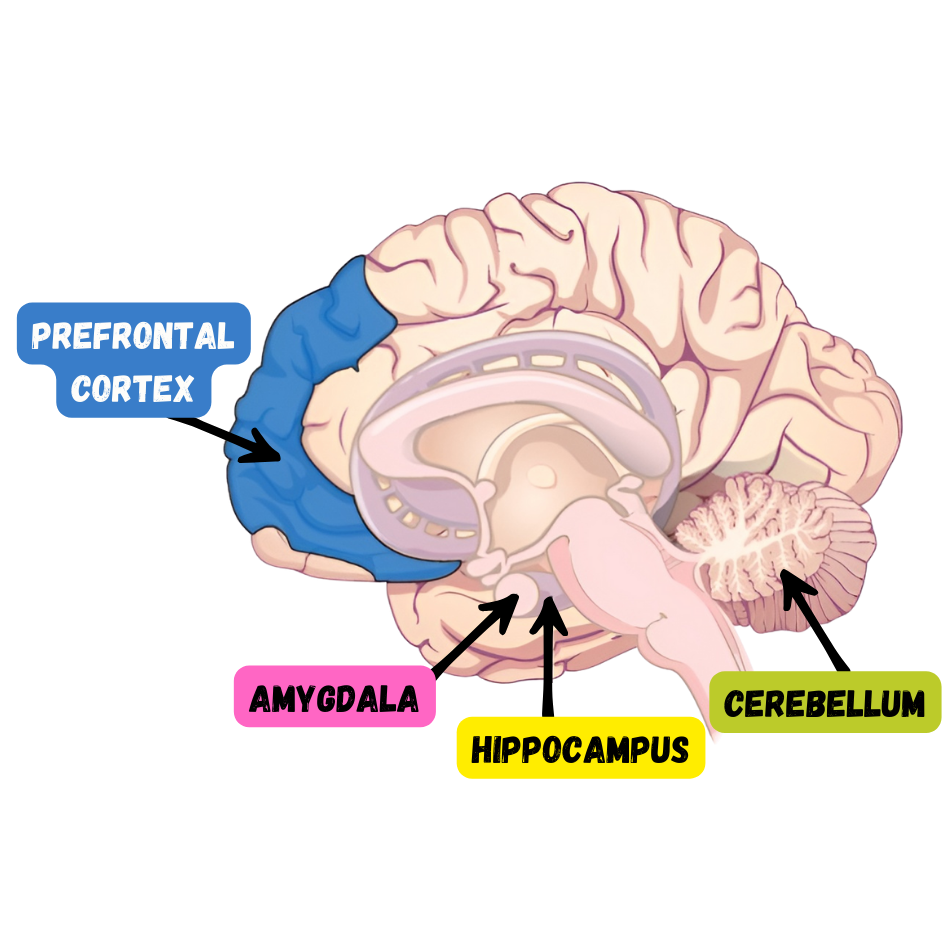
Amygdala involved in fear and fear memories (memory storage is influenced by stress hormones)
Hippocampus associated with explicit memory, recognition memory and spatial memory
Patient H.M had both temporal lobes removed (including hippocami) to help control his seizures
Cerebellum plays a role in processing procedural memories
- Damage prevents classical conditioning
Prefrontal cortex appears to be involved in remembering semantic tasks
- Encoding ➜ left frontal activity
- Retrieval of information ➜ right frontal activity
NEUROTRANSMITTERS
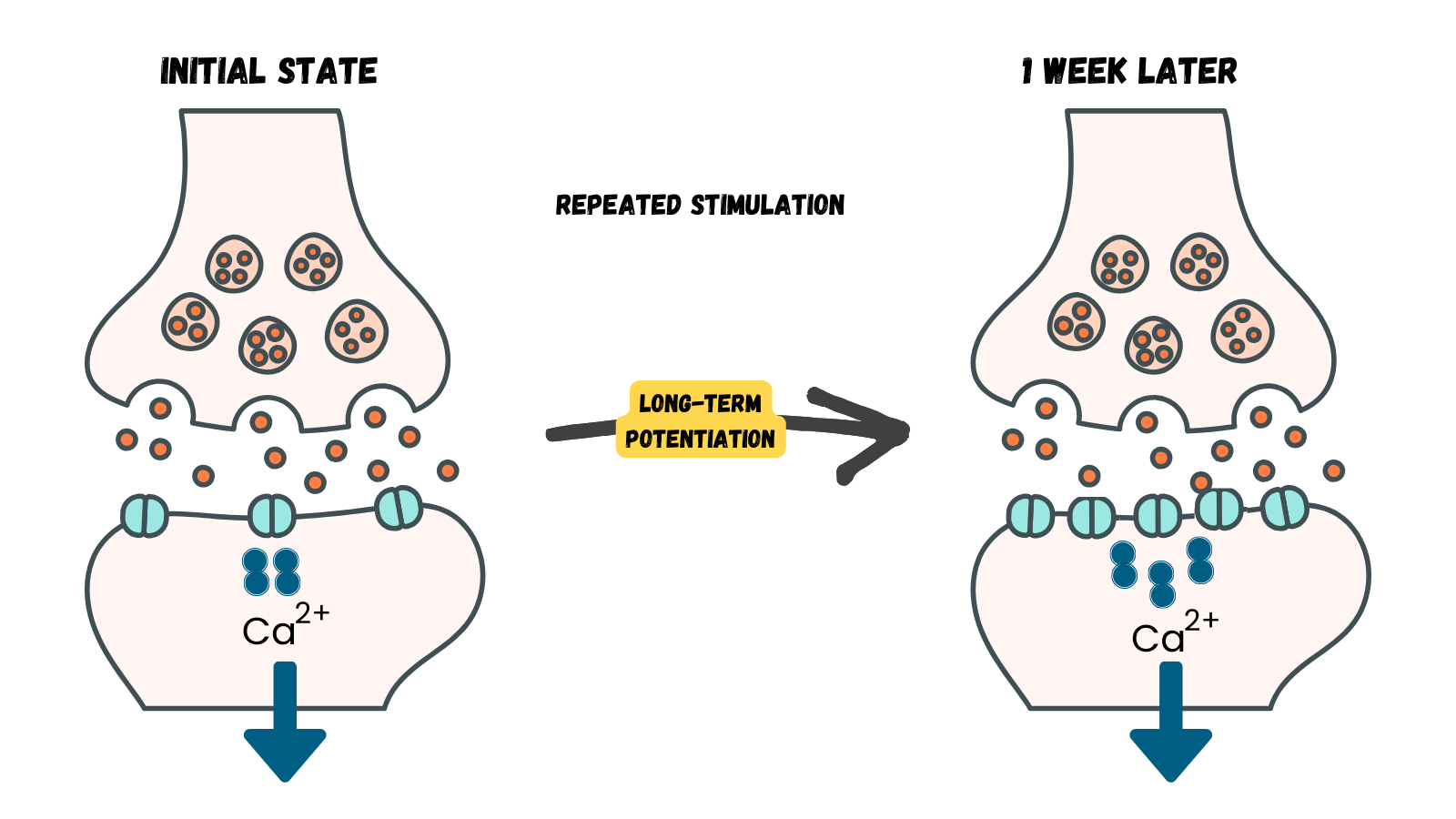
