🗓 Unit 5
Sensation & Perception
PSYC 181 – Intro to Psych
Emma Marshall – Instructor
July 23, 2024
What you will learn
![]()
Learning Objectives
- Understand how perception emerges from sensation
- Explore the processes of detecting stimuli and constructing useful information
- Examine the integration of sensation and perception in creating experiences
Sensation & Perception
![]()
Sensation:
Detection of external stimuli and transmission to the brain
Perception:
Processing, organization, and interpretation of sensory signals
Work together to create experiences
Bottom-up Processing
perception based on the physical features of the stimulus
Top-down Processing
Interpretation shaped by available knowledge, expectation, or past experiences
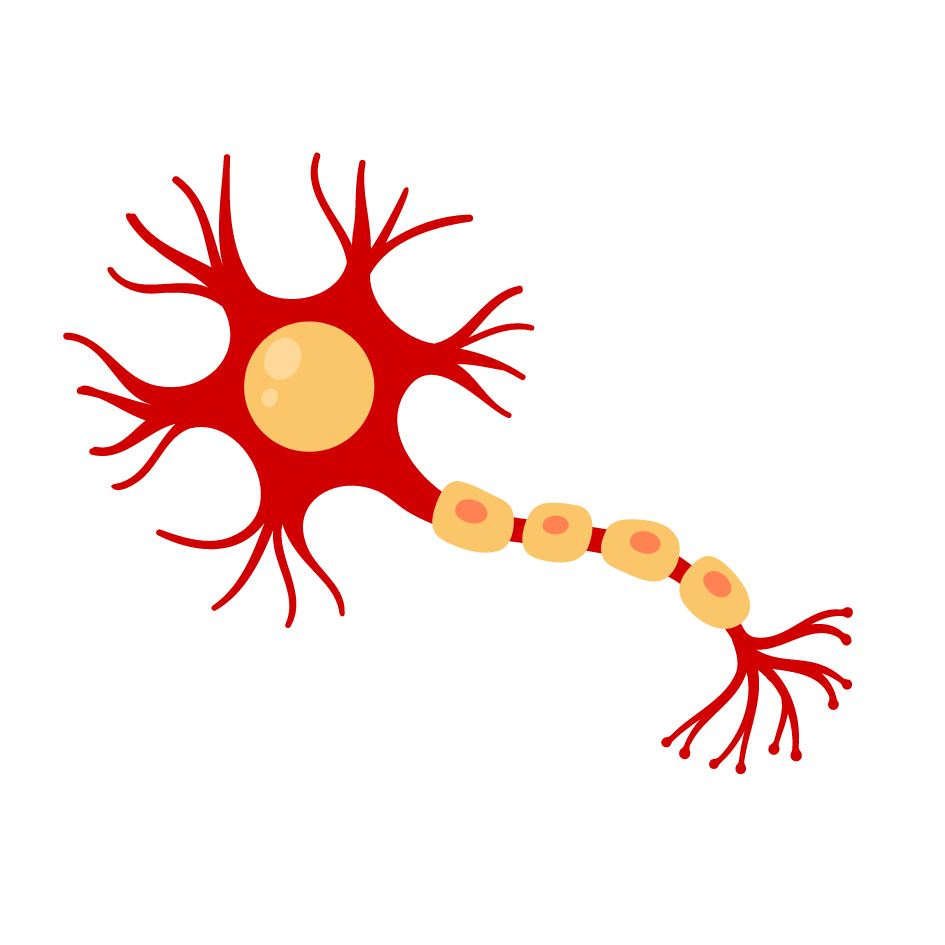
Sensory Coding
Sensory organs ➜ Sensory receptors ➜ Neural pathway ➜ Cortical regions
