🗓️Unit 4
Sleep
PSYC 181 – Intro to Psych
July 22, 2024
What you will learn
![]()
Learning Objectives
- Define consciousness
- Understand sleep and its stages
- Describe theories of why we sleep and dream
- Identify major sleep disorders
What is consciousness?
![]()
Consciousness: awareness of internal and external stimuli such as feelings of hunger and pain or detection of light
Wakefulness: high levels of sensory awareness, thought, and behavior
Biological Rhythms
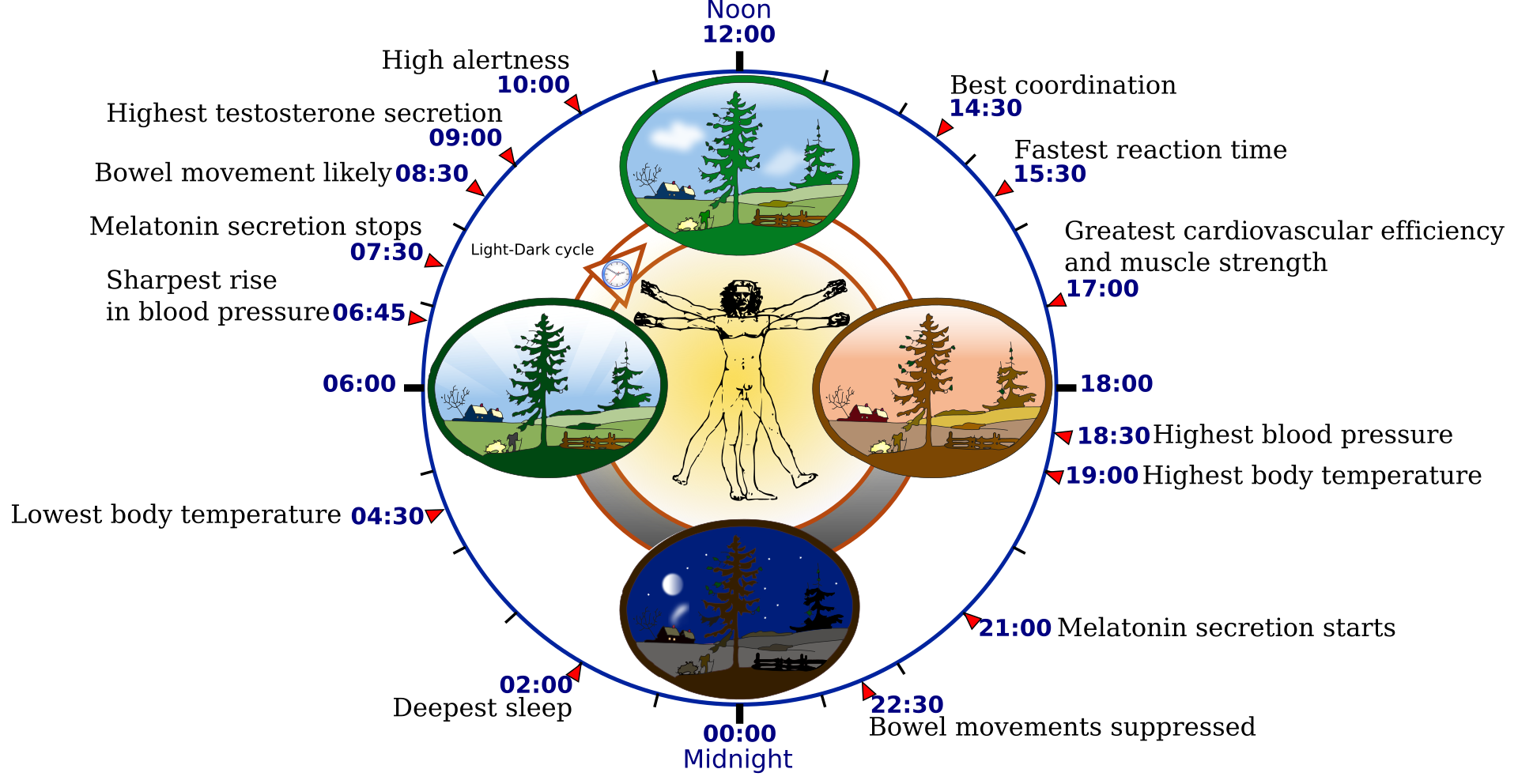