Memory Consolidation Repeated neuron activity ➜ increased neurotransmitters in the synapse ➜ stronger synaptic connections
Neurotransmitters
Epinephrine
Dopamine
Serotonin
Glutamate
Acetylcholine
Arousal Theory strong emotions trigger the formation of strong memories and weaker emotional experiences form weaker memories
FLASH BULB MEMORY

Flash bulb memory a record of an atypical and unusual event that has very strong emotional associations
AMNESIA

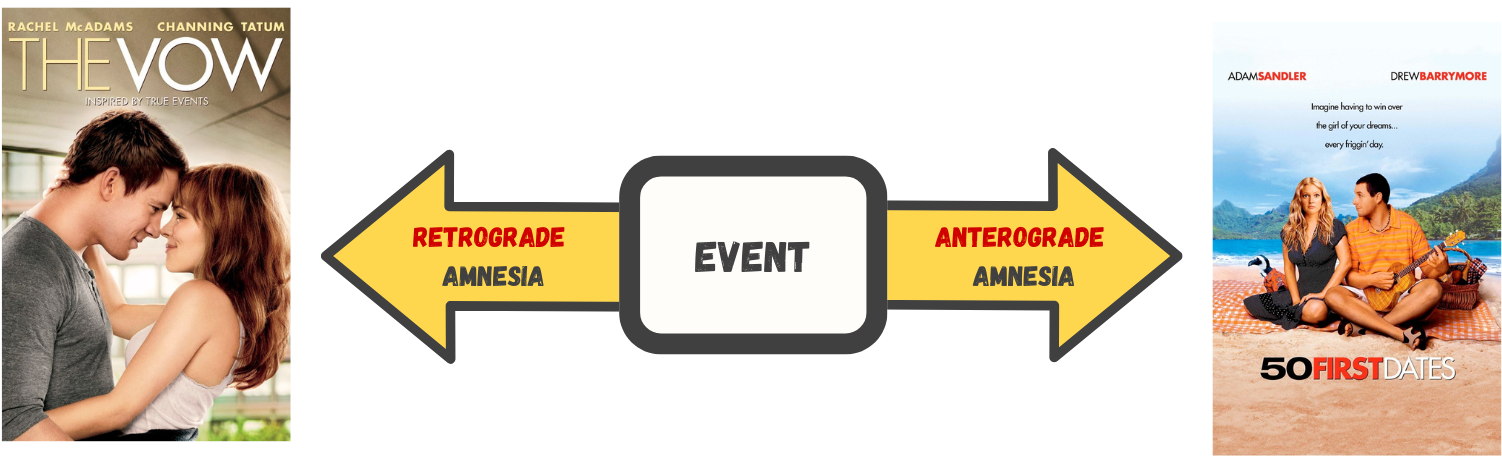
Amnesia loss of long-term memory that occurs as the result of disease, physical trauma, or psychological trauma