Sensory receptors
specialized neurons that respond to specific types of stimuli
Detection requires a certain amount of stimulus
Transduction
Transduction
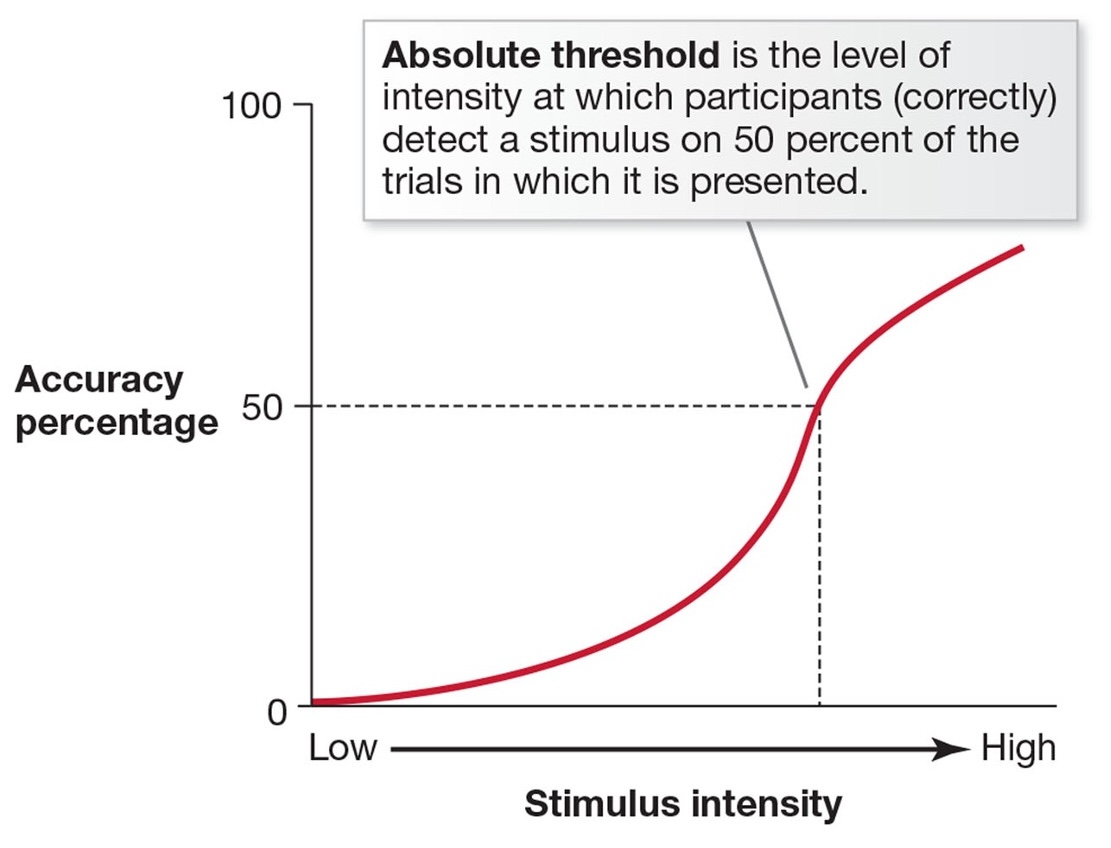
Absolute Thresholds
Minimum intensity before you experience a sensation
Sensory Coding
Transduction:
Conversion of sensory stimuli to neural signals
Transformation:
Transmission of electrical impulses to specific cortical regions
Sensory systems
Transduction ➜ Transformation
Vision
Hearing (audition)
Smell (olfaction)
Taste (gustation)
Touch (somatosensation)
Body Position (proprioception)
Movement (kinesthesia)
Pain (nociception)
Temperature (thermoception)
Balance (vestibular sense)
Sense Pathways
| SENSE | STIMULI | RECEPTORS | PATHWAYS TO THE BRAIN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vision | Light waves | Light-sensitive rods and cones in retina of eye | Optic nerve |