Circadian Rhythms
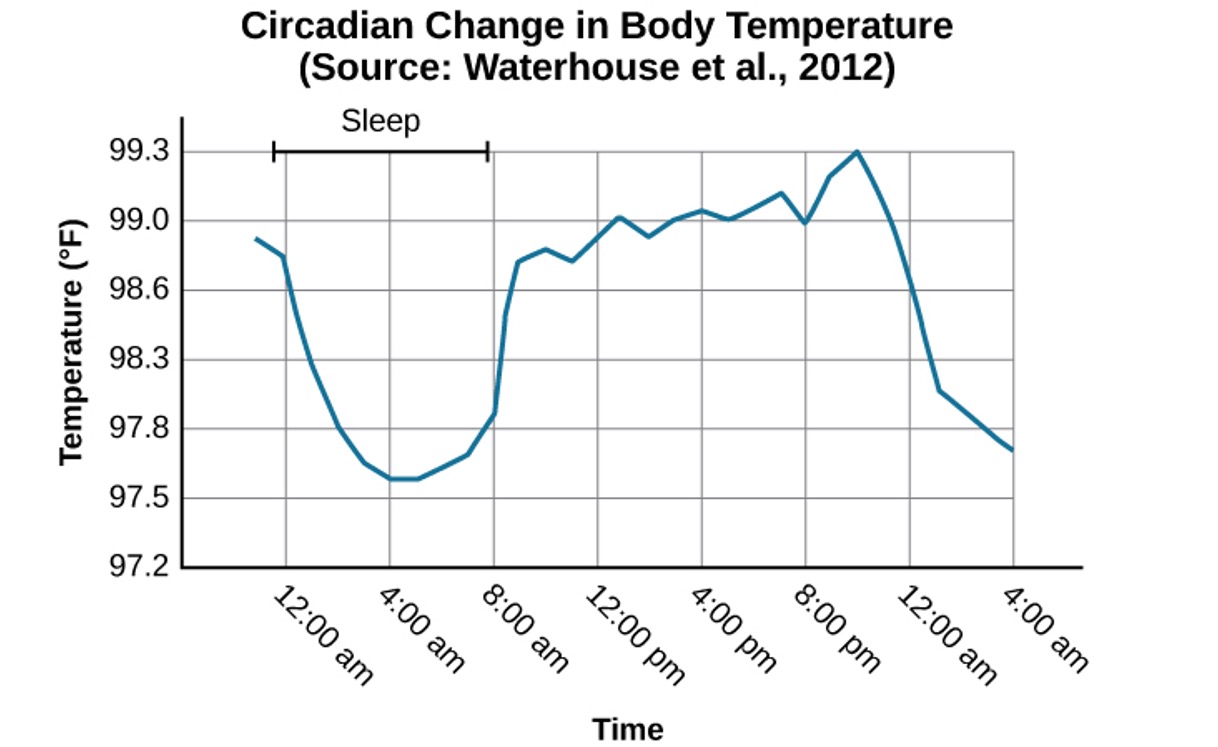
Occurs over approximately 24 hours
The Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)

serves as the brain’s clock mechanism
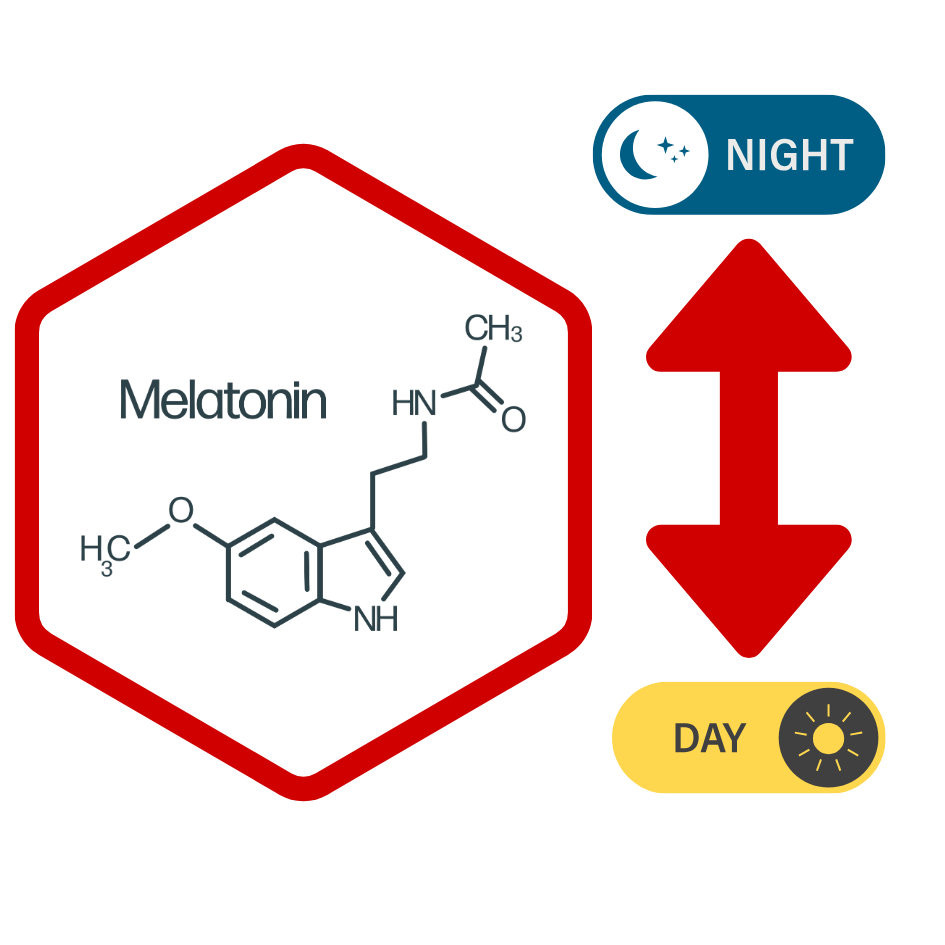
Melatonin and Sleep Regulation

Disruptions of Normal Sleep
Certain circumstances can throw off our circadian rhythms
Jet lag: mismatch between our internal circadian cycles and our environment
Rotating shift work: Becomes difficult for a normal circadian rhythm to be maintained.
