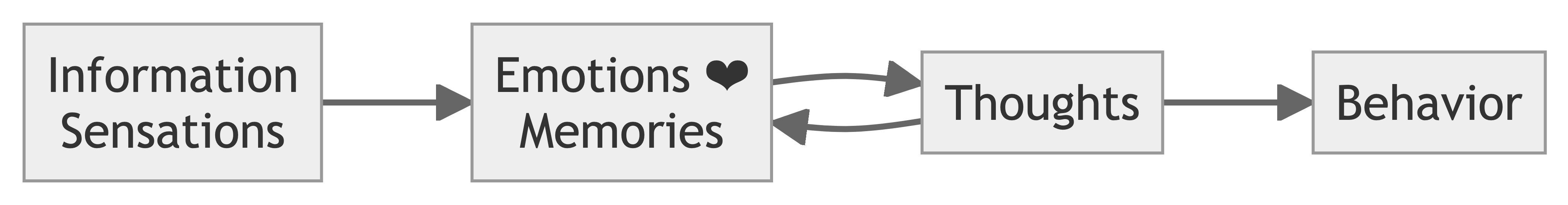
Sensations and information are received by our brains, filtered through emotions and memories, and processed to become thoughts.
PSYC 181 – Intro to Psych
July 29, 2024
![]()
Learning Objectives
![]()

Sensations and information are received by our brains, filtered through emotions and memories, and processed to become thoughts.
Concepts categories of linguistic information, images, ideas or memories
Prototypes the best example or representation of a concept



Natural Created through either direct or indirect experience

Artificial defined by a specific set of characteristics


Schema A mental construct consisting of a collection of related concepts
Role schema Makes assumptions about how individuals in certain roles will behave
Event schema A set of routine or automatic behaviors or cognitive script
Example: Texting & Driving in Lincoln Difficult to change because event schema’s are automatic


Trial & error keep trying until solved
Algorithm step-by-step formula
Heuristic mental short-cut or “rule of thumb”
Problem solving abilities can improve with practice.
Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper


| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Trial and error | Continue trying different solutions until problem is solved | turning technology off and back on |
| Algorithm | Step-by-step problem-solving formula | Instruction manual for installing new software on your computer |
| Heuristic | General problem-solving framework | Working backwards; breaking a task into steps |
“Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result” – Albert Einstein.
Functional fixedness inability to perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for

Mental sets a set way of looking at a problem
Anchoring bias Tendency to focus on one piece of information and adjust



Confirmation bias Tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs

Representative bias Tendency to unintentionally stereotype someone or something

Availability heuristic Tendency to make a decision based on readily available example, information, or recent experience
Hindsight biasKnowledge of an outcome makes that outcome appear more inevitable or foreseeable than it would have been beforehand