| Hearing | Sound waves | Pressure-sensitive hair cells in cochlea of inner ear | Auditory nerve |
| Taste | Molecules dissolved in fluid on the tongue | Cells in taste buds on the tongue | Portions of facial, glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves |
| Smell | Molecules dissolved in fluid on membranes in the nose | Sensitive ends of olfactory mucous neurons in the mucous membranes | Olfactory nerve |
| Touch | Pressure on the skin | Sensitive ends of touch neurons in skin | Cranial nerves for touch above the neck, spinal nerves for touch elsewhere |
Vision
Anatomy Of the Visual System
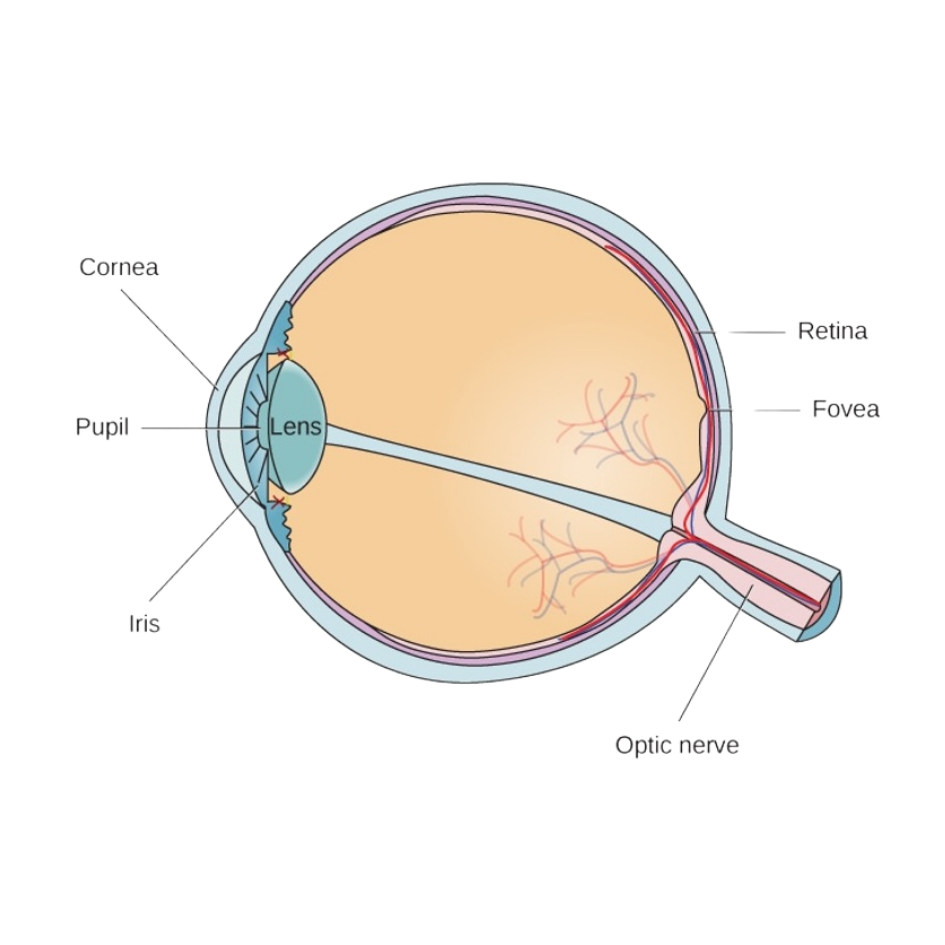
Light path: Cornea → Iris → Lens → Retina
Transmission: Ganglion cells → Optic nerve → Thalamus → Visual cortex
