🗓 Unit 6
Motivation & Emotion
PSYC 181 – Intro to Psych
July 25, 2024
What you will learn
![]()
Learning Objectives
- Explain several proposed theories of motivation
- Understand basic biological mechanisms regulating sexual behavior and motivation
- Explain the major theories of emotion
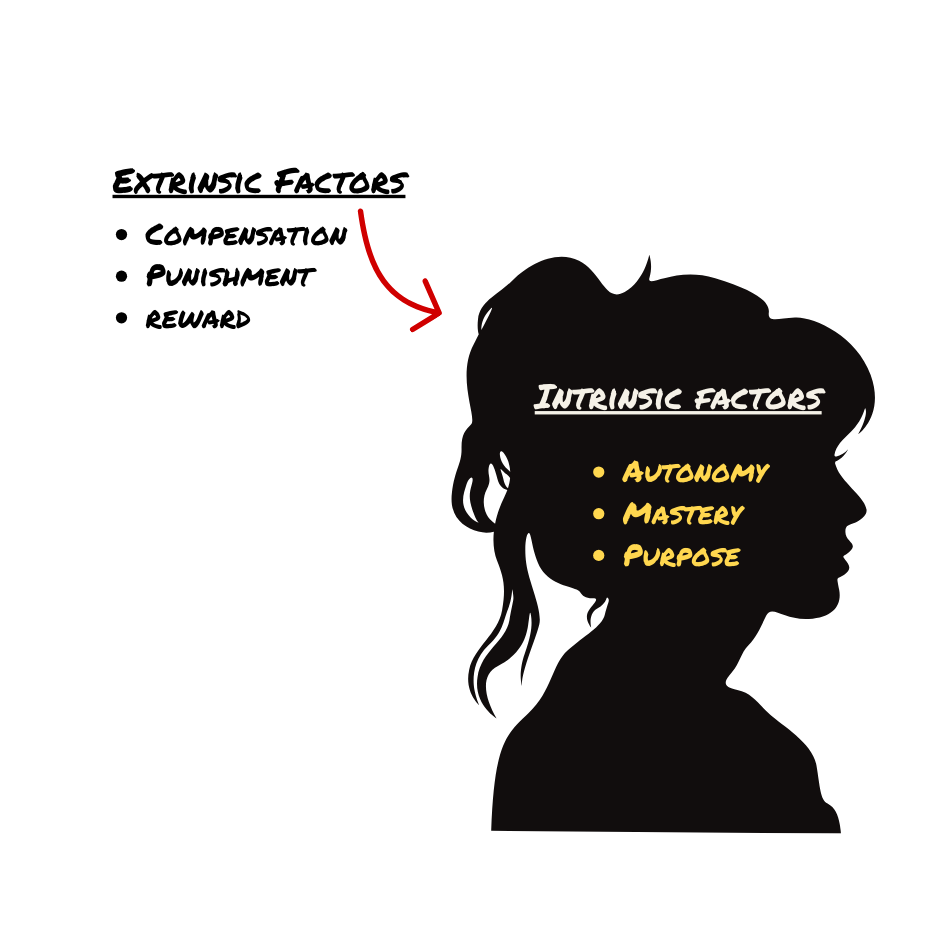
Intrinsic vs Extrinsic Motivation
External
receive something from others
Intrinsic
personal satisfaction
Over-Justification Effect
Intrinsic motivation can diminish when extrinsic rewards are given