ENCODING
Brain receives inputs from environment and…
- Labels/codes it
- Organizes it with other similar information
- Connects new concepts to existing concepts
Automatic processing: encoding of details like time, space, frequency, and the meaning of words
- Usually done without conscious awareness
Effortful processing encoding of details that takes time and effort
TYPES OF ENCODING
Semantic encoding encoding of words and their meanings
- attach meaning to facilitate recall (most effective)
- Involves a deeper level of processing
Visual encoding encoding of images
- (concrete) words that create a mental image easier to recall than (abstract) words
TYPES OF ENCODING
Acoustic encoding encoding of sounds
Self-reference effect tendency to have better memory for information that relates to oneself
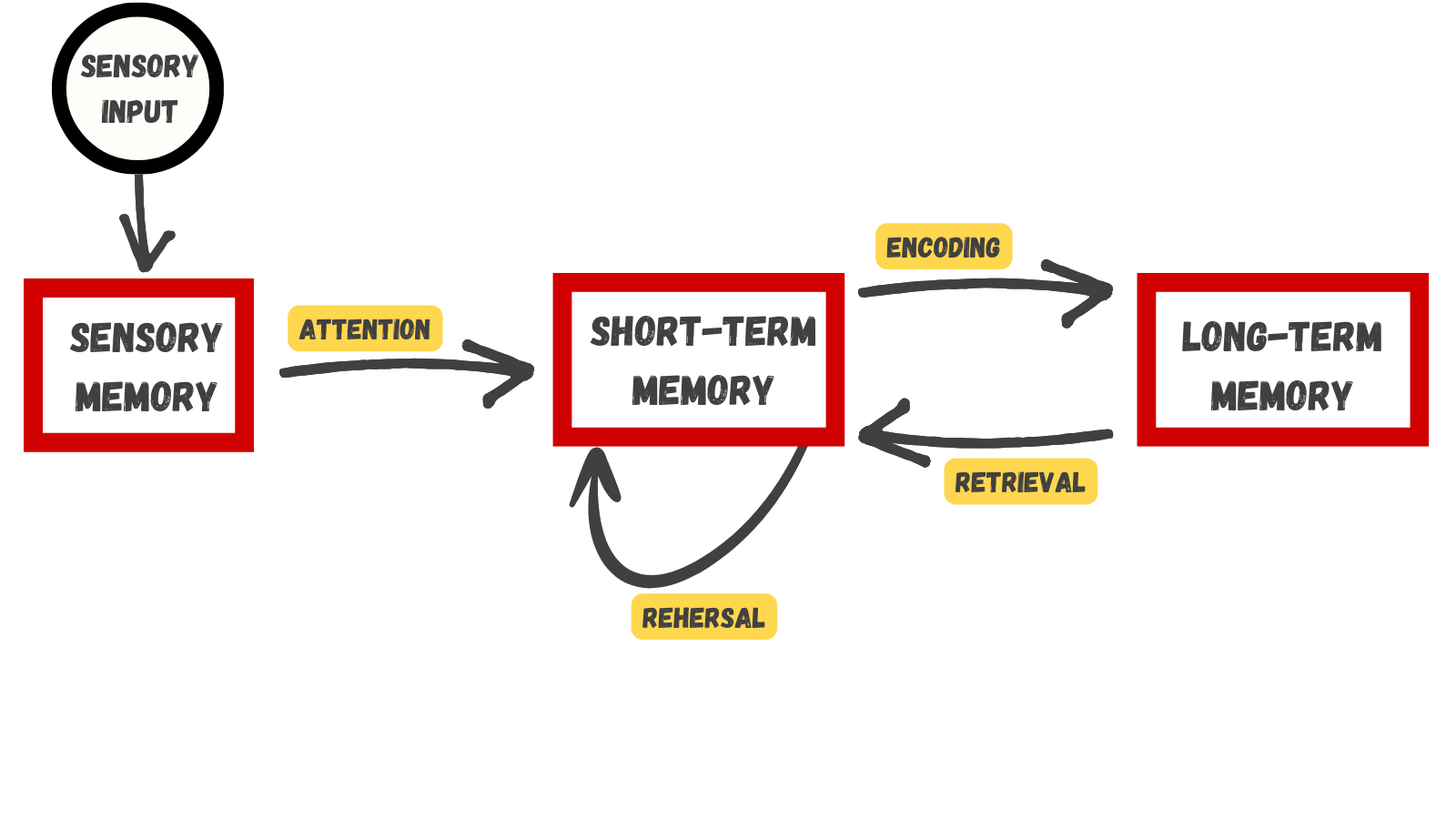
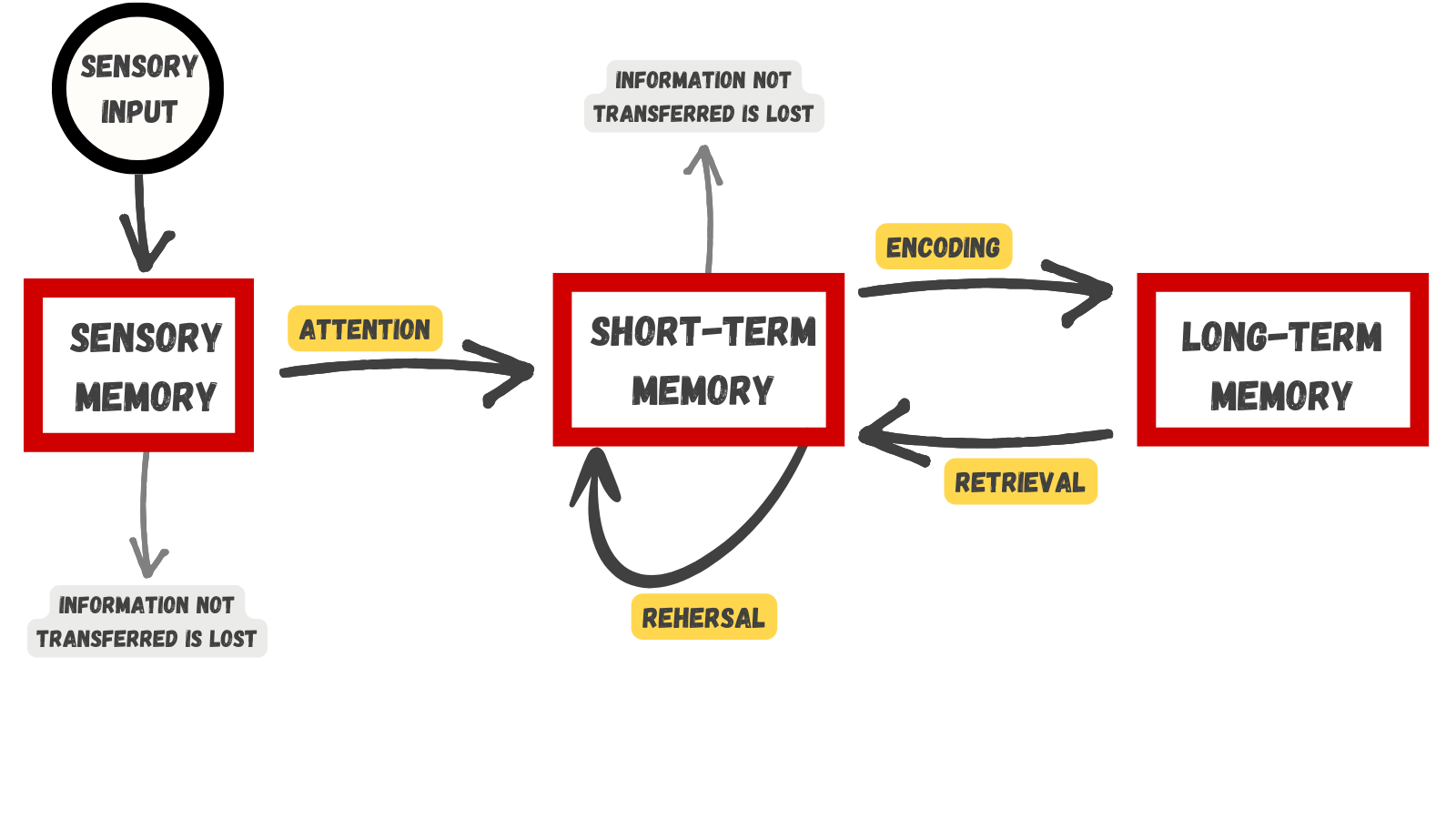
Atkinson-Shiffrin Model of Memory
Storage creation of a permanent record of information
THE STROOP EFFECT
Blue
Green
Black
Green
Red
Green
Black
Green
Green
Blue
Green
Black
Green
Black
Red
Blue
BADDELEY & HITCH MODEL
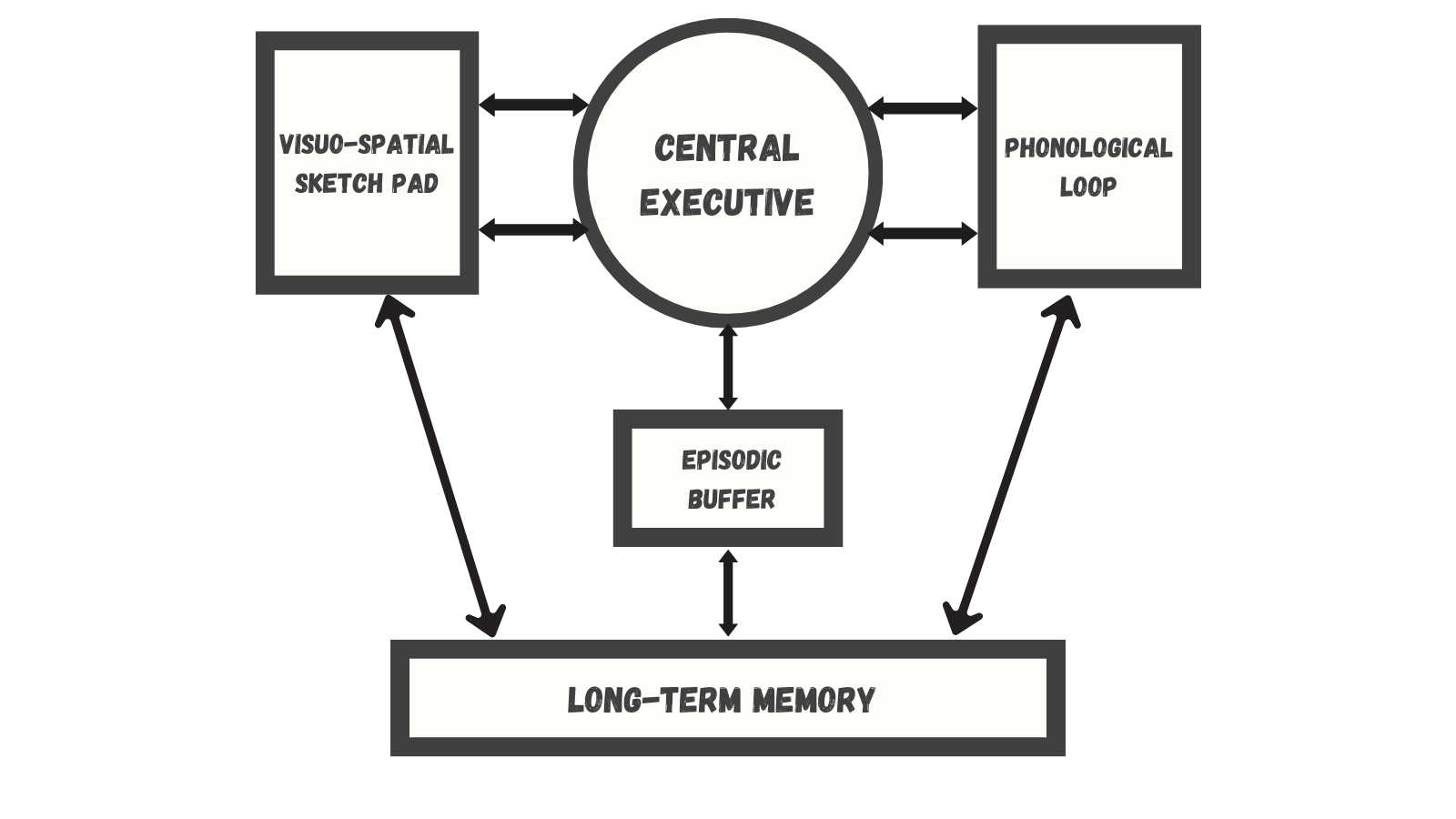
SHORT-TERM Working MEMORY

Working memory a temporary storage system that processes incoming sensory memory