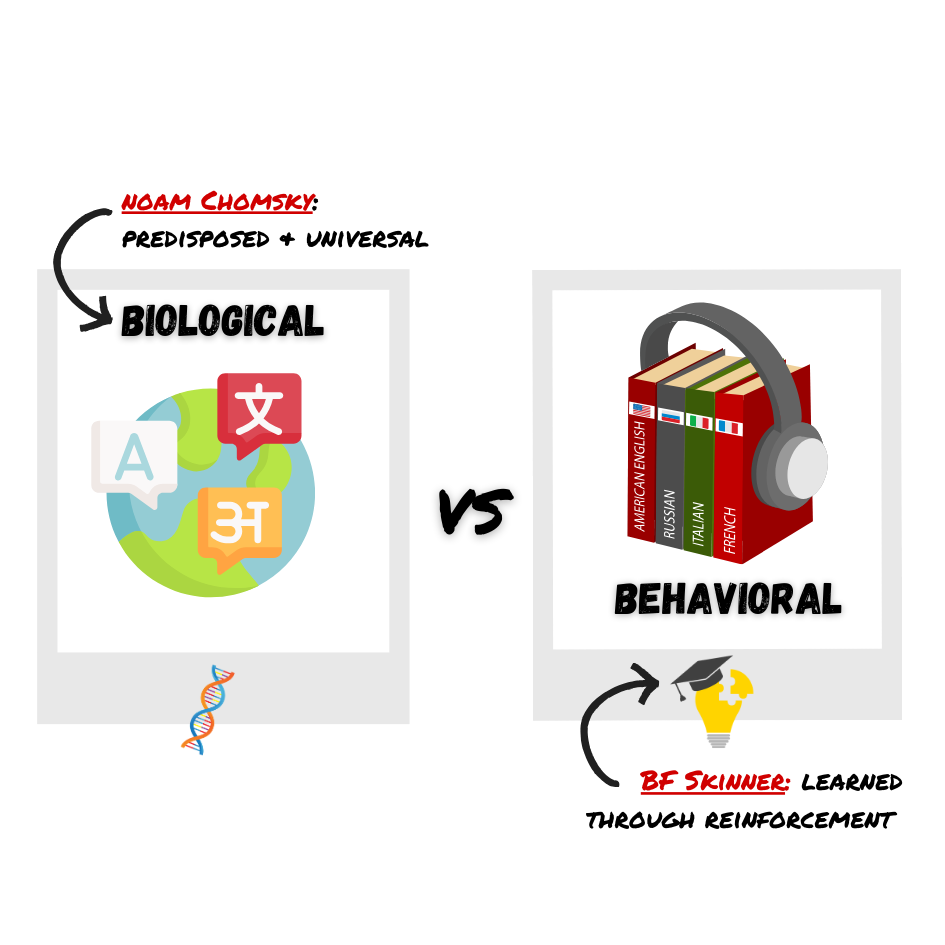
Language a communication system that involves using words and systematic rules to transmit information from one individual to another
Phoneme short, sound units (ah, eh)
Morphemes the smallest units that convey meaning
Lexicon the words of a given language
Grammar the set of rules that are used to convey meaning through the use of the lexicon.
Semanticsthe meaning we derive from morphemes and words
Syntax the way words are organized into sentences
Critical period Proficiency at acquiring language is maximal early in life
| Stage | Age | Developmental Language & Communication |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0-3 Months | Reflexive communication |
| 2 | 3-8 Months | Reflexive communication; interest in others |
| 3 | 8-13 Months | Intentional communication; sociability |
| 4 | 12-18 Months | First words |
| 5 | 18-24 Months | Simple sentences (two words) |
| 6 | 2-3 Years | Sentences (three or more words) |
| 7 | 3-5 Years | Complex sentences; conversations |
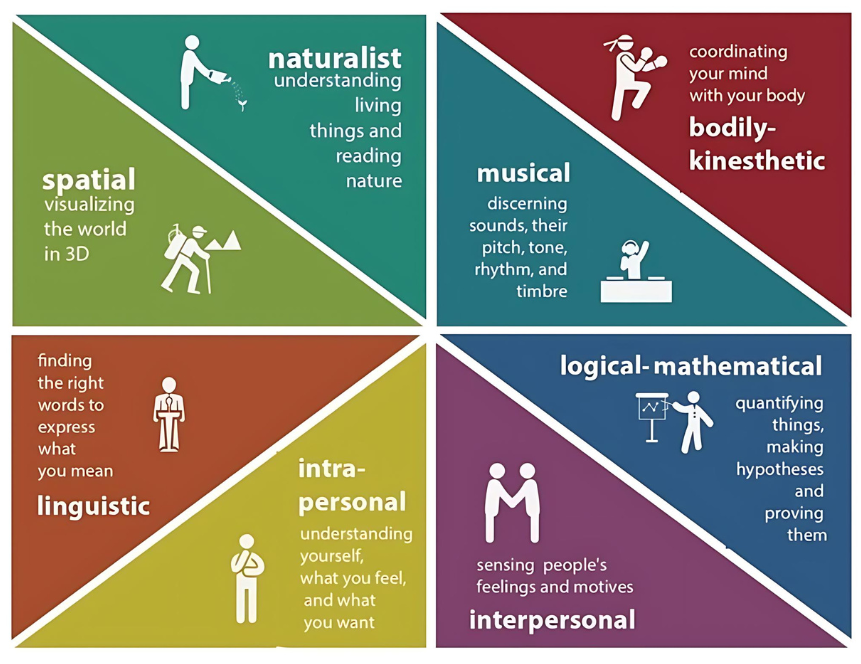