Explanations?
- Type of reinforcement
- Tangible rewards → decrease intrinsic
- Intangible rewards → increase intrinsic
- Expectation of extrinsic reward
- Intrinsic motivation → decreases if external reward expected
Theories of Motivation
Instinct Theory
Behaviors driven by instincts that aid survival
Drive Theory
Behaviors are driven to maintain homeostasis
Arousal Theory
Individuals seek an optimal level of arousal
Instinct Theory of Motivation
William James

Behavior driven by instincts (which aid survival)
But what about role of learning?
Drive Theory of Motivation
Deviations from homeostasis → create physiological needs → psychological drive states

Emphasizes role habits play in behavioral responses → If a behavior reduces a drive successfully, we are more likely to do it again
Arousal Theory
underaroused → bored → seek stimulation
overaroused → overwhelmed → behaviors to reduce arousal

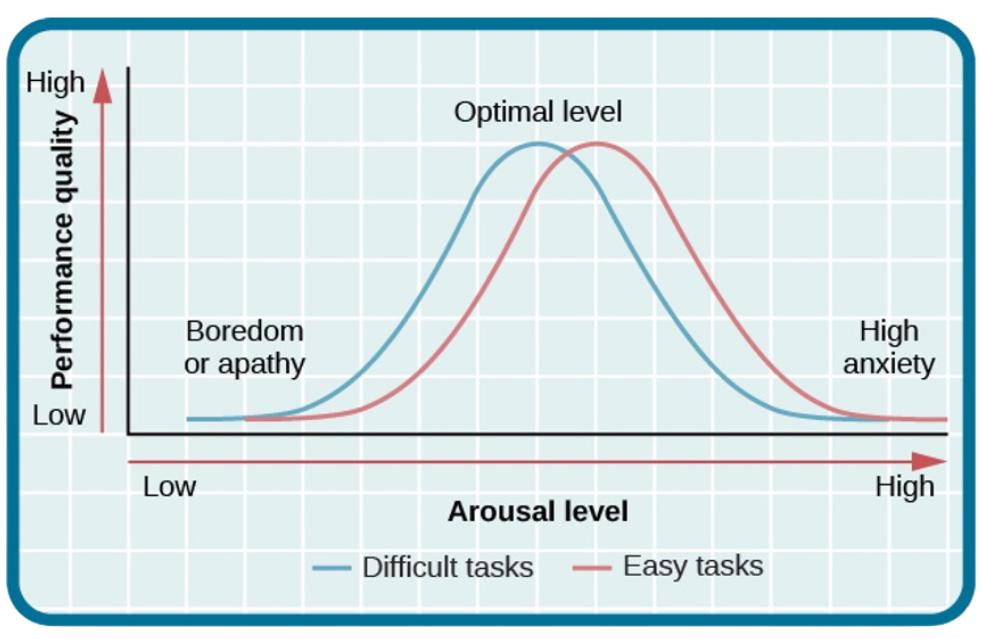
Yerks & Dodson Law