- Lasts about 20 seconds
- Capacity is usually about 7 items +/- 2
- Either discarded or stored in long-term memory
Chunking
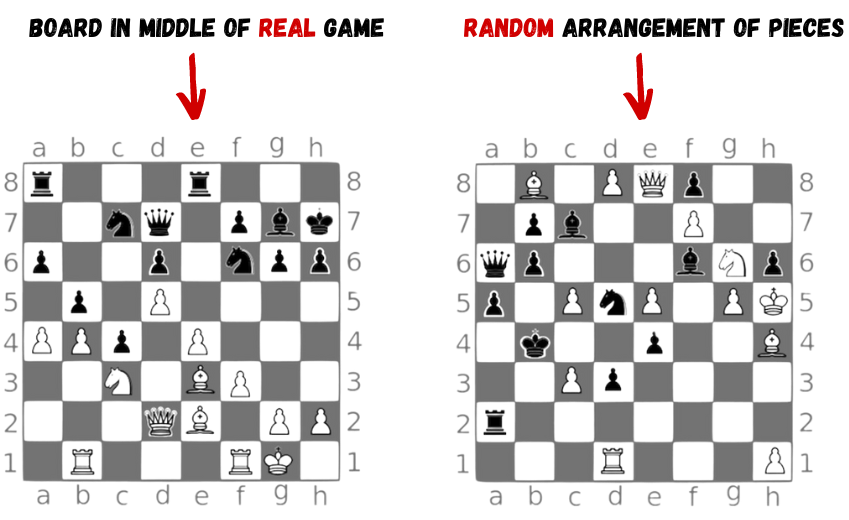
Chase & Simon (1973)
LONG-TERM MEMORY (LTM)
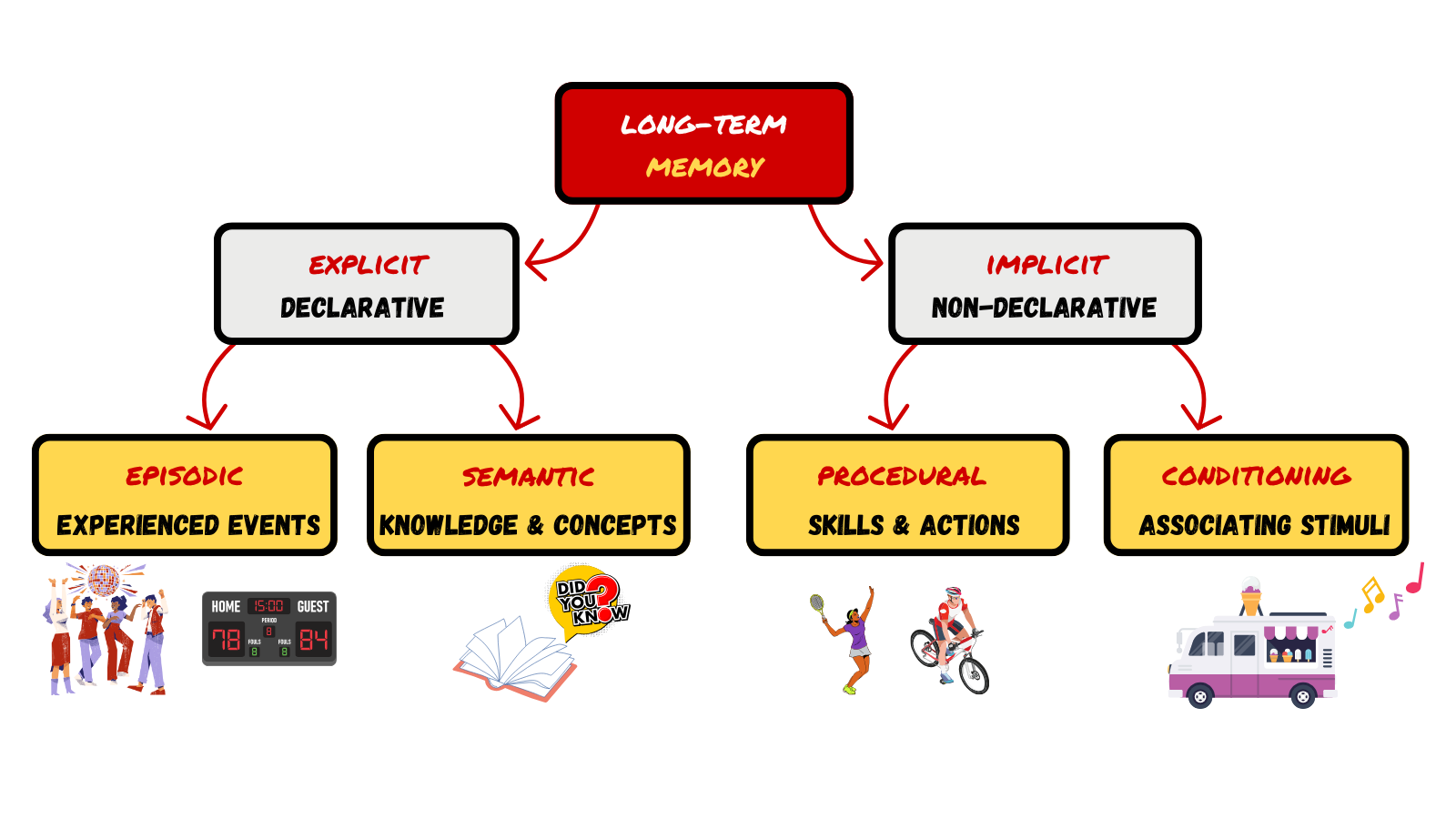
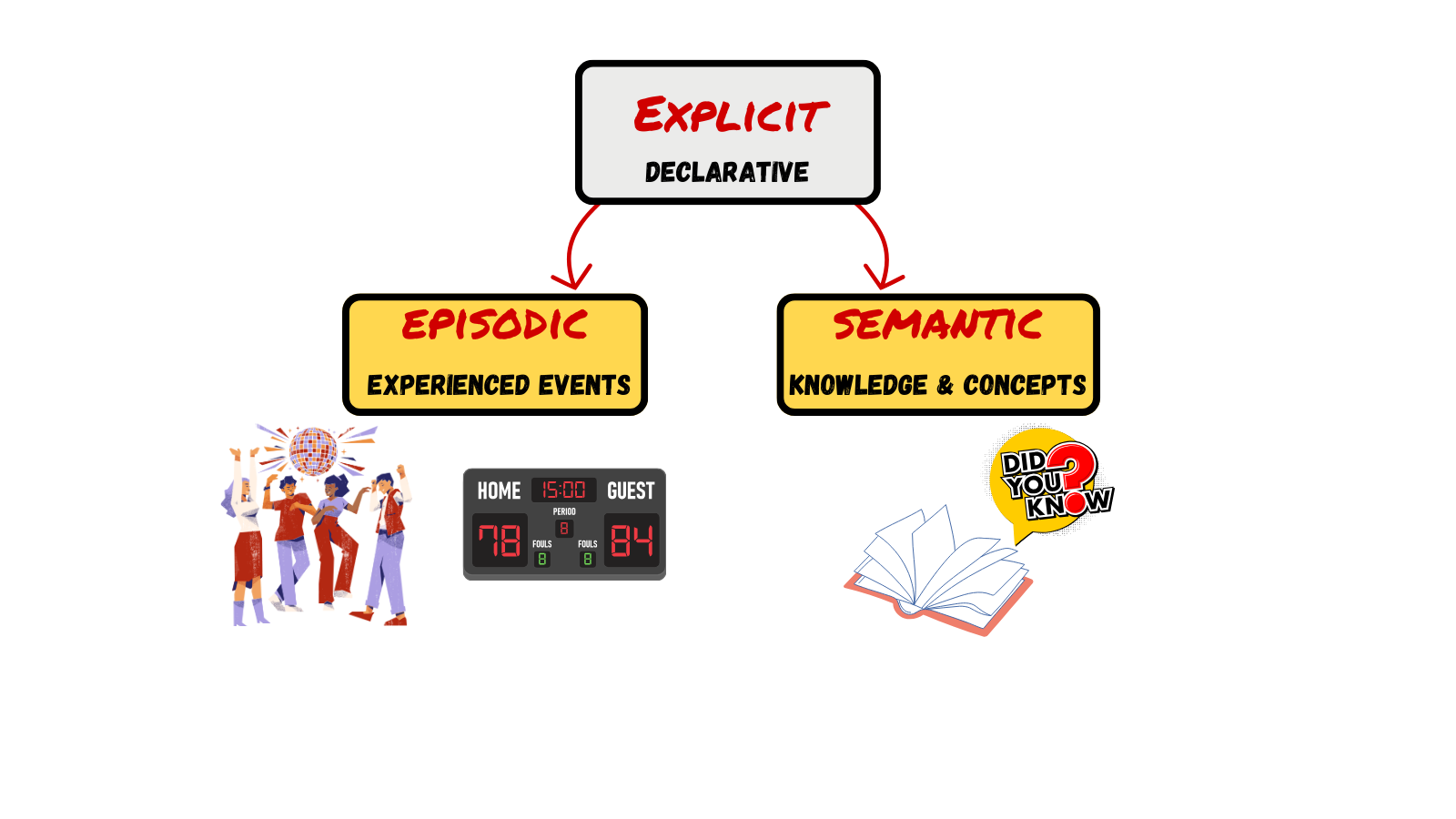
LTM: EXPLICIT MEMORY
Explicit memory memories of facts and events we can consciously remember and recall/declare
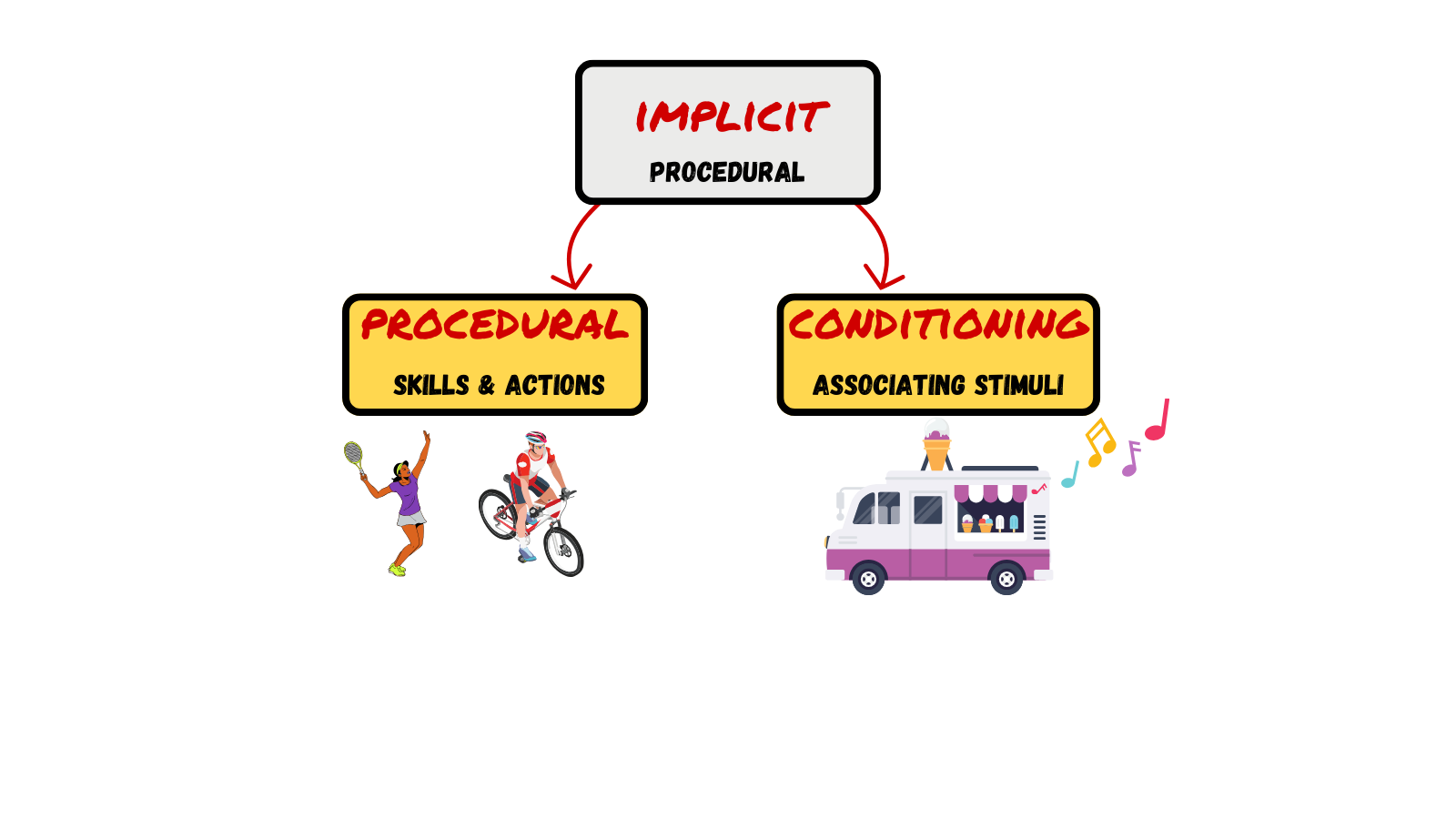
LTM: IMPLICIT MEMORIES
Implicit memory memories not part of our consciousness
RETRIEVAL
How to you get information back out of storage?