Creativity the ability to generate, create, or discover new ideas, solutions, and possibilities
Divergent thinking thinking outside the box
Convergent thinking ability to provide a correct or well-established answer or solution to a problem
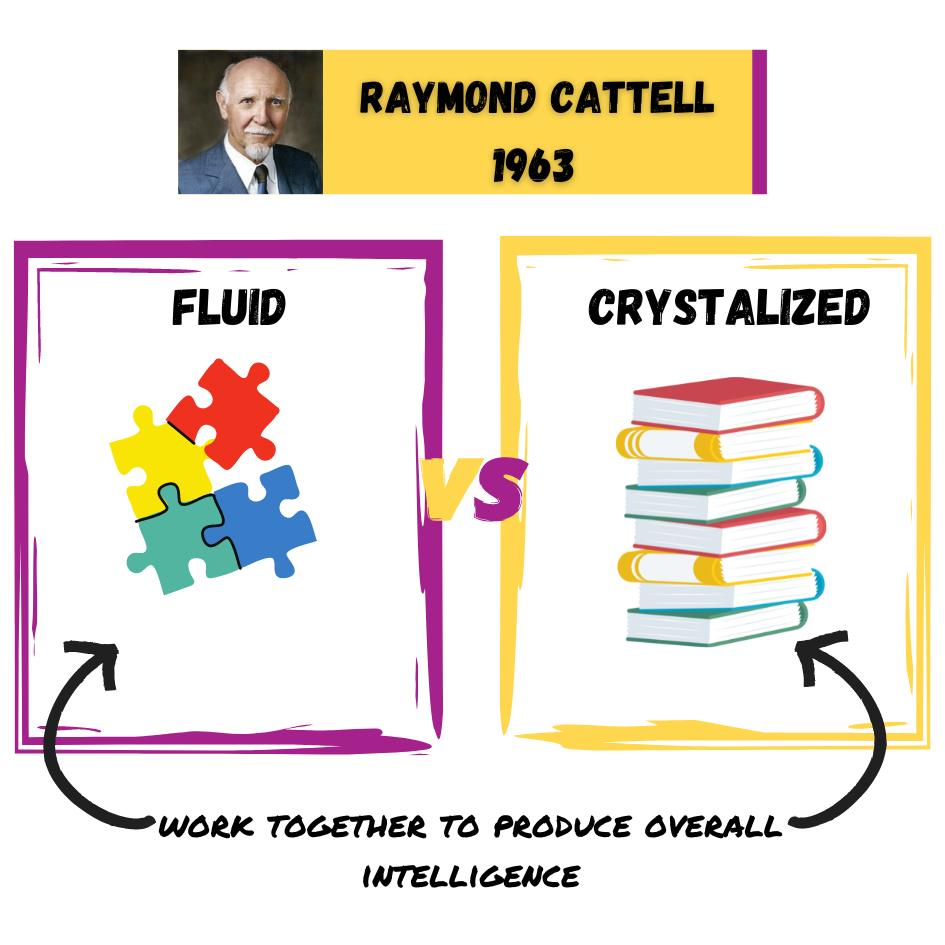
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) score earned on a test designed to measure intelligence
Flynn Effect each generation has a significantly higher IQ than the last
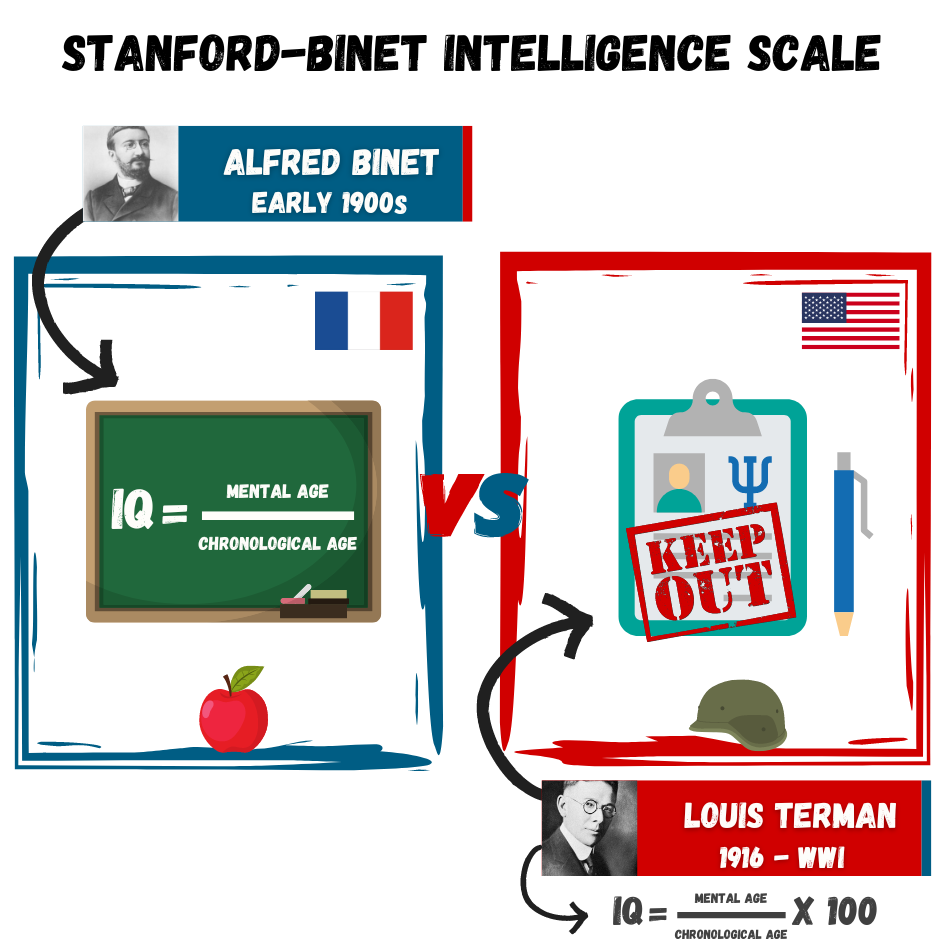