optimal arousal depends on complexity and difficulty of the task
Self-Efficacy & Social Motivation
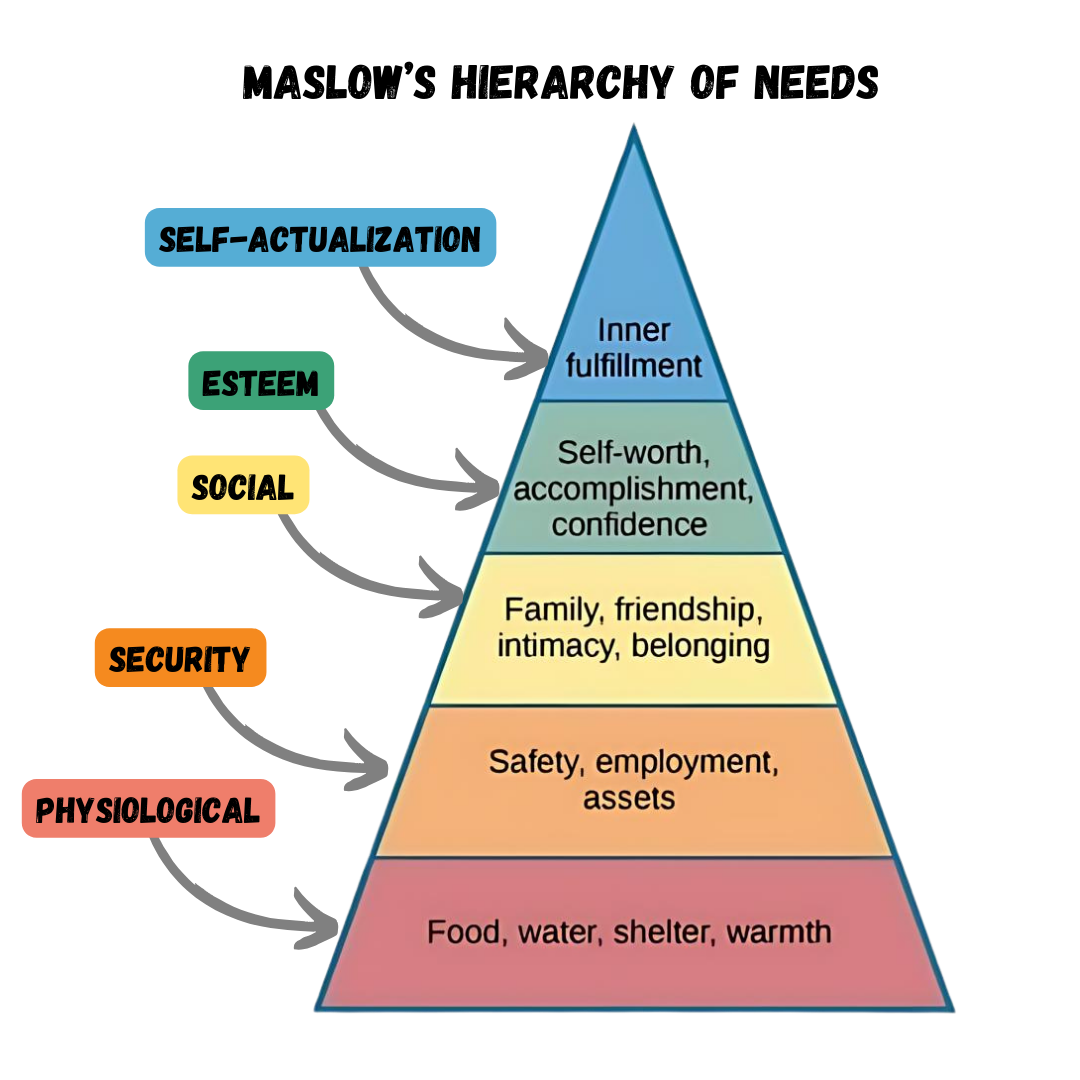
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Sexual Behavior
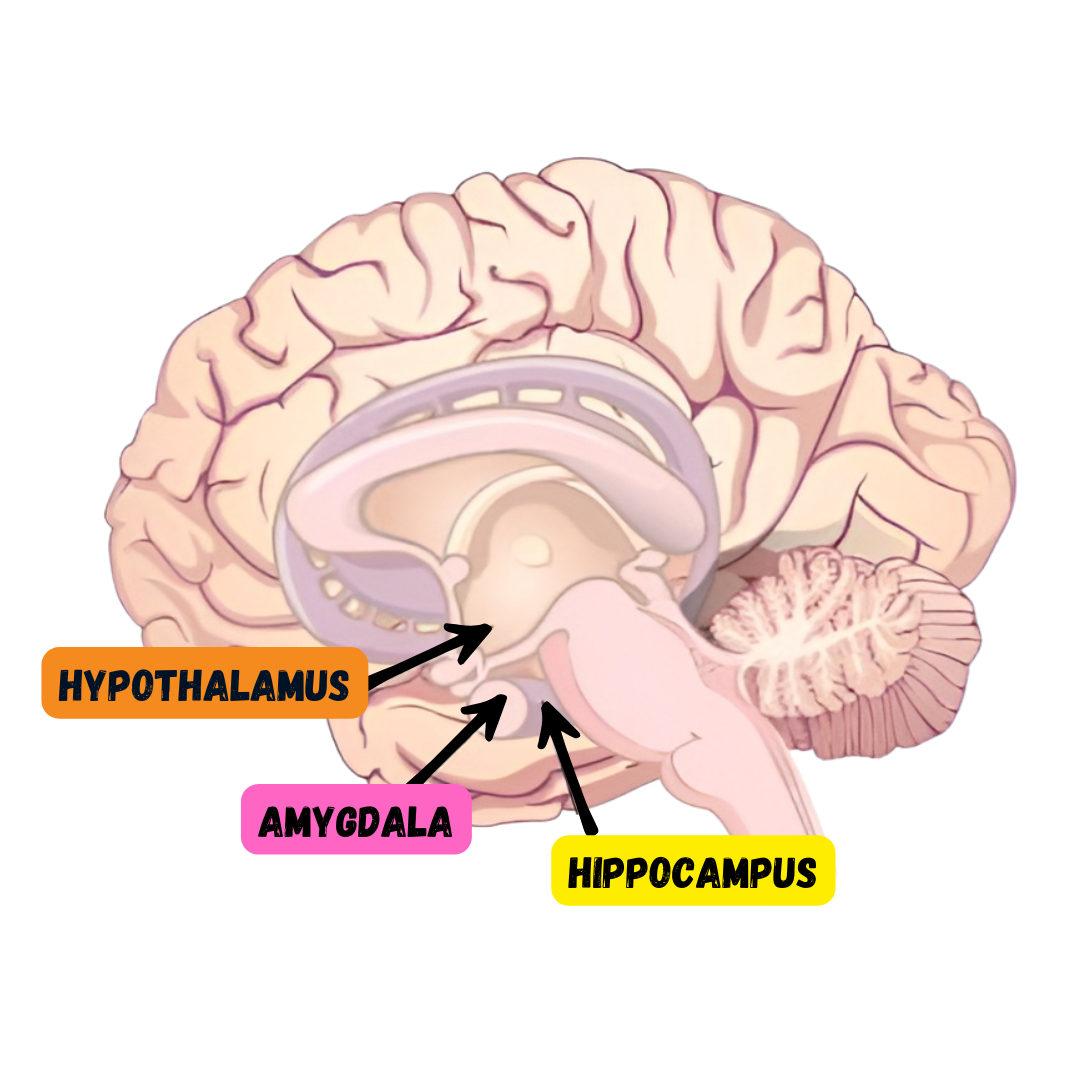
Physiological mechanisms
Hypothalamus
Amygdala & Nucleus Accumbens



Kinsey’s research
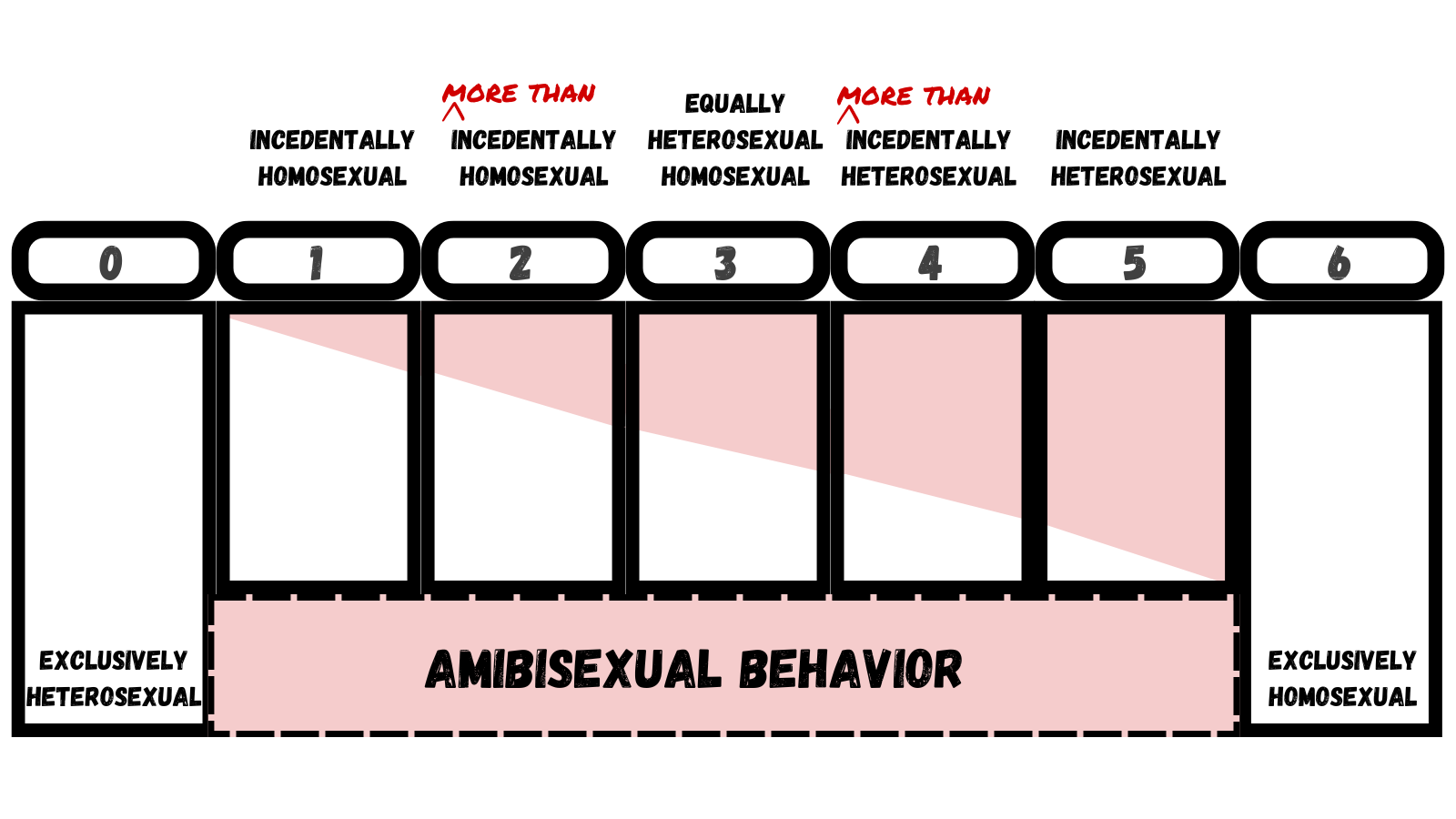
Masters & Johnson’s Research
Sexual Response Cycle
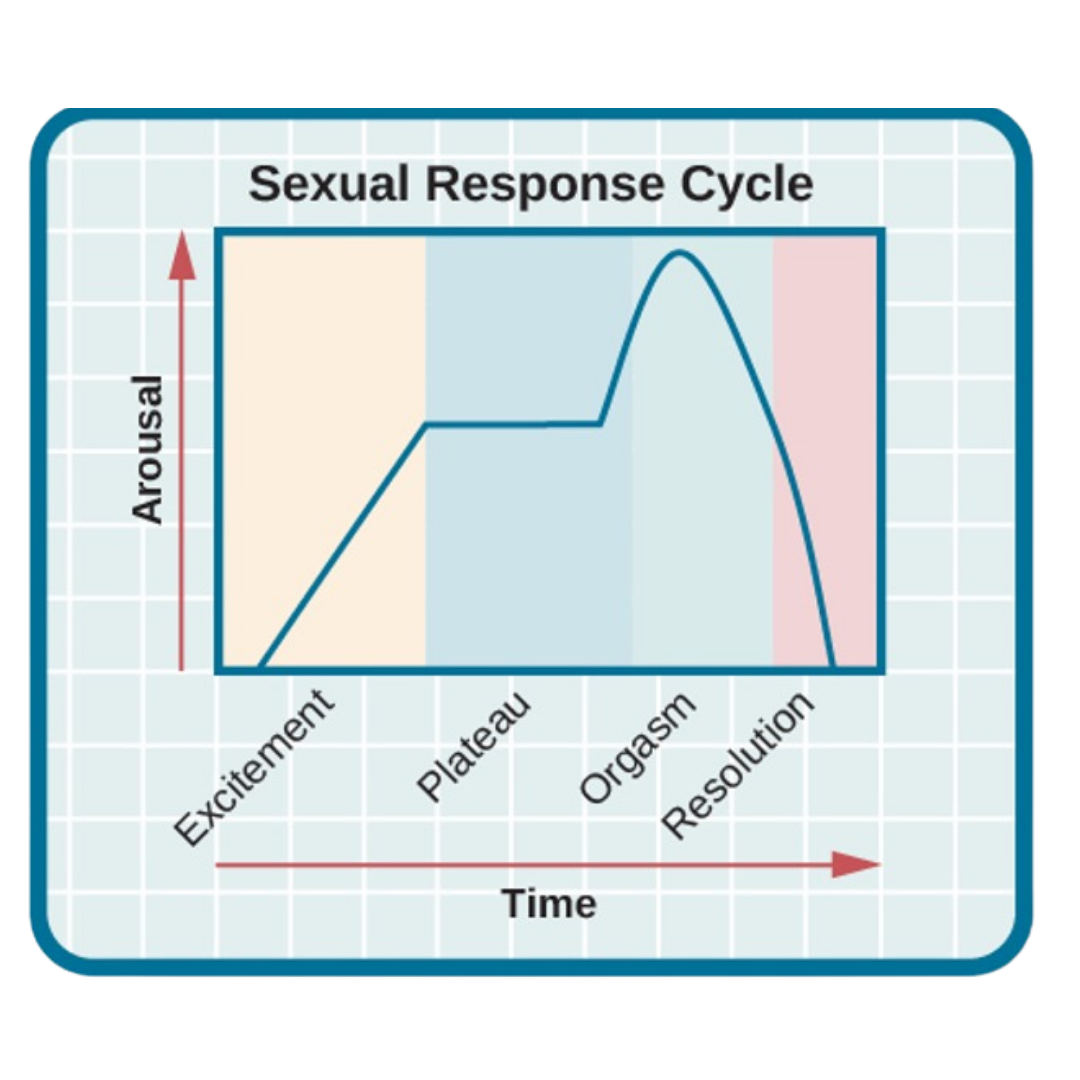
Stages