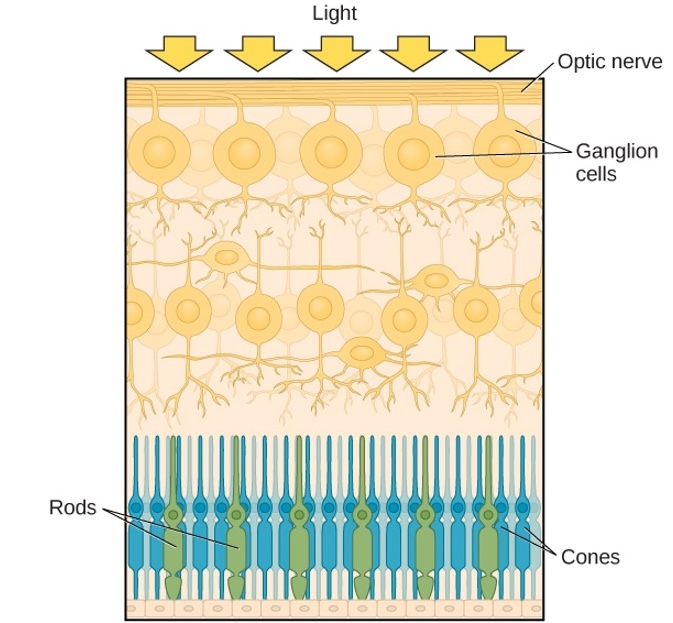
photoreceptors
Receptor cells: Rods (low light) and Cones (color, higher light)
Optic Chiasm
Optic nerve of each eye merges in x-shape
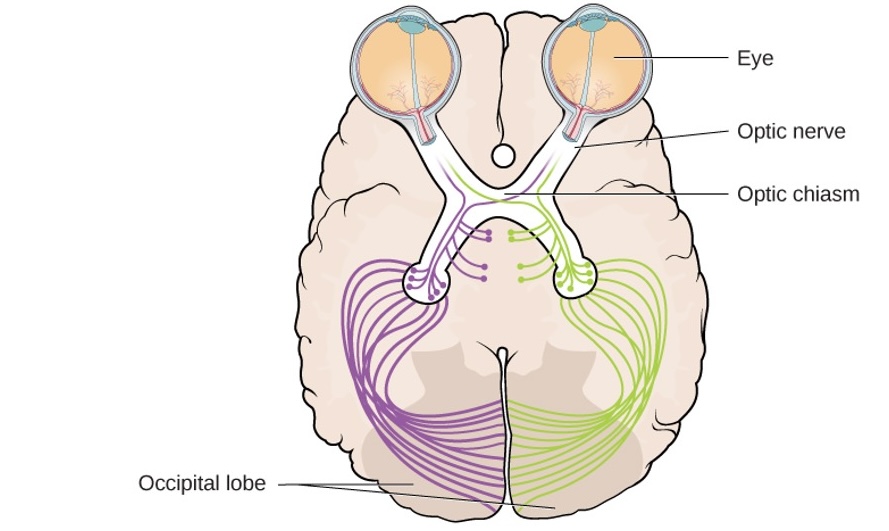
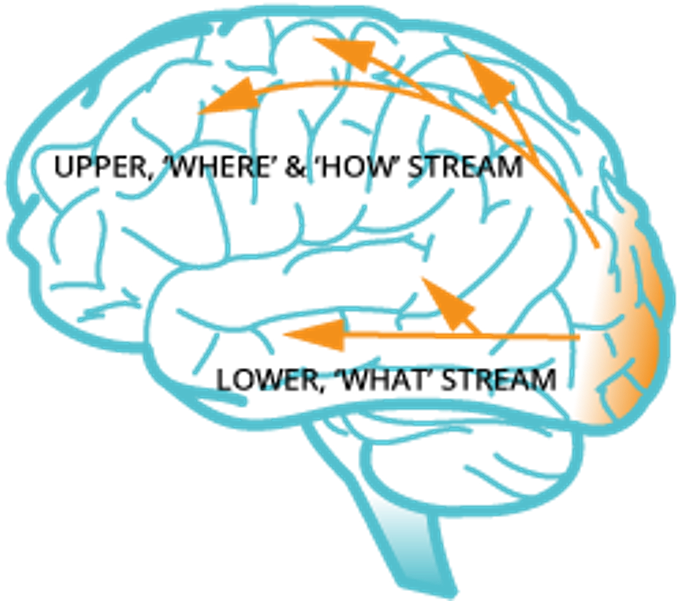
Visual Pathways
- The “WHAT” pathway:
- recognition
- identification
- The “where/how” pathway
- localization
- what to do
Waves
amplitude and wavelength
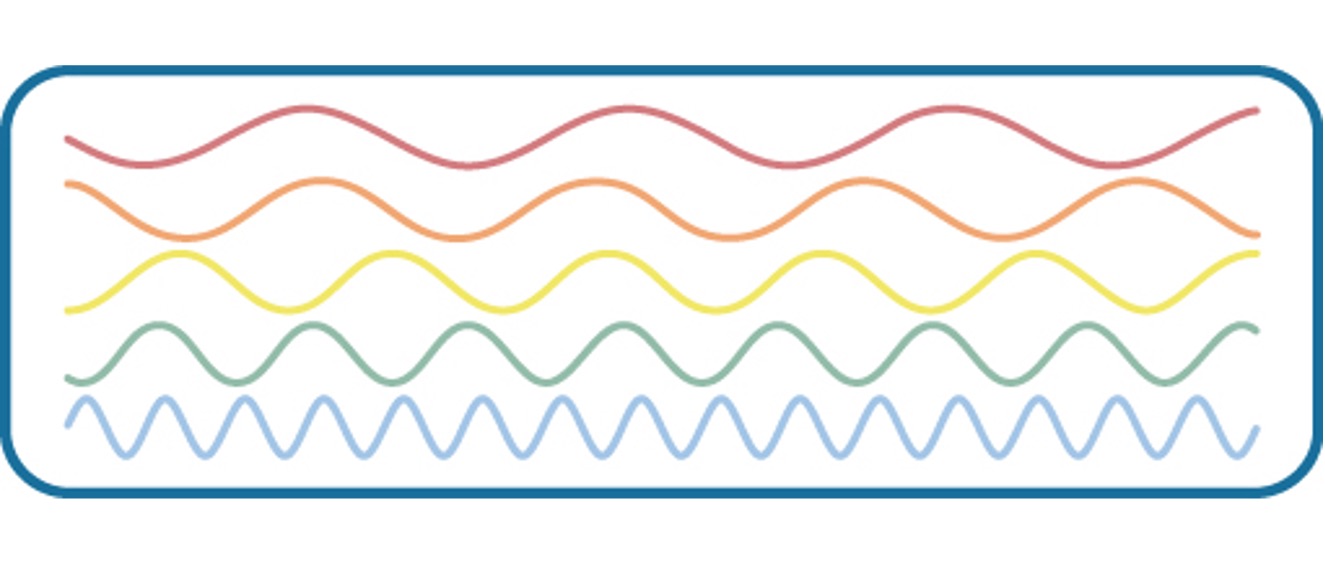
wavelenth is directly related to frequency or number of waves
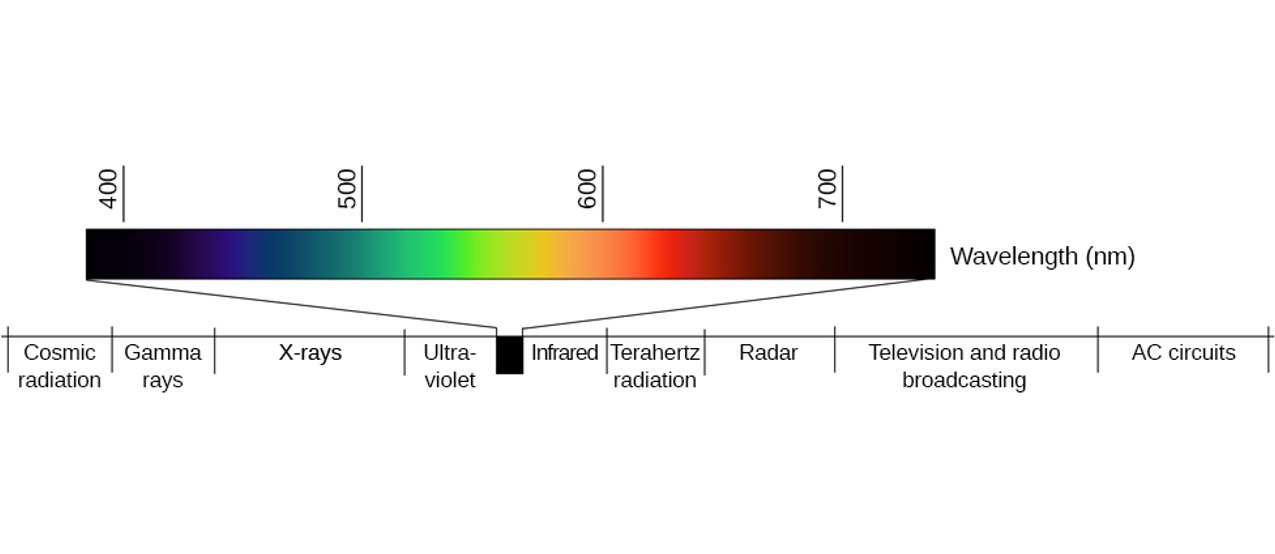
Light waves
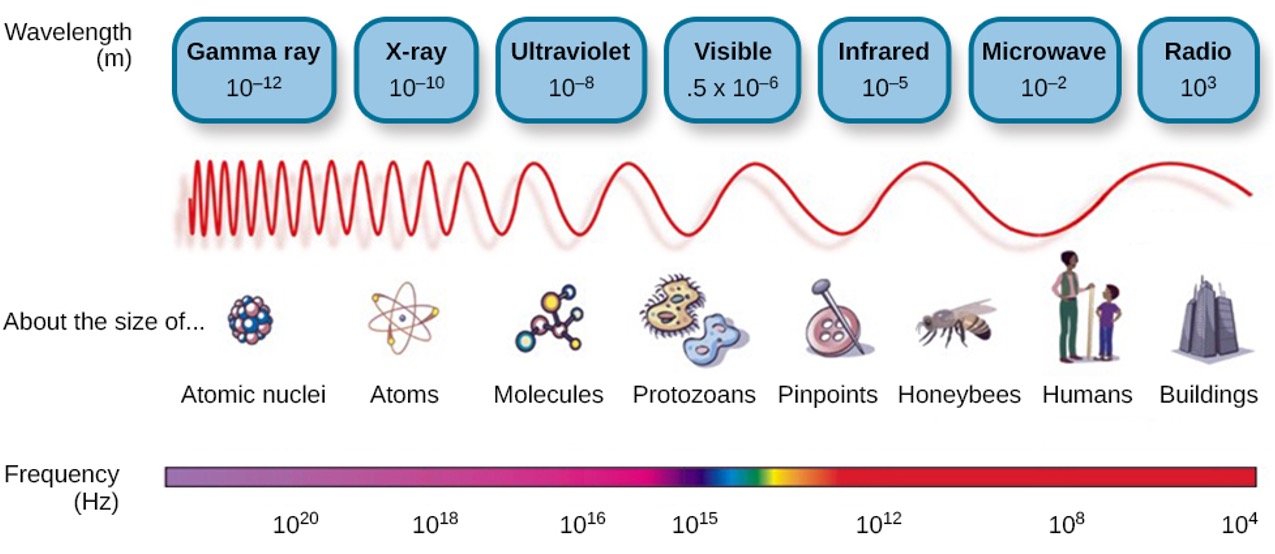
Perception of Color
Wavelength ➜ Color
- Longer wavelengths = reds
- Intermediate wavelengths = greens
- Shorter wavelengths = blues and violets
Amplitude ➜ brightness/intensity
- Larger amplitudes = brighter
Color Vision