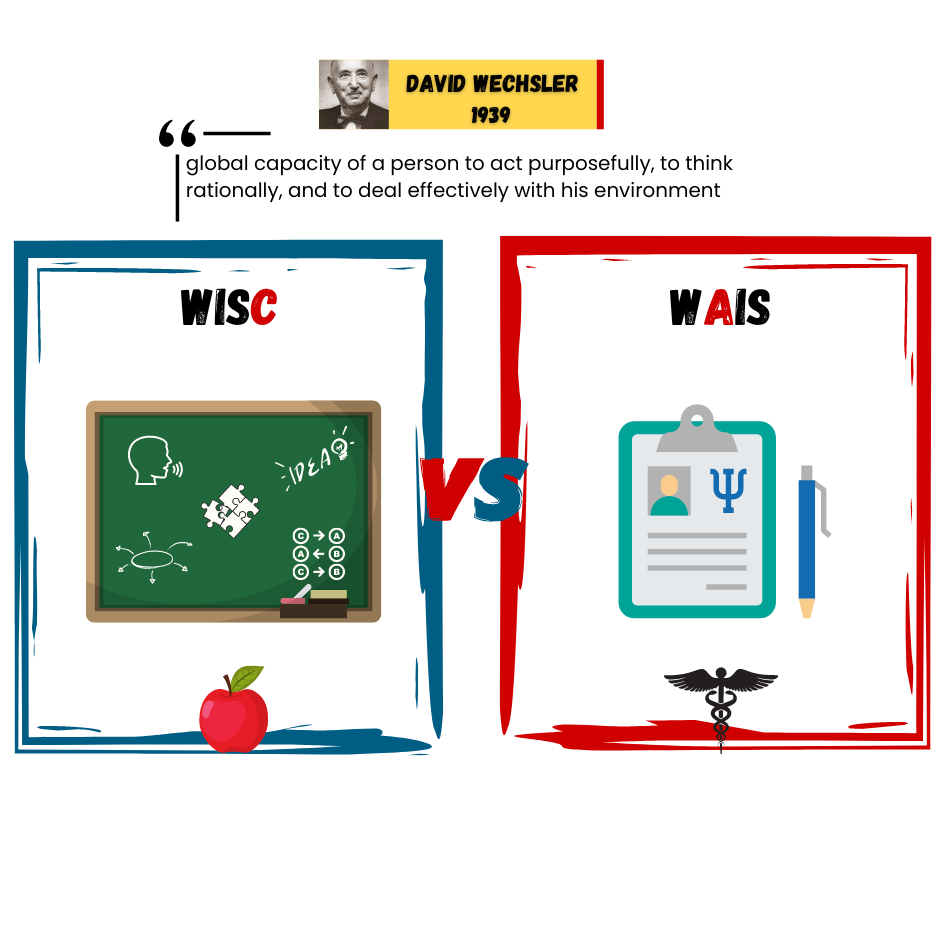
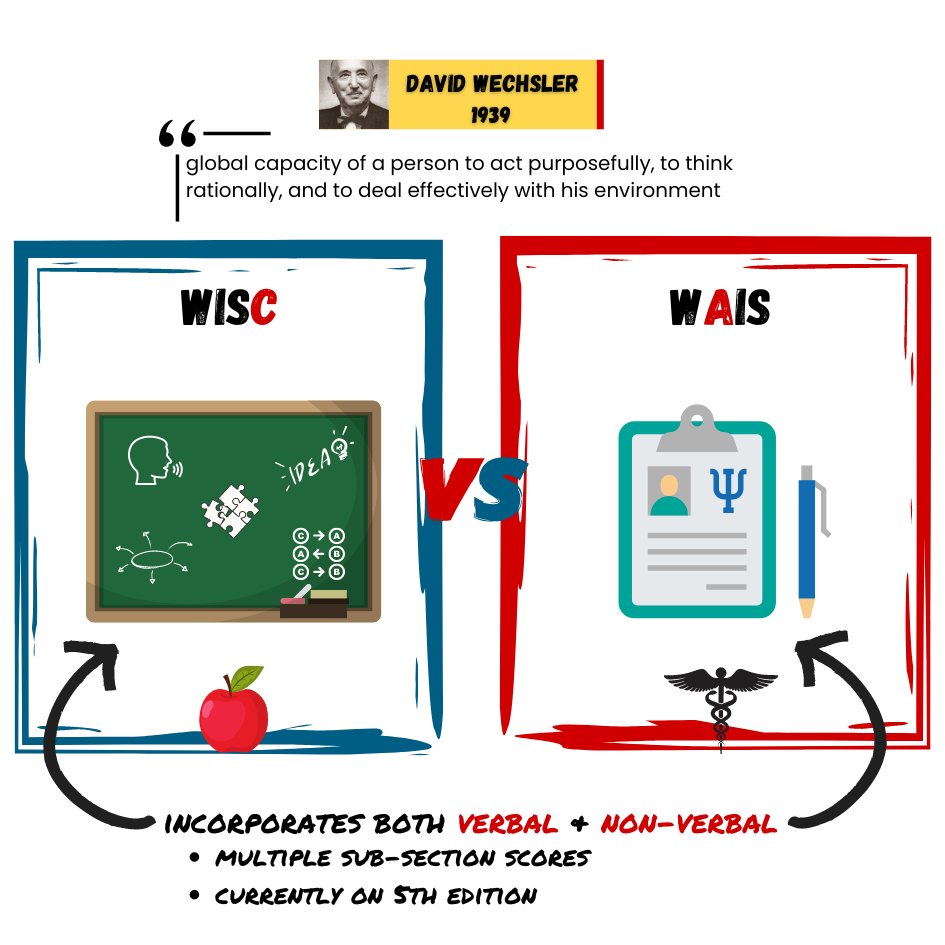
Are you of below-average, average, or above-average height?