- Excitement: arousal phase (erection, lubrication)
- Plateau: Increased swelling and blood flow to labia minora, pre-ejaculatory fluid
- Orgasm: rhythmic contractions, ejaculation
- Resolution: return to unaroused state
Sex vs. Gender vs. Orientation
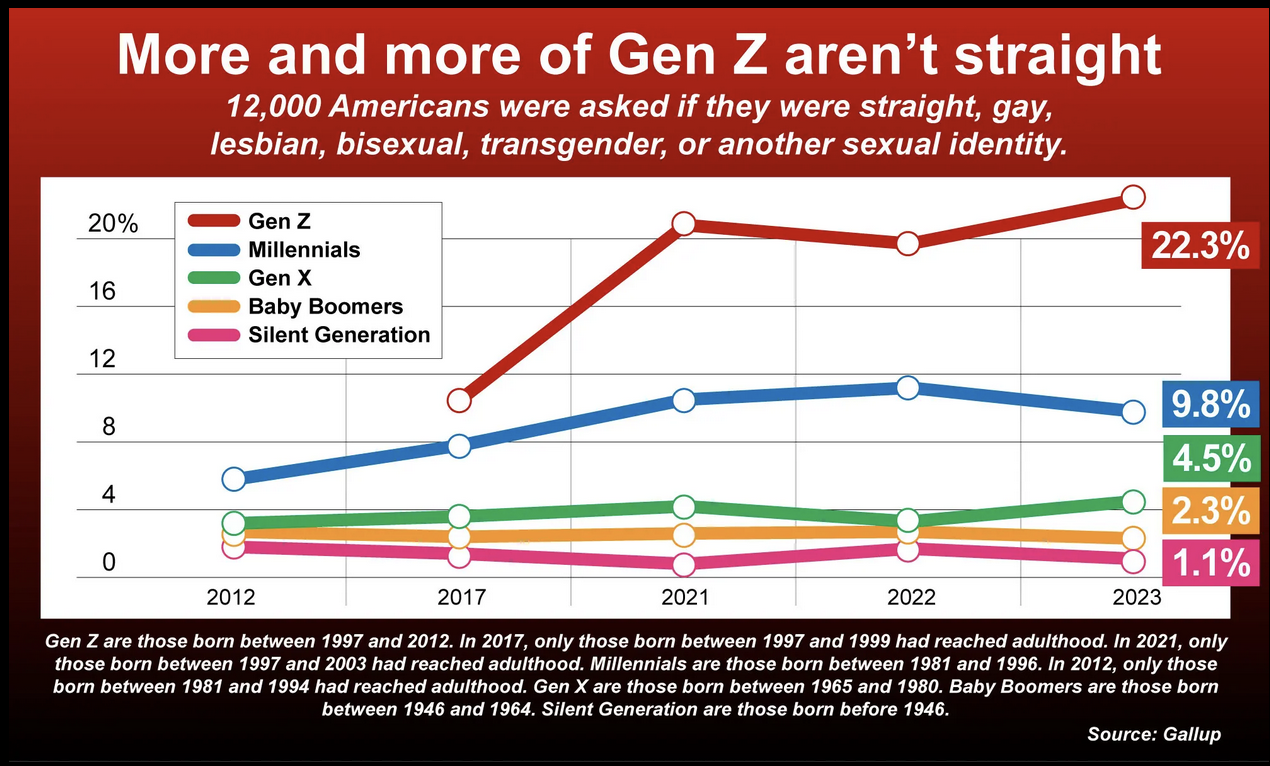
Sexual Orientation
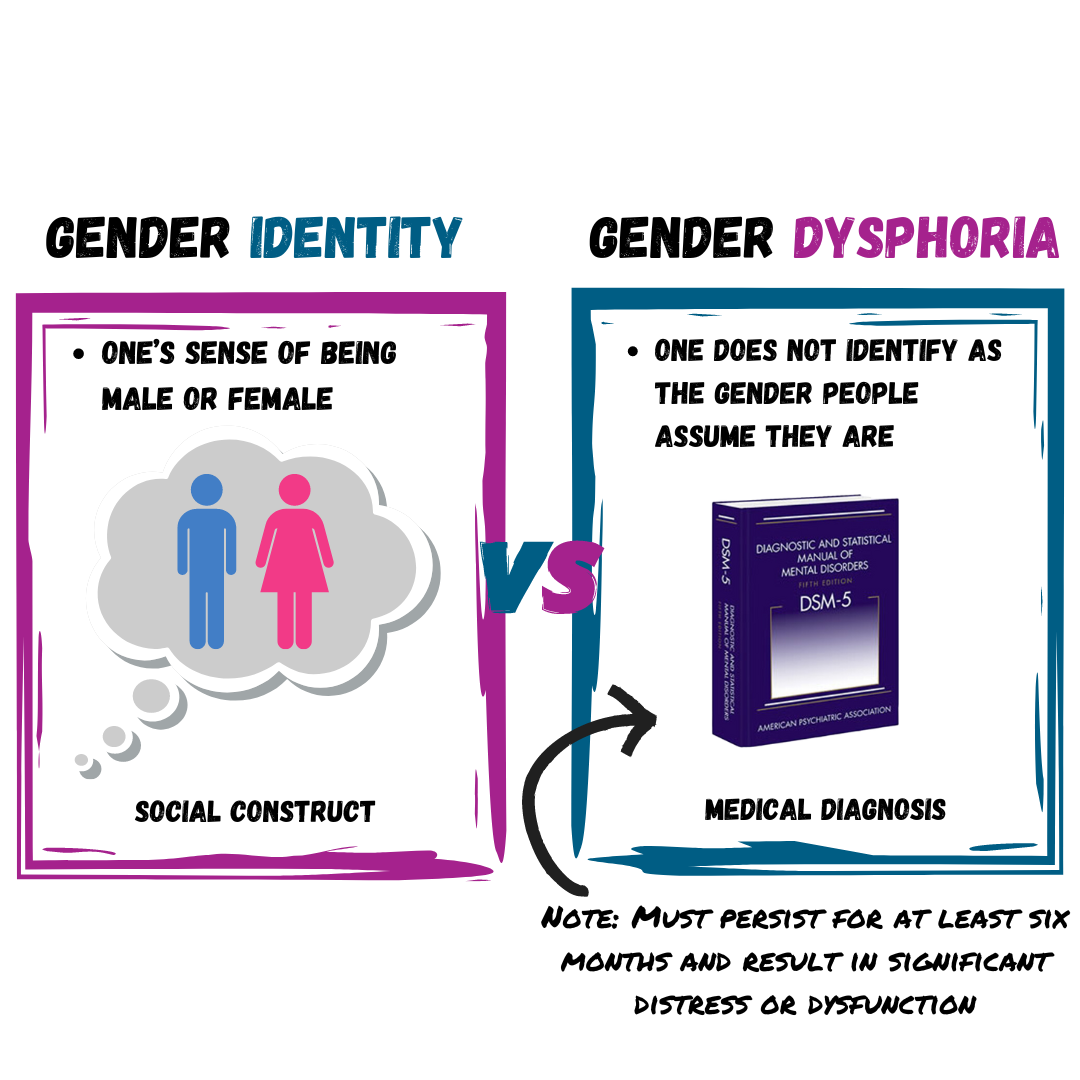
Gender Identity
Emotion
Feeling are complicated (optional)
Components of emotion
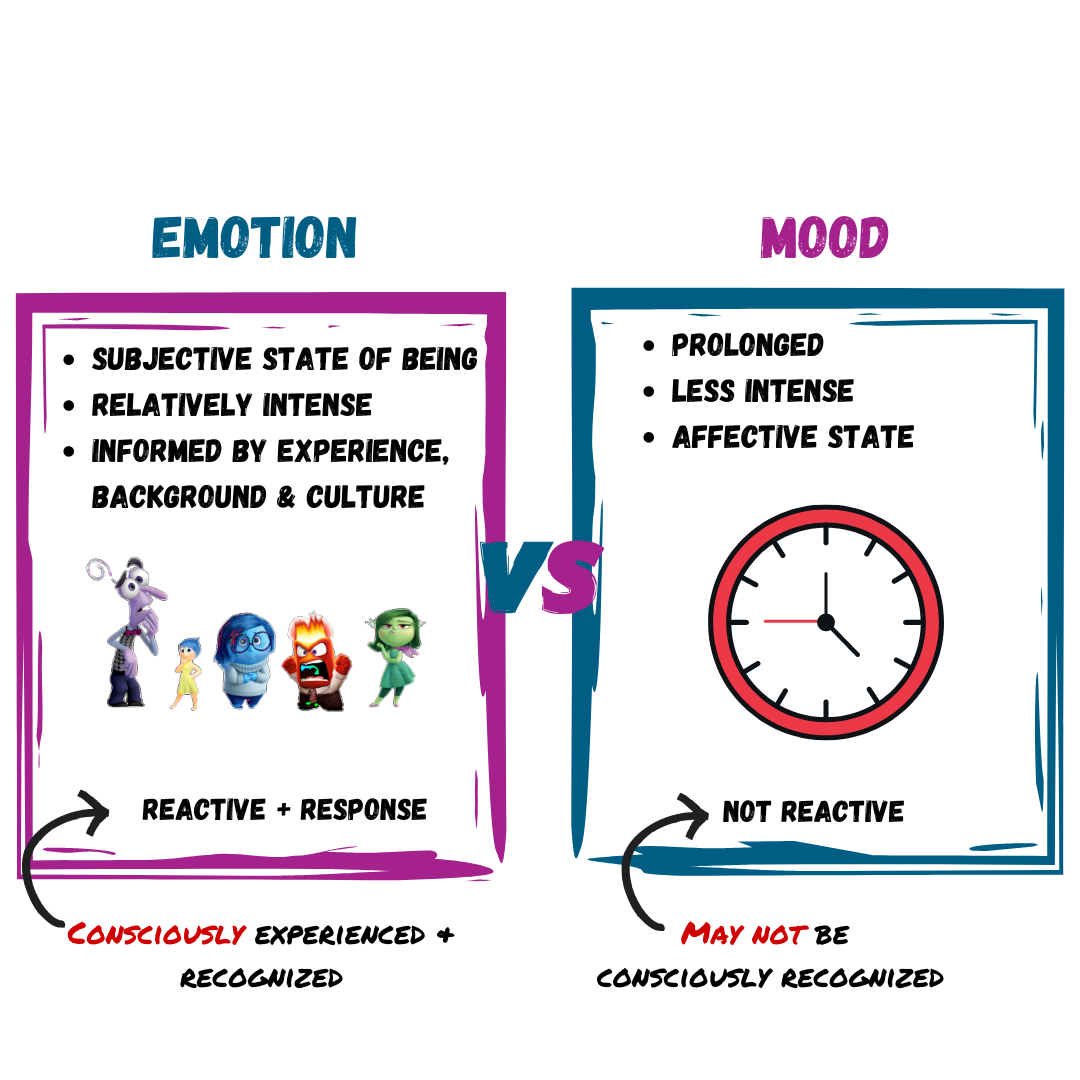
Theories of emotion
Theories of emotion