- Trichromatic Theory: Combine red, green, and blue
- Opponent-Process Theory: Color coded in opponent pairs
- Black – White
- Yellow – Blue
- Green – Red
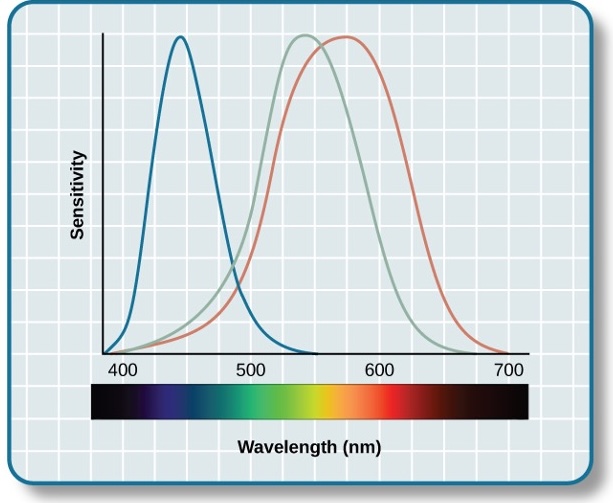
Opponent-Process Theory
Afterimage: continuation of a visual sensation after removal of stimulus
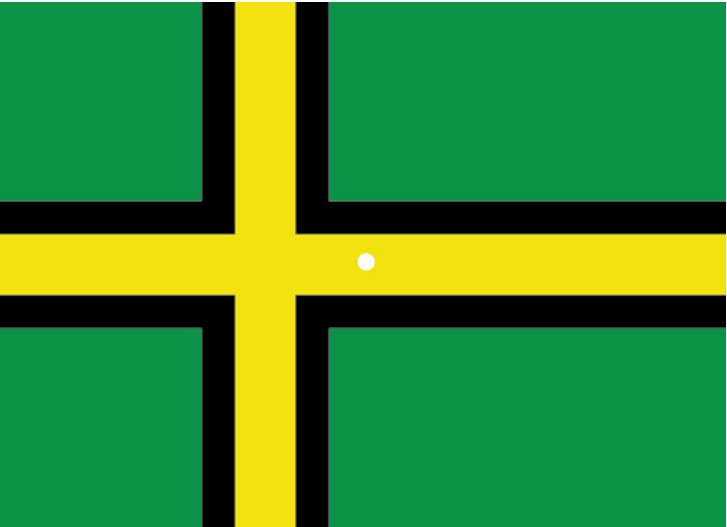

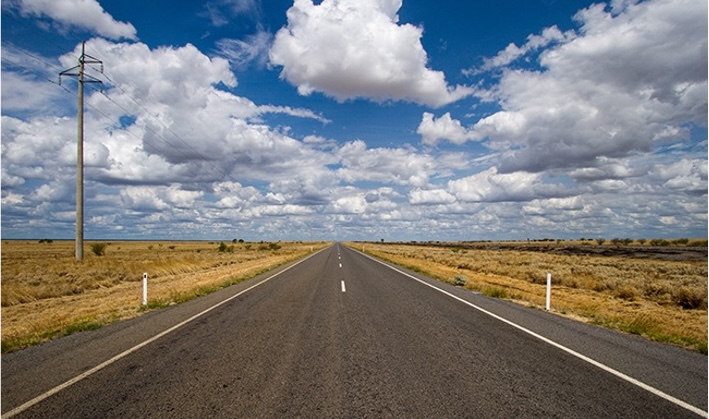
Depth Perception
Our ability to perceive spatial relationships in 3-D
- Binocular cues: Use both eyes (e.g., binocular disparity)
- Monocular cues: Use one eye (e.g., linear perspective, interposition)

Hearing
Anatomy of the auditory system
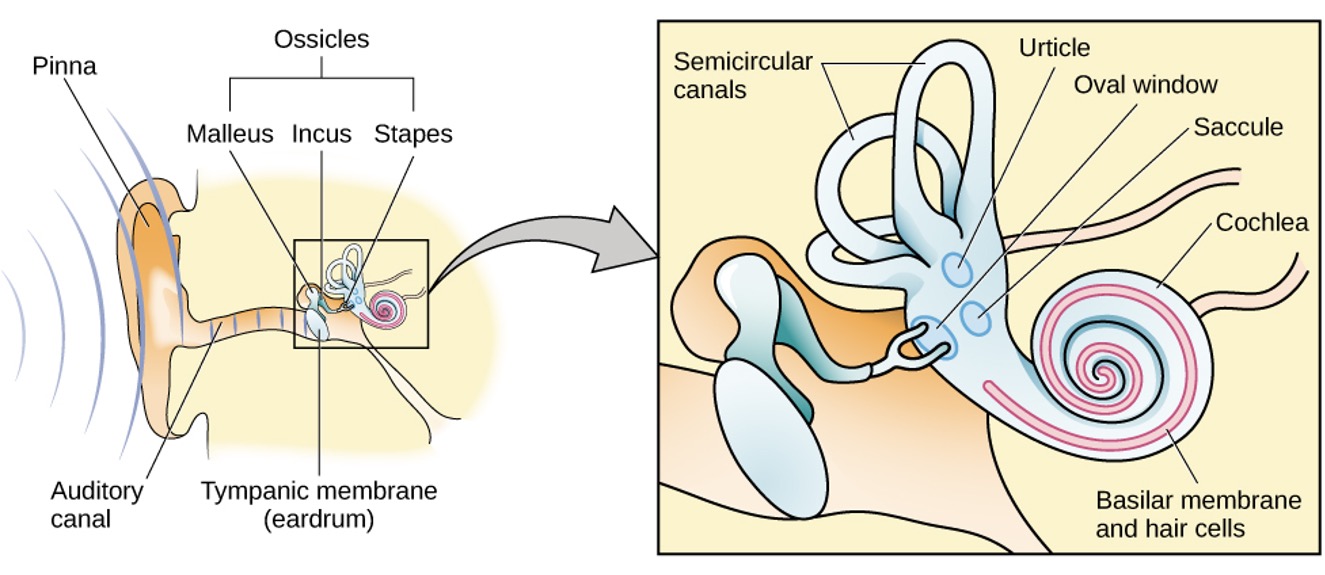
- Outer: pinna and tympanic membrane
- Middle: the three ossicles: malleus, incus, and stapes
- Inner: cochlea and basilar membrane
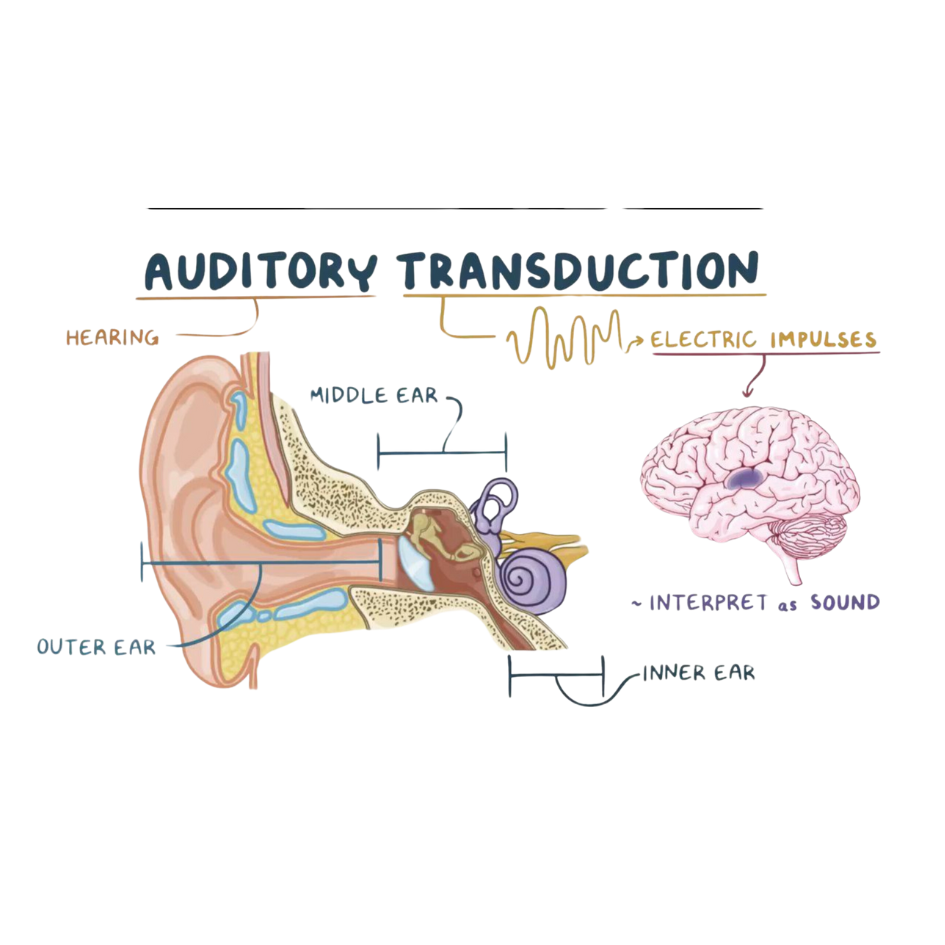
Auditory transduction