Representative sample a subset of the population that accurately represents the general population
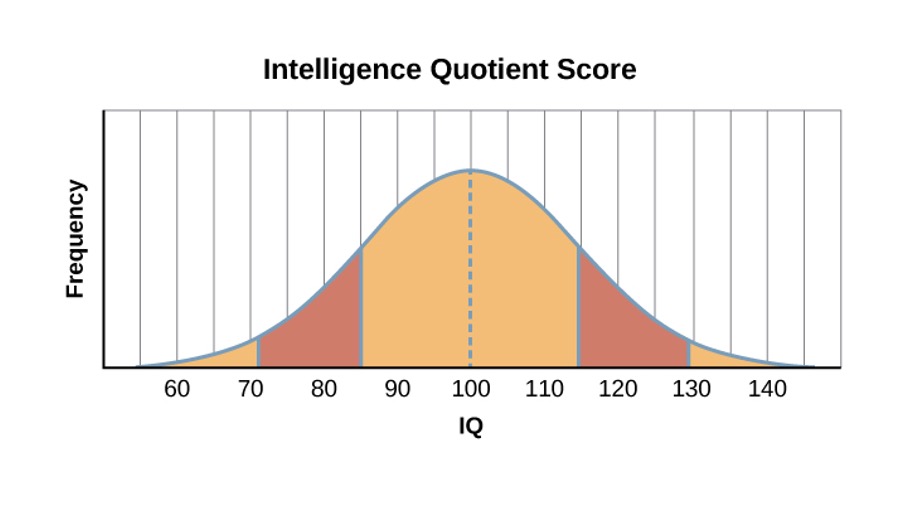