![]()
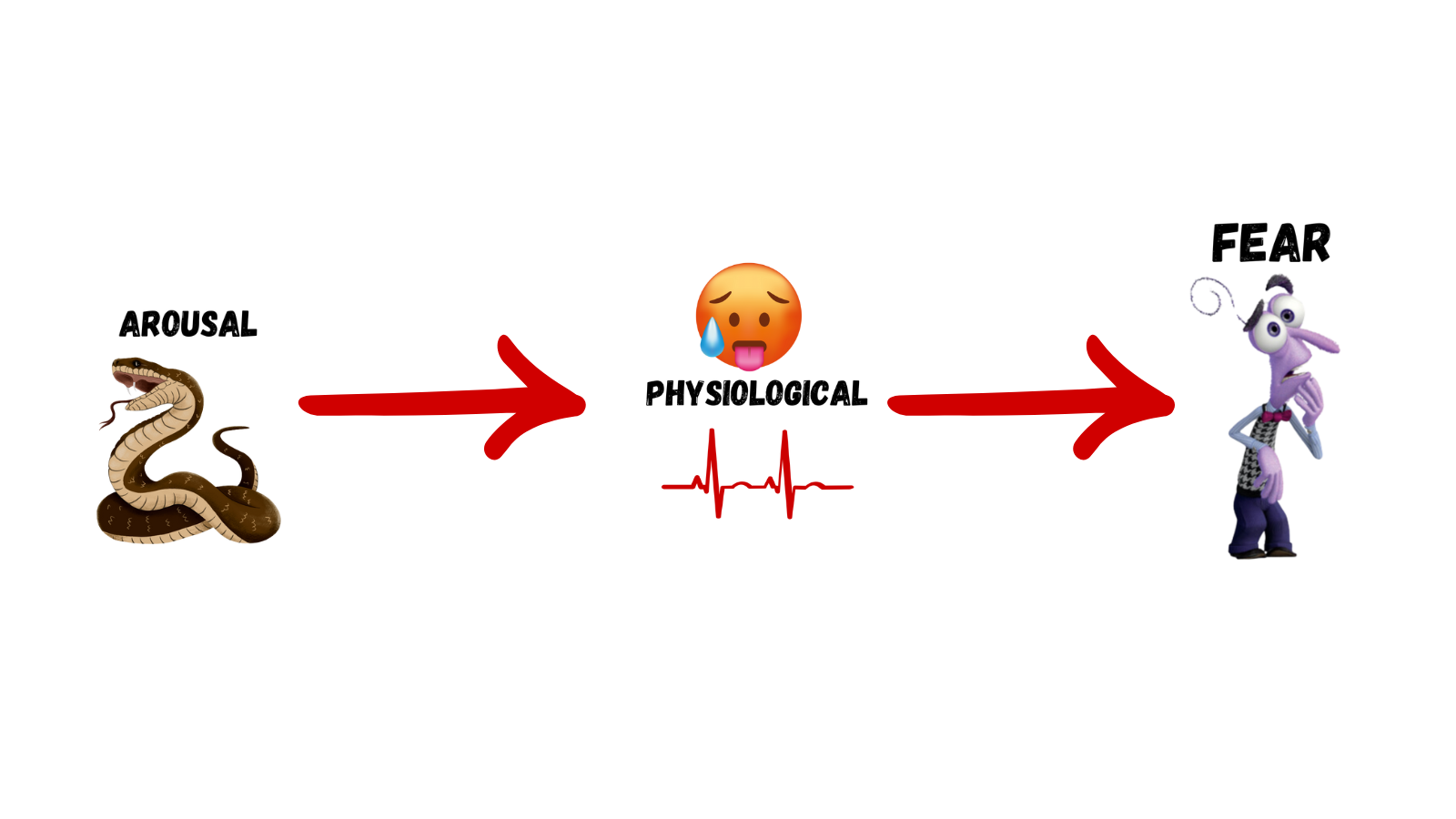
James-Lange Theory
Arises from physiological arousal
Cannon-Bard Theory
physiological arousal and emotion co-occur
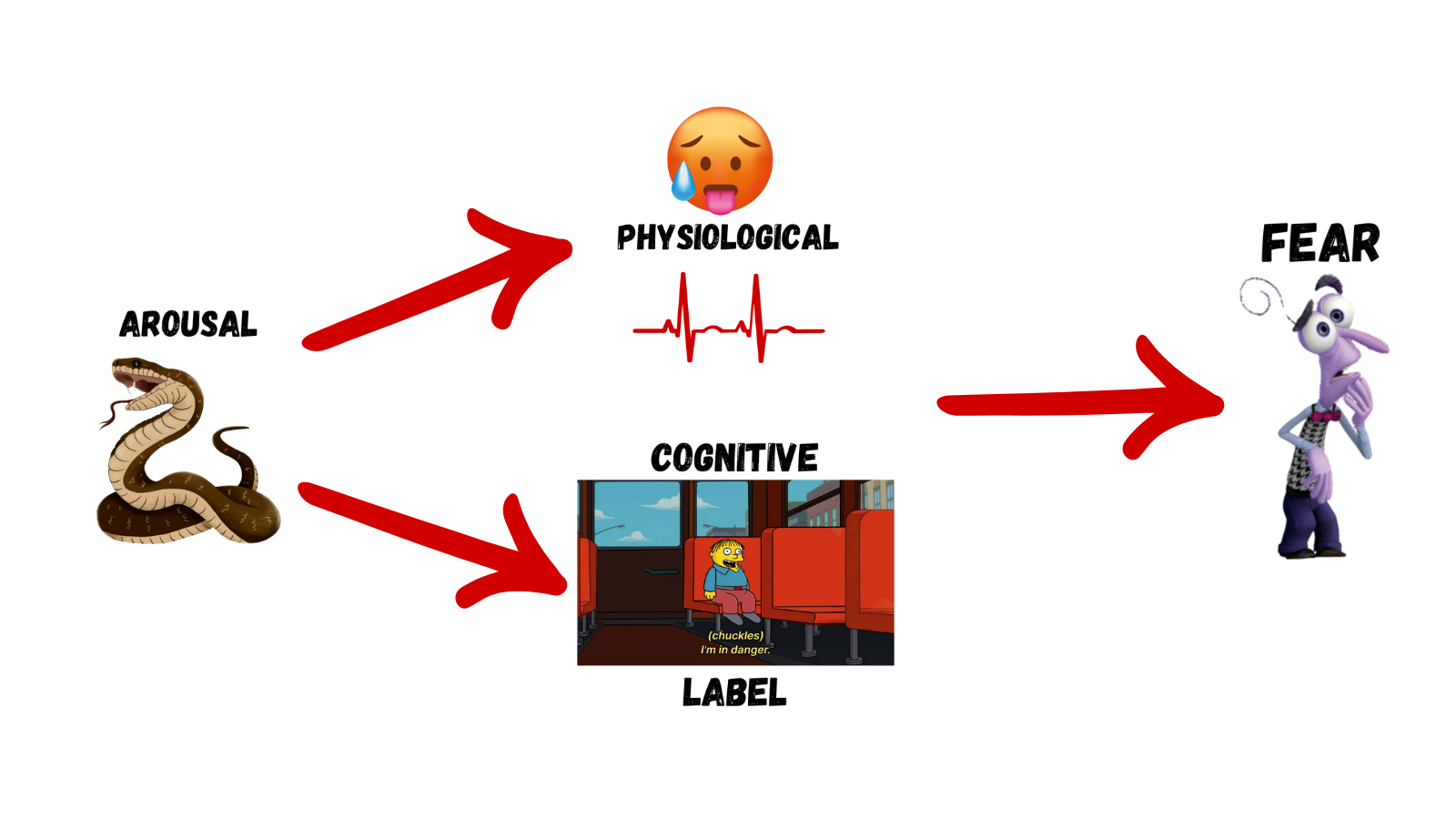
Schacter-Singer Two-Factor Theory
Composed of physiological and cognitive components
Lazarus’ Cognitive-Mediational Theory
Determined by appraisal of stimulus
James-Lange Theory
See snake → heart and respiration rate increase (physiological arousal) → feeling of fear
Cannon-Bard Theory