MEMORY CONSTRUCTION & RECONSTRUCTION
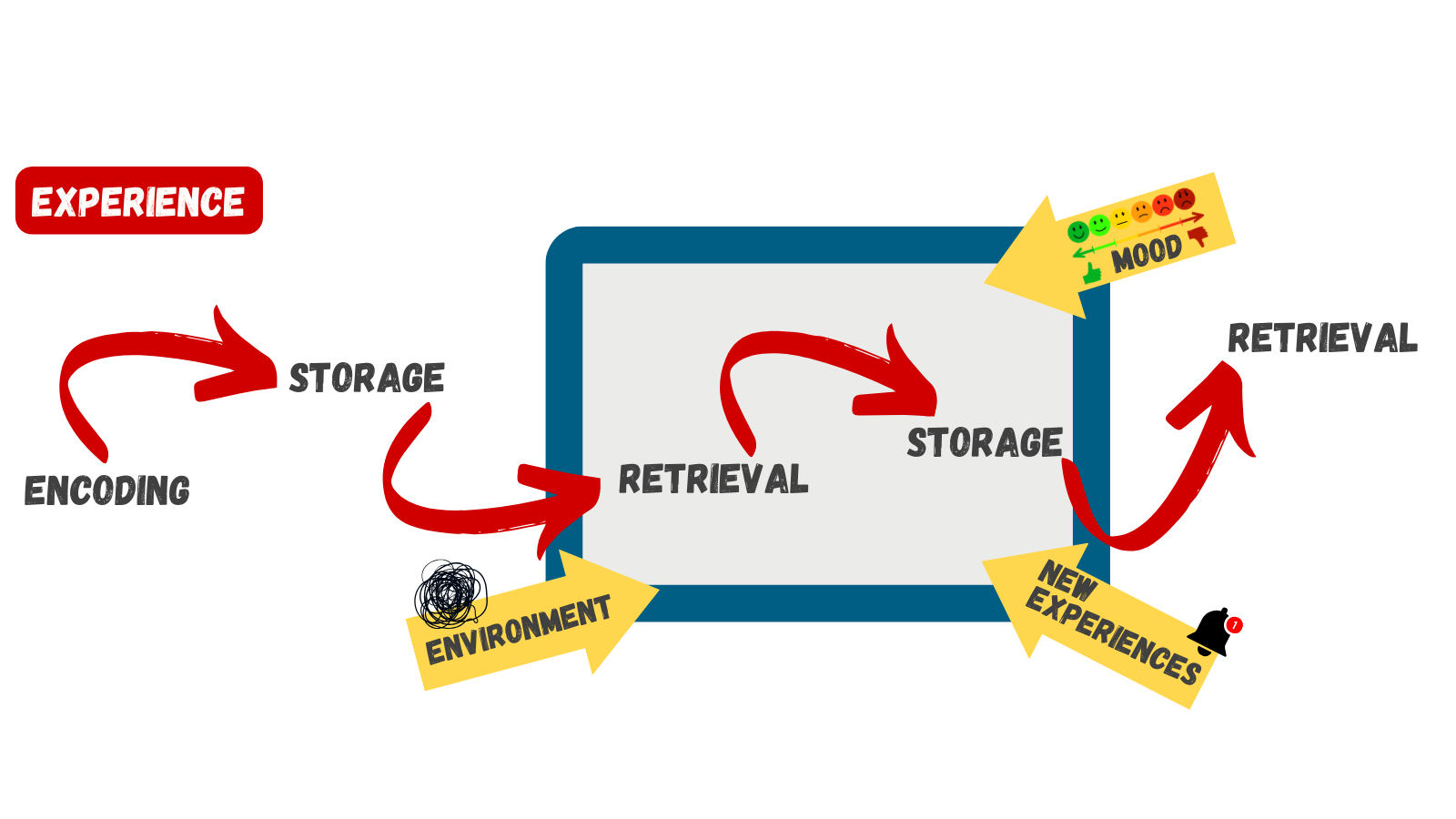
Construction formulation of new memories
Reconstruction process of bringing up old memories
Eyewitness Memory
Wells et al (1998)
Eyewitness Lineup
EYEWITNESS MISIDENTIFICATION
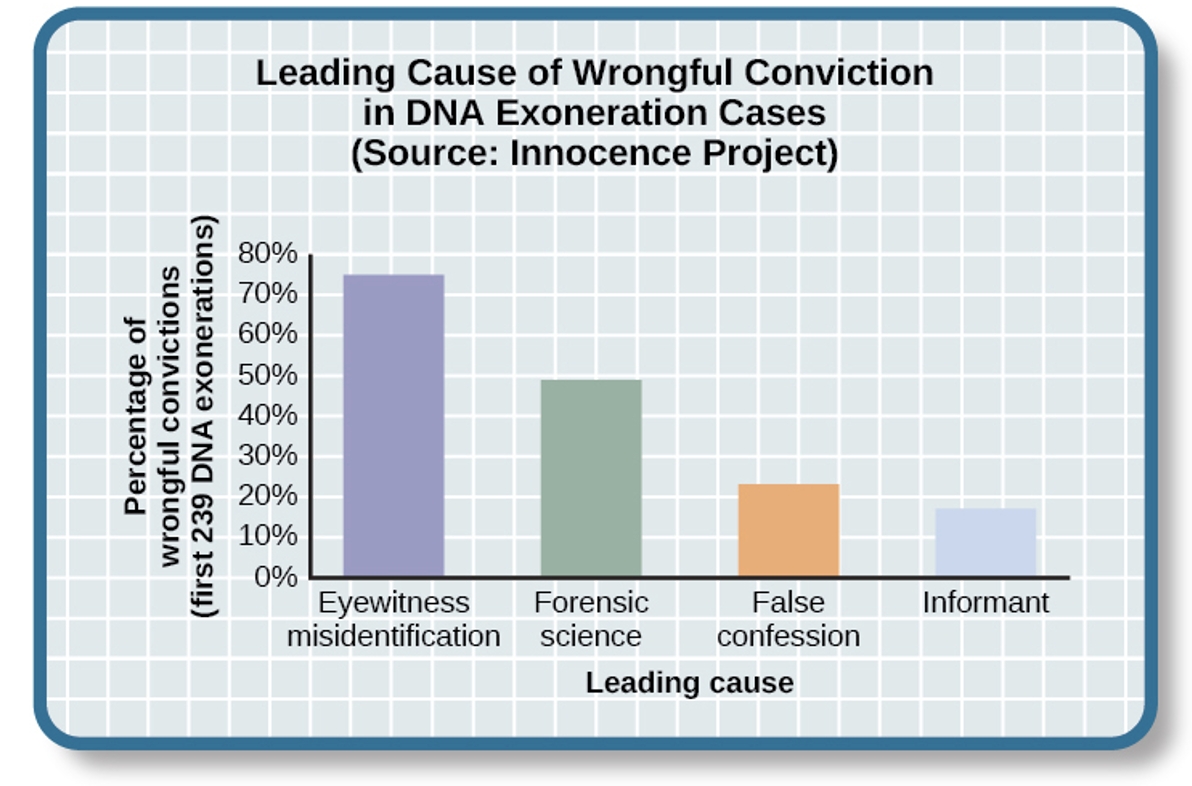
THE MISINFORMATION EFFECT
Loftus & Palmer (1974)
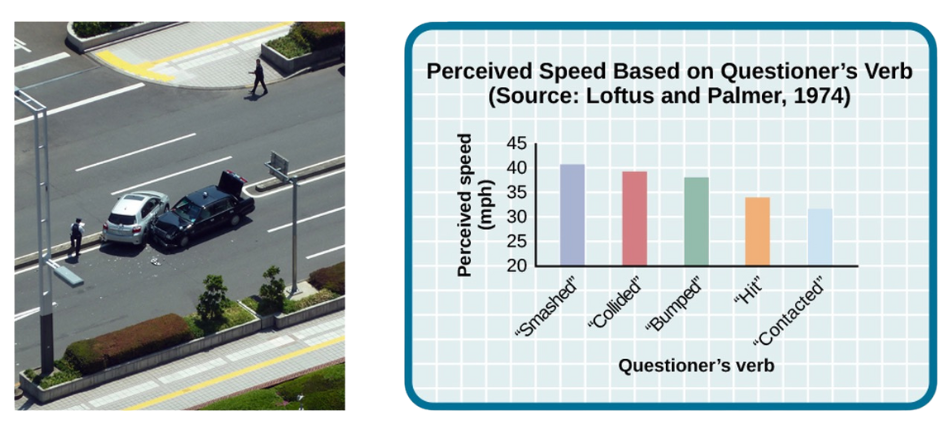
When people are asked leading questions about an event, their memory of the event may be altered
Loftus on Memory
REPRESSED & RECOVERED MEMORIES
False memory syndrome recall of false autobiographical memories
Repressed memories some psychologists believe can completely repress traumatic childhood memories
But Loftus does not agree!