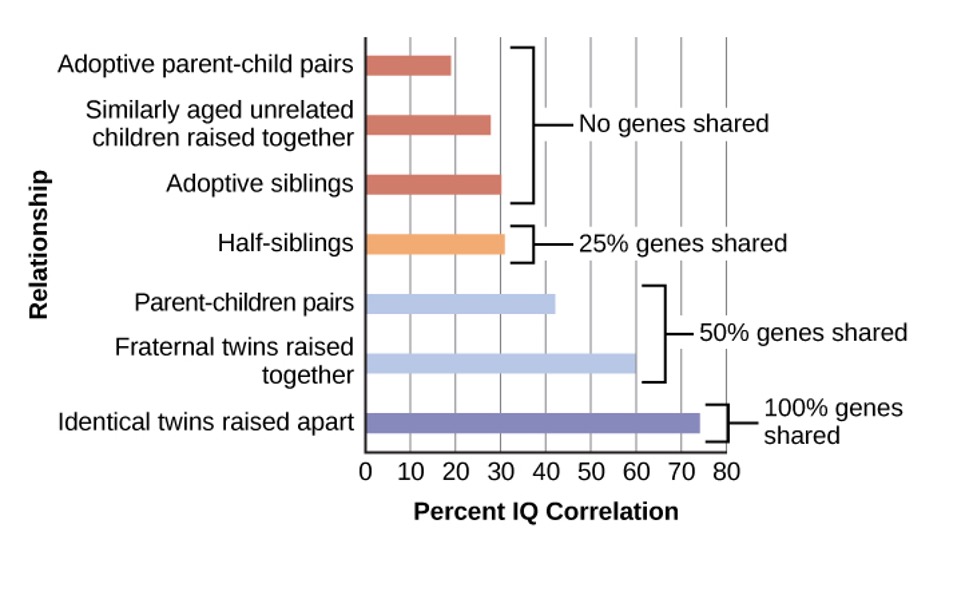
Range of reaction theory that each person responds to the environment in a unique way based on genetic makeup

Dysgraphia results in struggle to write legibly
Dyslexia an inability to correctly process letters