See snake → physiological arousal AND feel fear
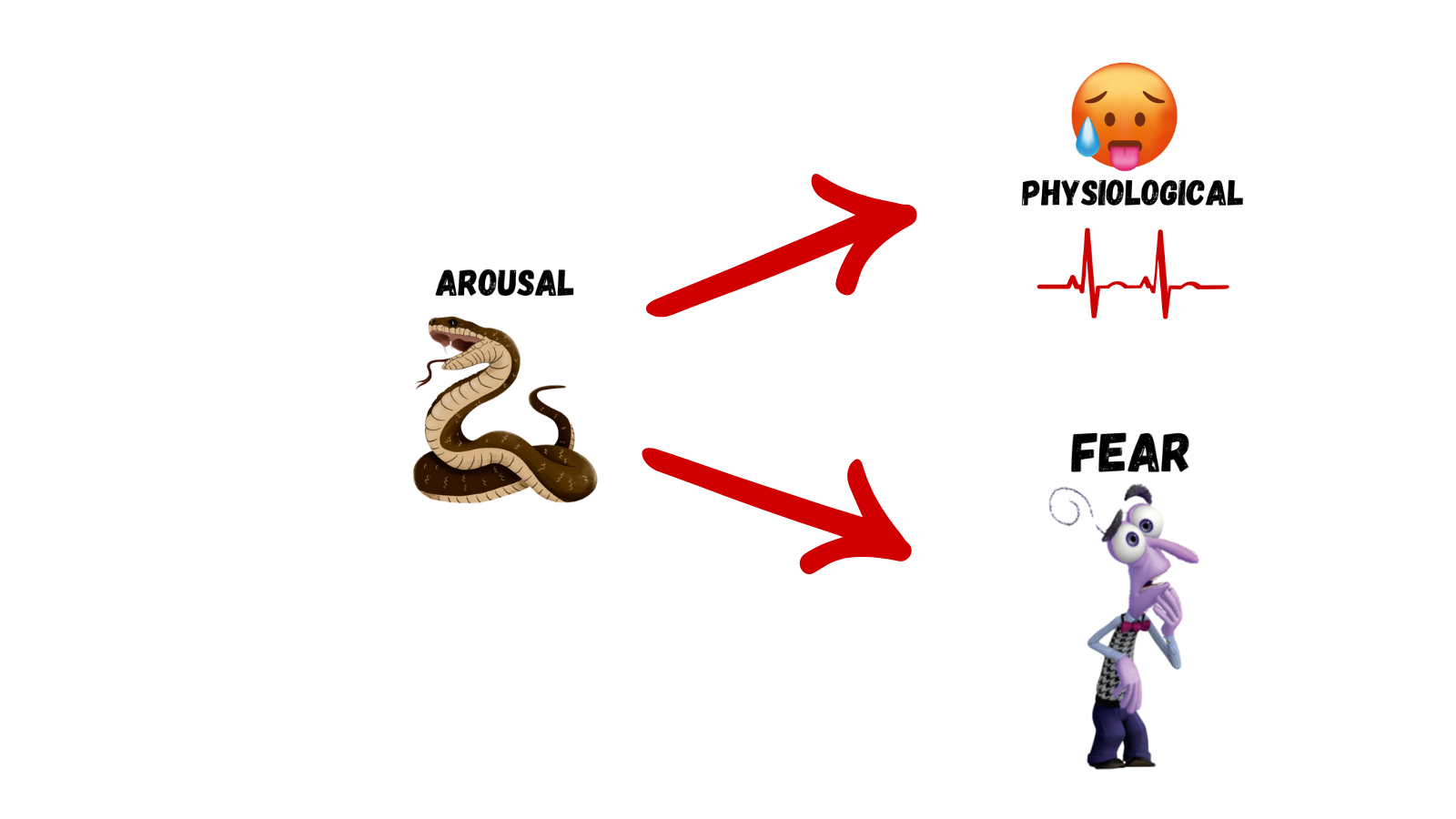 ::: ::: :::
::: ::: :::
Schachter-Singer Two-Factor Theory
See snake → physiological arousal and cognitive labels → experience fear
Lazarus’ Cognitive-Mediational Theory
Appraisal = Emotion
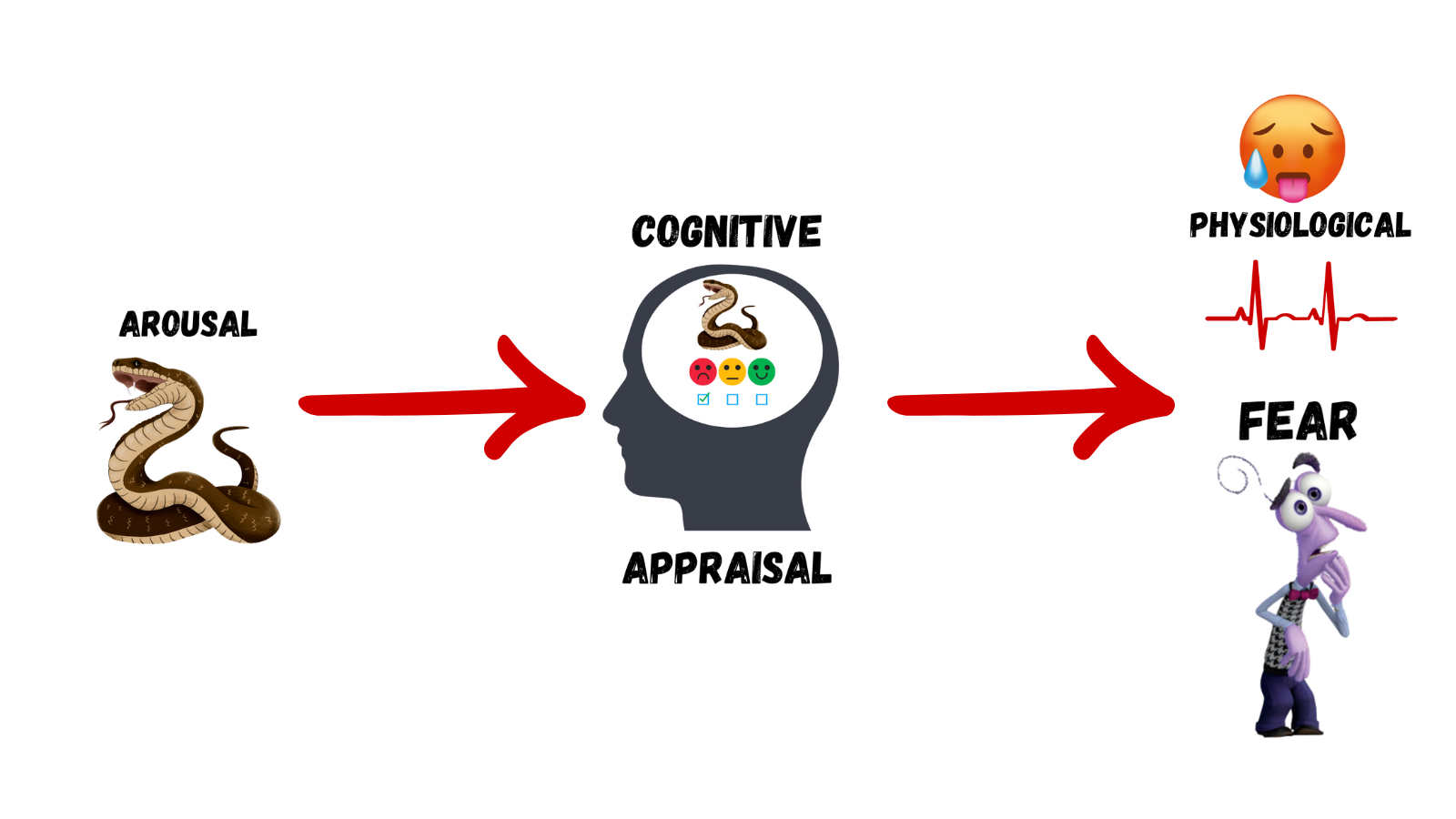
The biology of emotions
Limbic System → mediating emotional response and memory
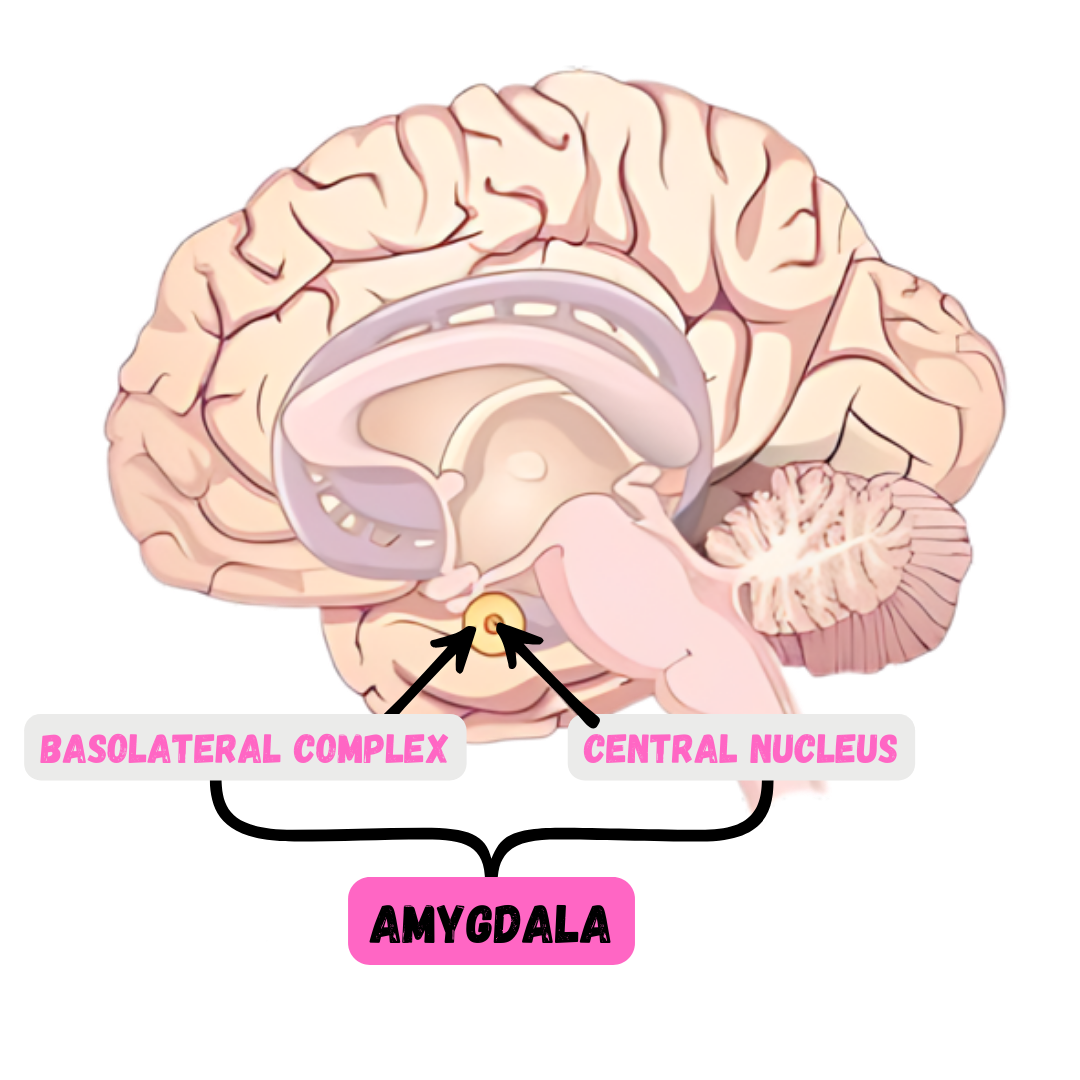
Amygdala
Facial expression and recognition of emotions