- Sound waves → Tympanic membrane
- Ossicles movement → Cochlea
- Hair cell stimulation → Neural impulses
- Auditory nerve → Brain processing
Pitch Perception
Temporal Theory: Frequency coded by neuron activity level
Place Theory: Different basilar membrane portions sensitive to different frequencies
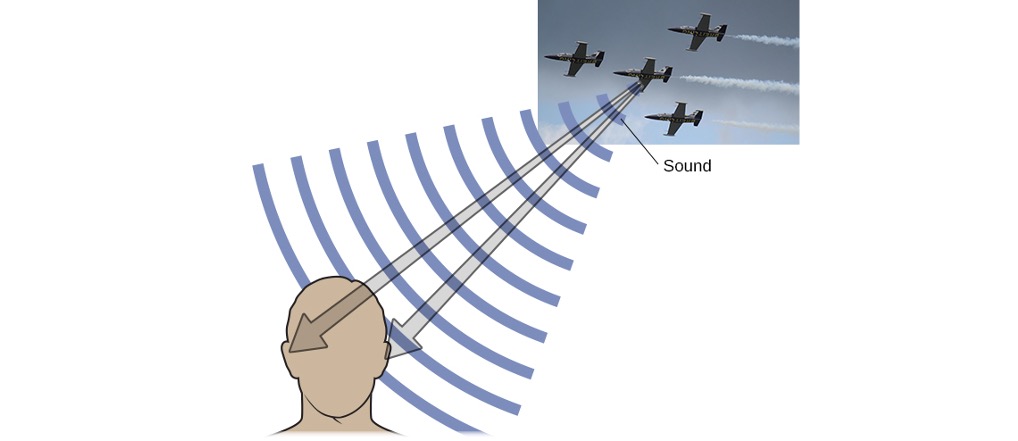
Sound Localization
- Monaural cues: One ear
- Binaural cues: Two ears (interaural level and timing differences)
Hearing Loss
Deafness
Congenital deafness
Conductive hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss
Other Senses
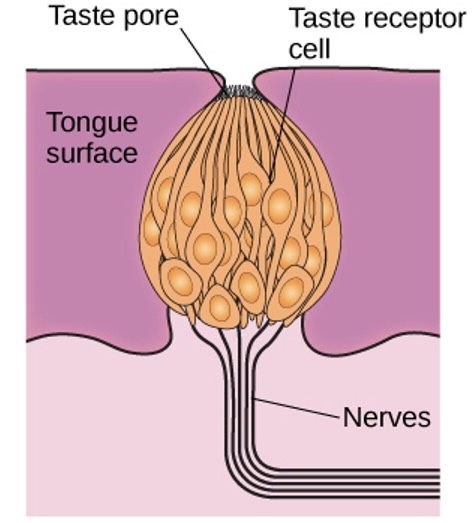
Gustation (Taste)
- Six basic tastes: Sweet, Salty, Sour, Bitter, Umami, fat
- Taste buds and receptor cells
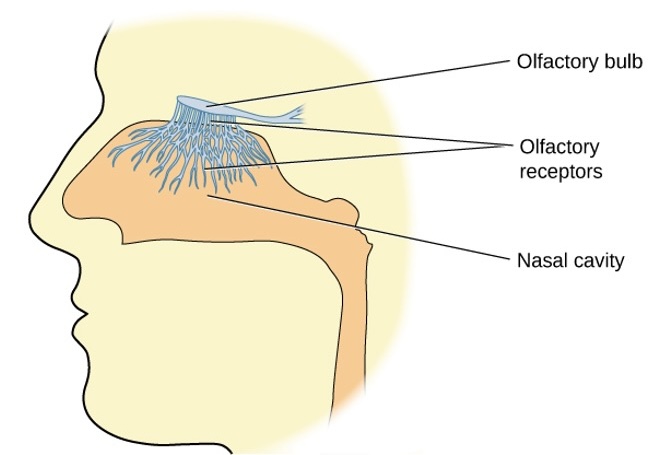
Olfaction (Smell)
- Odor molecules bind to receptors