WHY DO WE FORGET?
Forgetting loss of information from long-term memory
Encoding Failure occurs when the memory is never stored in the first place

Mandella Effect

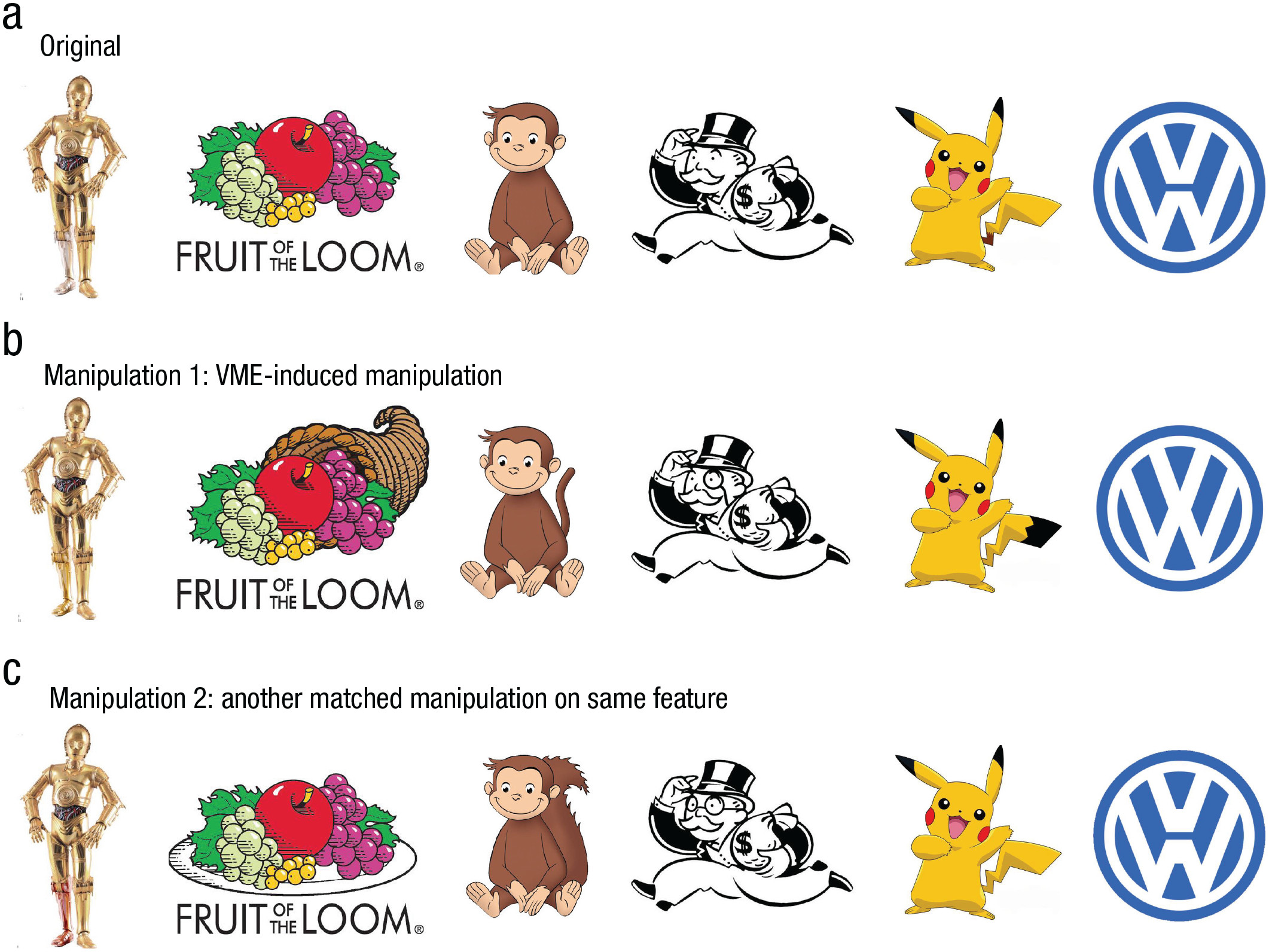
Rasad & Bainbridge (2022)

Rasad & Bainbridge (2022)
MEMORY ERRORS: Schacter’s 7 sins of memory
Forgetting type
1. Transience accessibility of memory decreases over time (storage decay)
2. Absentmindedness forgetting caused by lapses in attention
3. Blocking accessibility of information is temporarily blocked (aka tip-of-the-tongue phenomenon)
Distortion type
4. Misattribution source of memory is confused
5. Suggestibility false memories
6. Bias memories distorted by current belief system
Intrusion type
7. Persistence inability to forget undesirable memories
TRANSIENCE/STORAGE DECAY
Overtime, unused information tends to fade away.
Ebbinghaus (1885) showed how quickly memory for new information decays
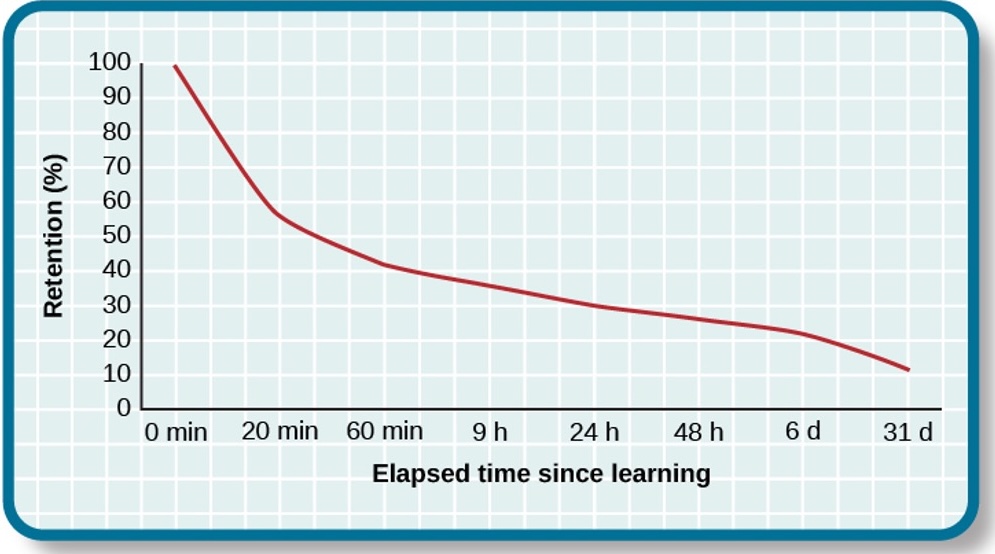
- 50% after 20 minutes
- 70% after 24 hours
Memory BIASES
Stereotypical bias after presenting people with a list of names, they more frequently incorrectly remembered typical African American names to be associated with the occupation basketball player, and typical white names to be associated with the occupation politician
Egocentric bias people remember events in a way that makes them look better