BUT recognition and production of facial expressions of certain emotions are universal
Seven Universal facial expressions of emotion

Credit: modification of work by Cory Zanker
Carney Landis (1924)
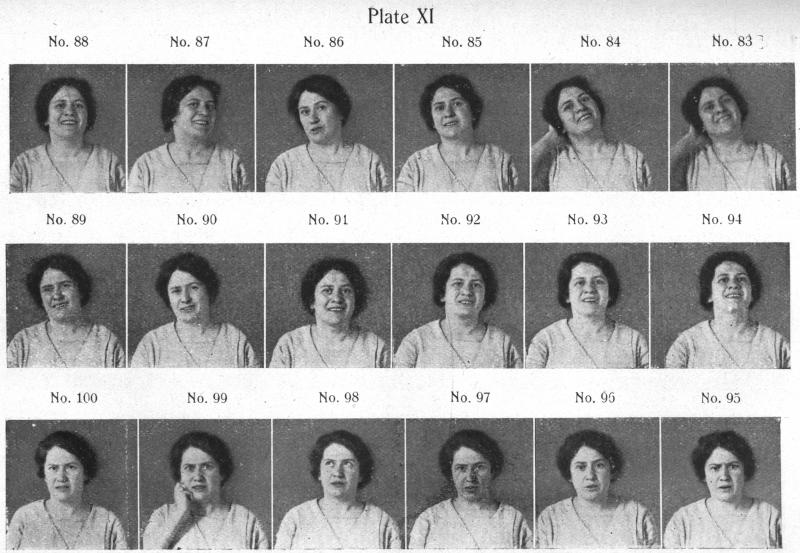

Facial feedback hypothesis
Does smiling make you happy or does being happy make you smile?
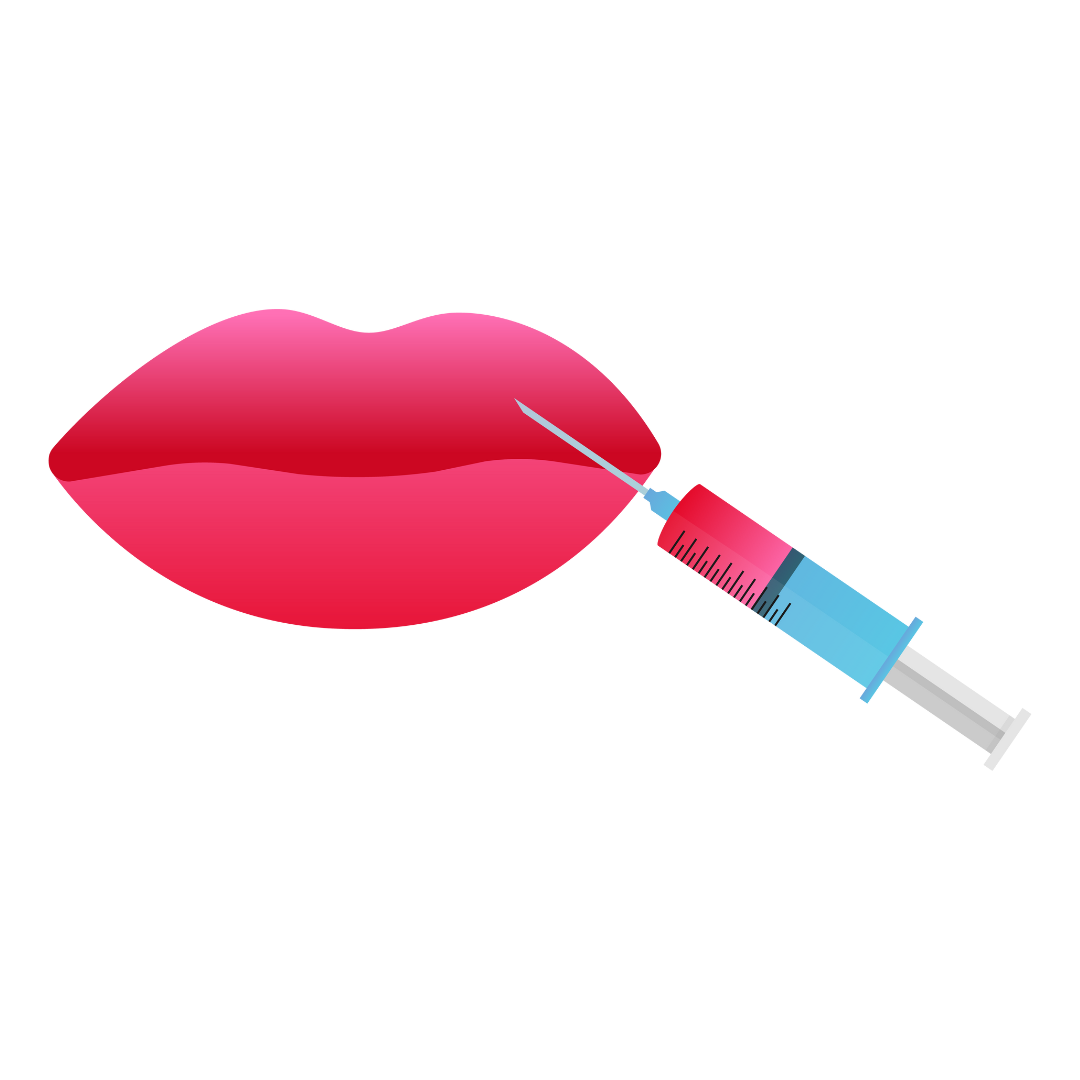

Depressed individuals reported less depression after paralysis of their frowning muscles with Botox injections.
Lie detection?