- Signals sent to olfactory bulb and cortex
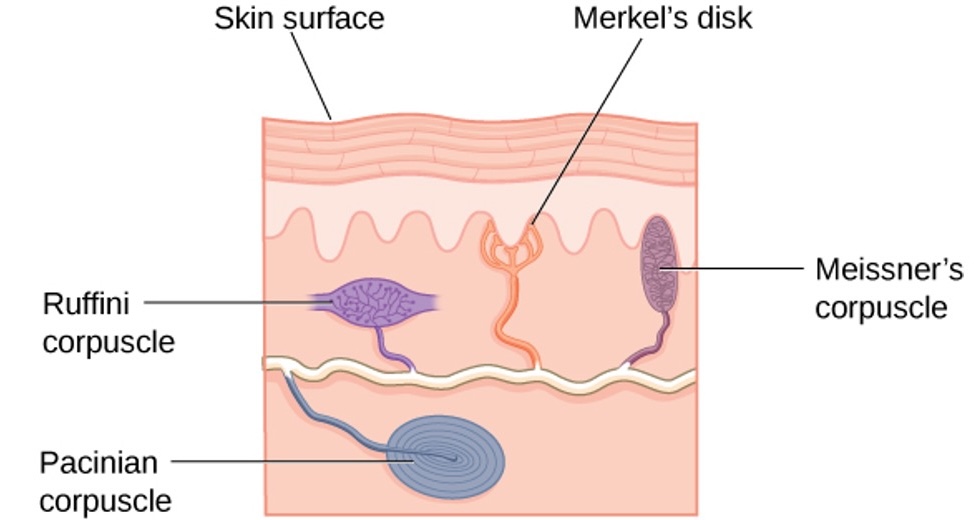
Somatosensation
Touch
- Meisnerr’s corpuscles: respond to pressure and lower-frequency vibrations
- Pacinian corpuscles: detect transient pressure and higher-frequency vibrations
- Merkel’s disks: respond to light pressure
- Ruffini corpuscles: detect stretch
Thermoception: Temperature perception
Nociception: Pain perception
Pain Perception

Inflammatory pain vs. Neuropathic pain
Vestibular Sense
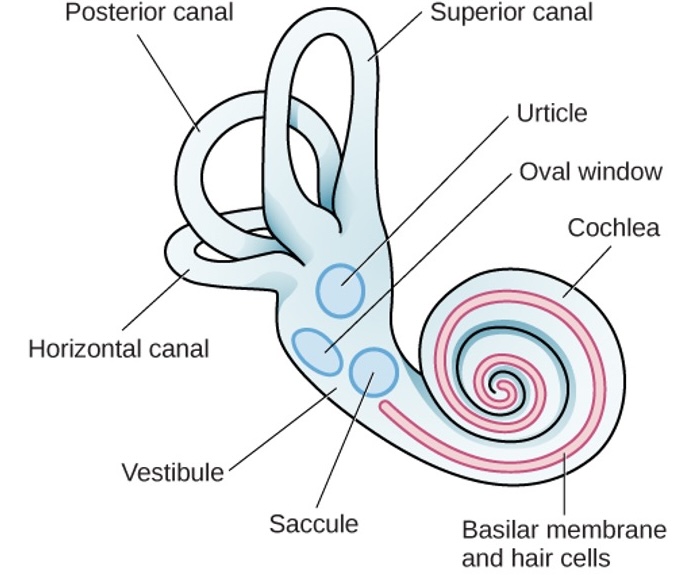
Proprioception & kinesthesia
- Proprioception: Balance and body posture
- Kinesthesia: Perception of body position and movement

Perception Principles
Gestalt Principles
- Figure-ground relationship
- Proximity
- Similarity
- Continuity
- Closure
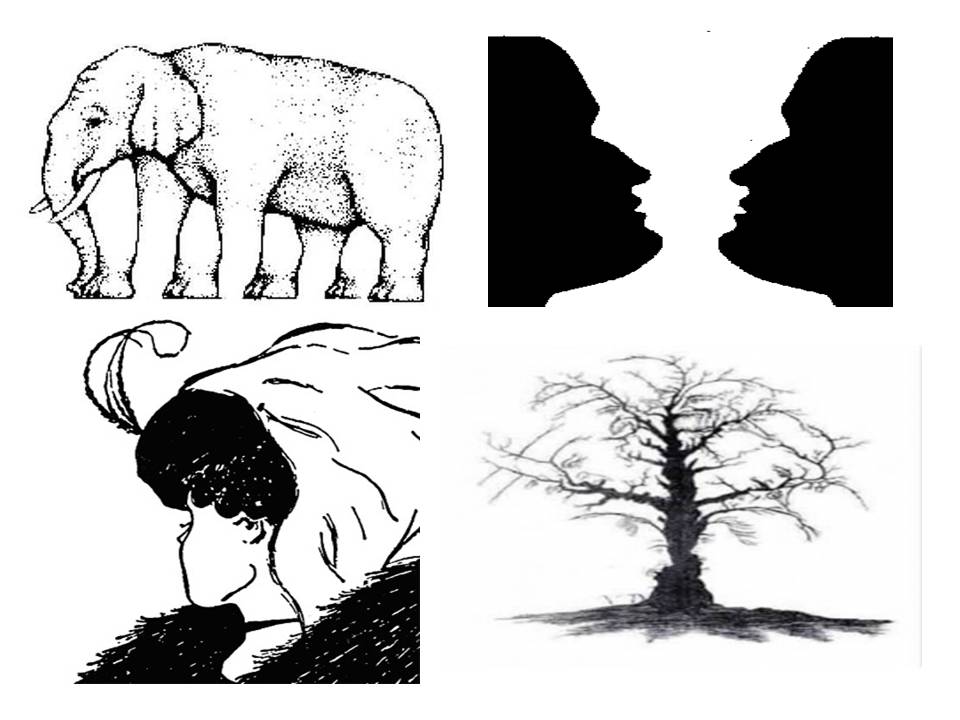
Gestalt Principles of perception