Hindsight bias the tendency to think you knew the answer all along
Example: How many neck bones does a giraffe have? Answer: Seven
Blank, H., & Nestler, S. (2007); Bernstein et al. (2011)
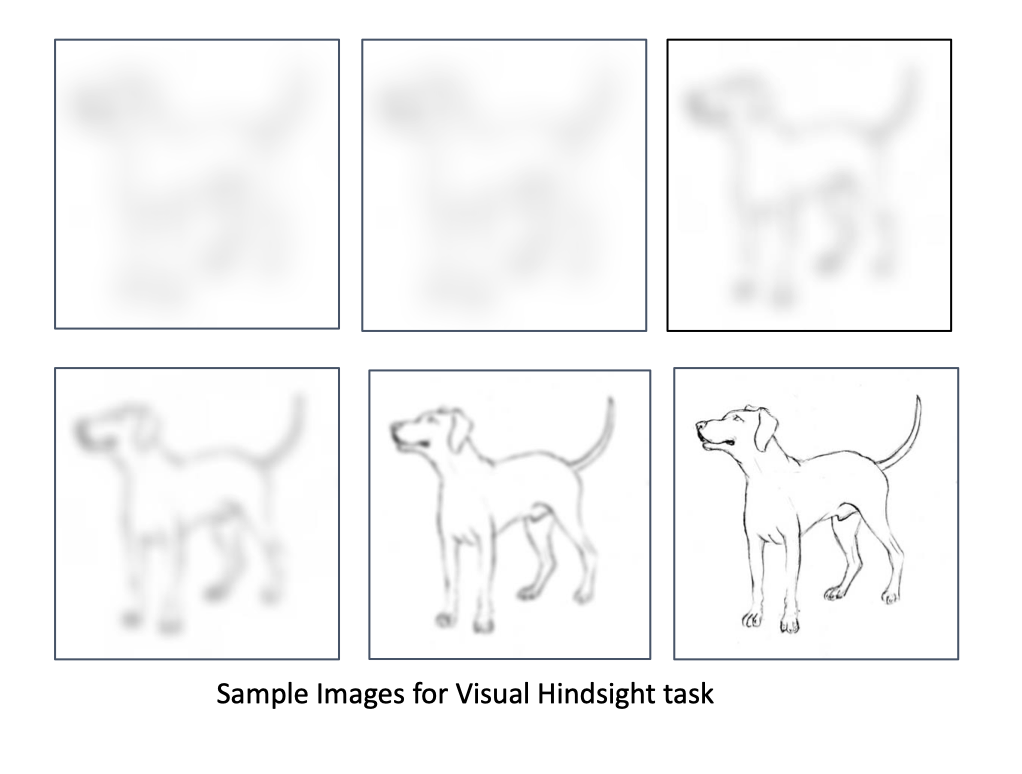
Blank, H., & Nestler, S. (2007); Bernstein et al. (2011)
PERSISTENCE

INTERFERENCE
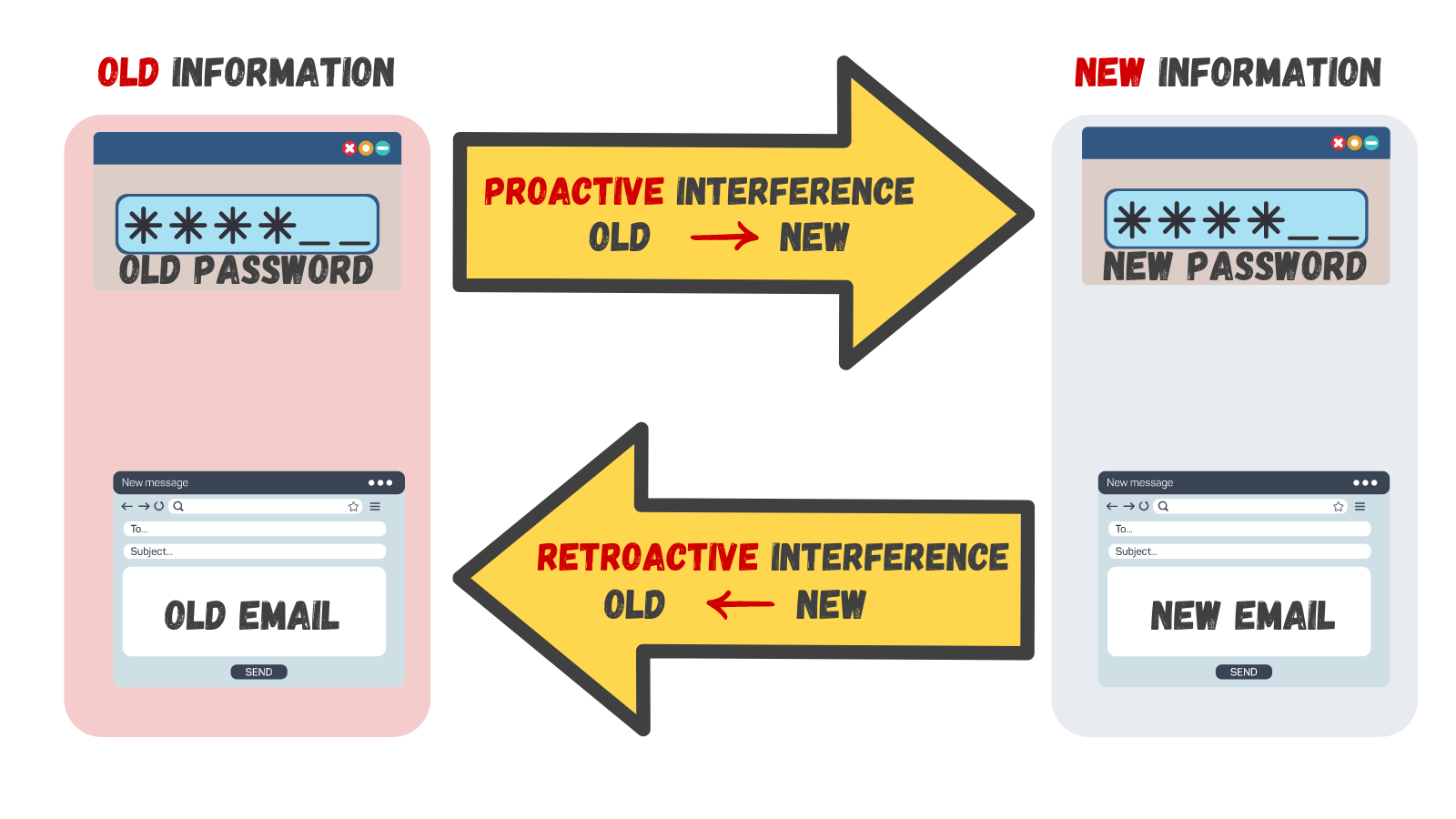
WAYS TO ENHANCE MEMORY
Rehearsal conscious repetition of information to be remembered
Chunking organizing information into manageable bits or chunks
Elaborative rehearsal technique in which you think about the meaning of the new information and its relation to knowledge already stored in your memory
Mnemonic device memory aids that help us organize information for encoding
MNEMONIC DEVICES

HOW TO STUDY EFFECTIVELY
Memory techniques can be useful when studying for class.
- Use elaborative rehearsal: link information to other information/memories to make it more meaningful.
- Apply the self-reference effect: make information personally meaningful to YOU
- Don’t forget the forgetting curve: keep studying to prevent storage decay.
- Rehearse
- Be aware of interference: study without distractions.
- Keep moving: aerobic exercise promotes neurogenesis (growth of new brain cells in the hippocampus).
- Get enough sleep: the brain consolidates memories while sleeping
- Make use of mnemonic devices!!