Idea that the whole is different from the sum of its parts
Figure-Ground relationship
- Figure: focus of visual field
- Ground: background

Gestalt Principle of proximity
things that are close tend to be grouped together
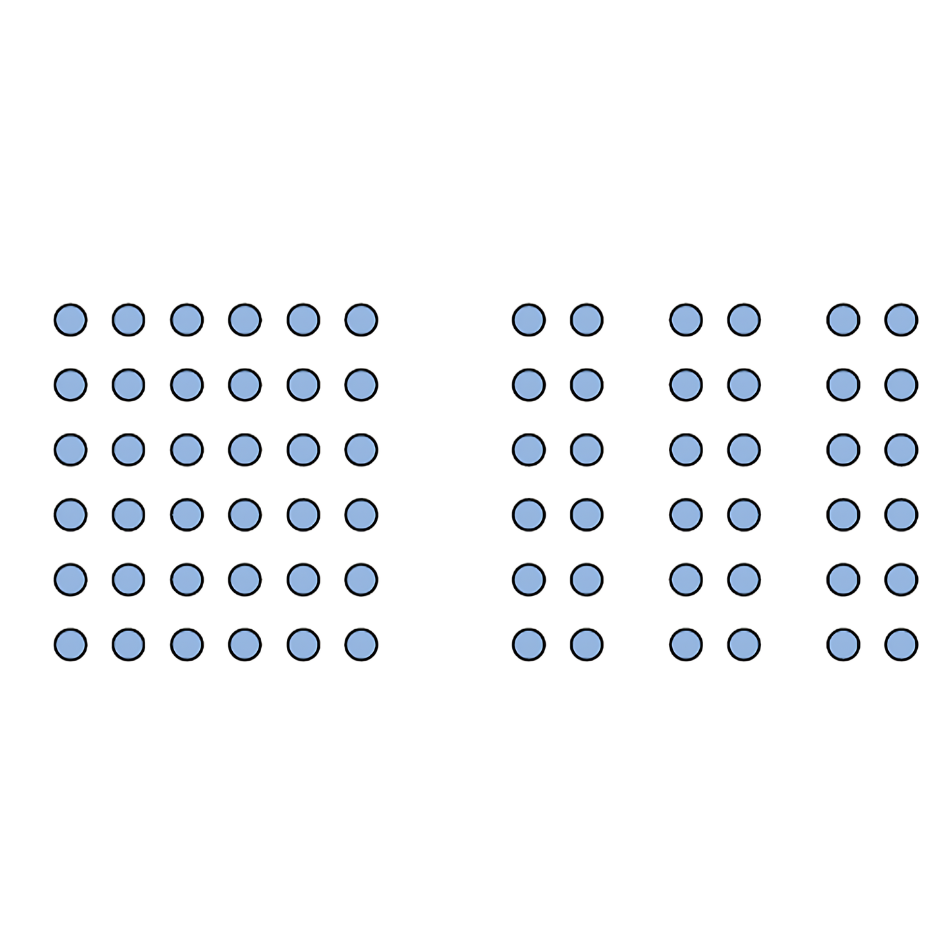
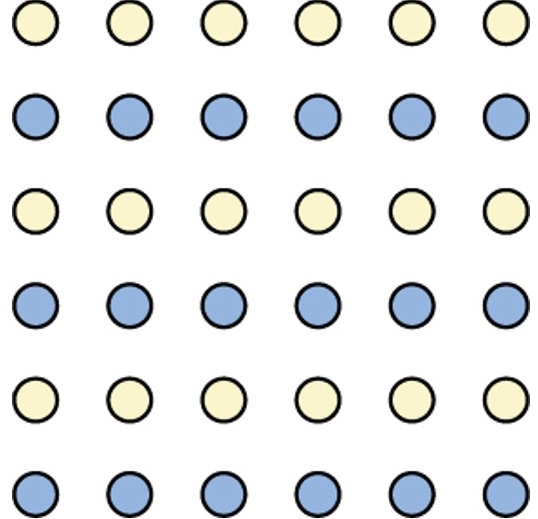
Gestalt Principle of similarity
The idea that things that are alike tend to be grouped together
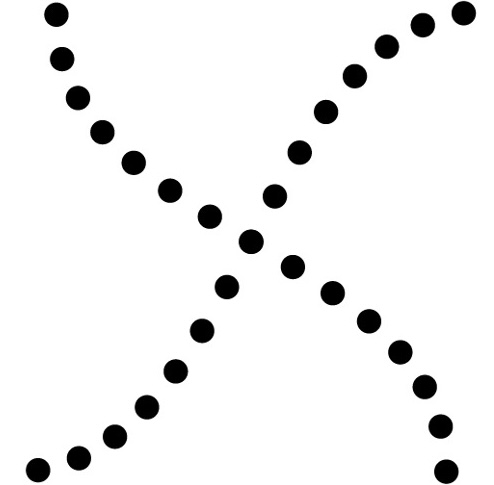
Gestalt Principle of continuity
more likely to percieve continuous, smoot flowing lines
Gestalt Principle of Closure
look for complete objects rather than parts

Duck or Rabbit?
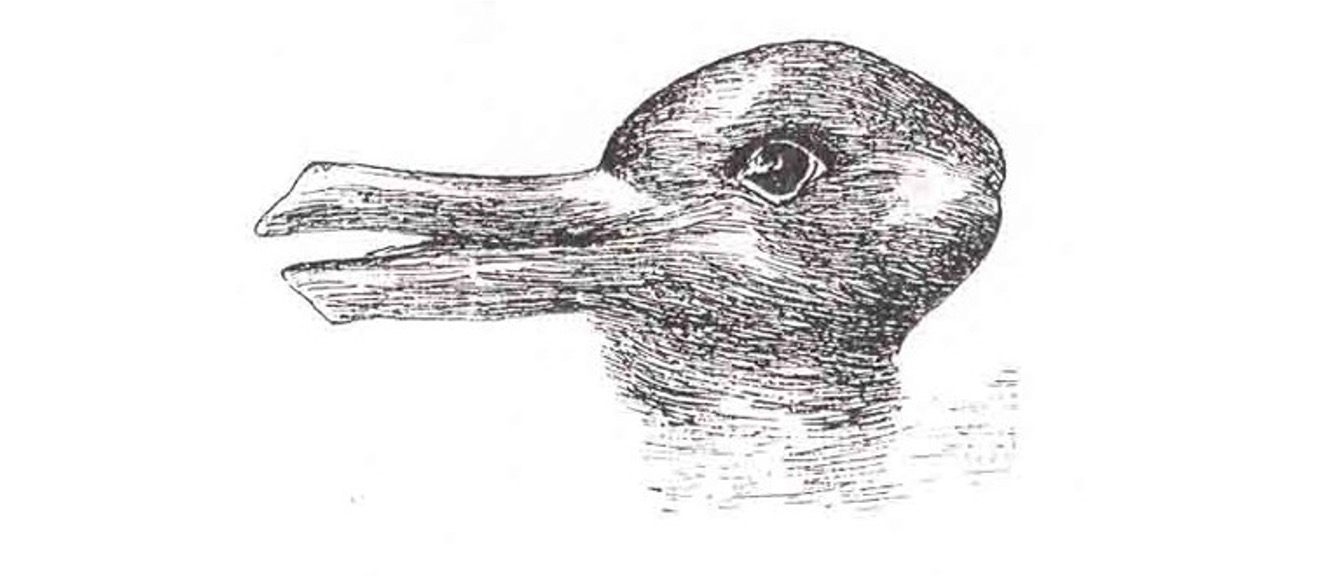
Factors Affecting Perception
- Sensory adaptation
- Attention (e.g., inattentional blindness)
- Motivation
- Beliefs, values, and expectations
- Cultural experiences
Muller-Lyer Illusion