Bright light
Bright light can be used to realign our biological clocks with the external environment
Sleep Needs at Different Ages
| Age | Recommended | May be appropriate | Not recommended |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–3 months | 14–17 hours | 11–13 hours 18–19 hours | Fewer than 11 hours More than 19 hours |
| 4–11 months | 12–15 hours | 10–11 hours 16–18 hours | Fewer than 10 hours More than 18 hours |
| 1–2 years | 11–14 hours | 9–10 hours 15–16 hours | Fewer than 9 hours More than 16 hours |
| 3–5 years | 10–13 hours | 8–9 hours 14 hours | Fewer than 8 hours More than 14 hours |
| 6–13 years | 9–11 hours | 7–8 hours 12 hours | Fewer than 7 hours More than 12 hours |
| 14–17 years | 8–10 hours | 7 hours 11 hours | Fewer than 7 hours More than 11 hours |
| 18–25 years | 7–9 hours | 6 hours 10–11 hours | Fewer than 6 hours More than 11 hours |
| 26–64 years | 7–9 hours | 6 hours 10 hours | Fewer than 6 hours More than 10 hours |
| ≥65 years | 7–8 hours | 5–6 hours 9 hours | Fewer than 5 hours More than 9 hours |
Individual Differences
Morning vs. Night person

Sleep deprivation
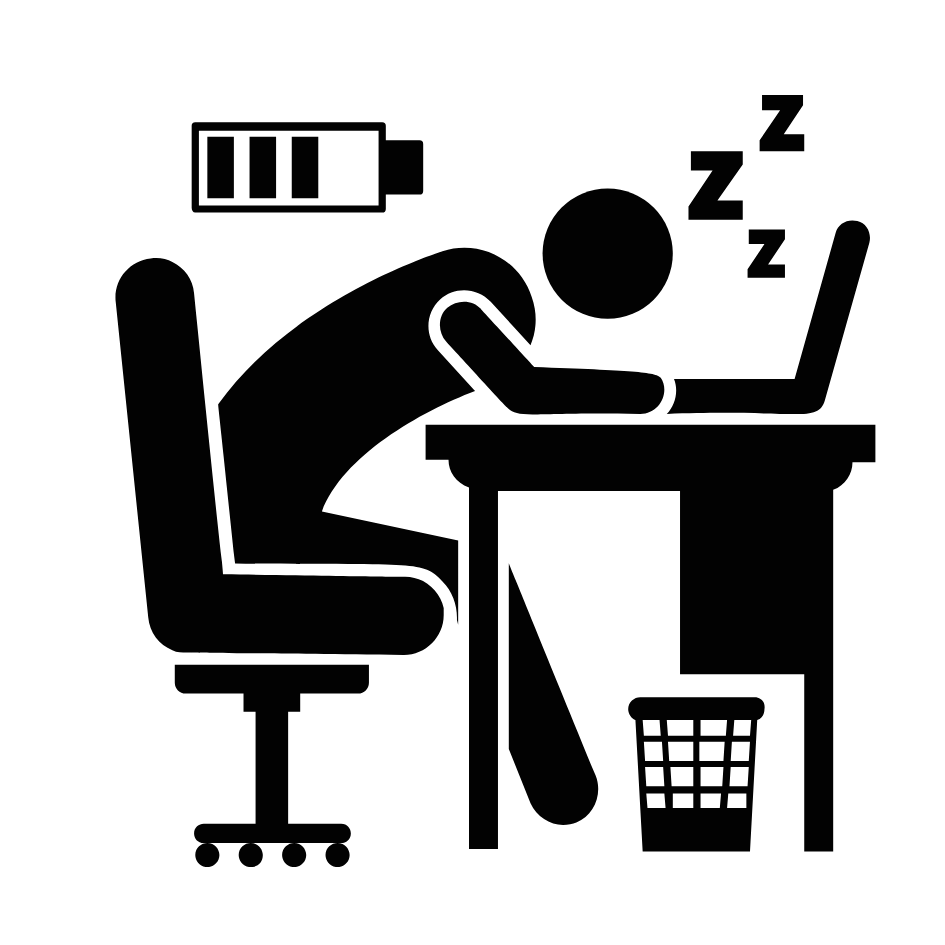

Sleep debt: result of insufficient sleep on a chronic basis.
Sleep rebound: a sleep-deprived individual will fall asleep quicker
This figure illustrates some of the negative consequences of sleep deprivation. While cognitive deficits may be the most obvious, many body systems are negatively impacted by lack of sleep.
Sleep Debt and College Students
What is sleep?
Sleep is associated with the secretion and regulation of many hormones including:
- Melatonin
- Follicle stimulating hormone
- Luteinizing hormone
- Growth hormone
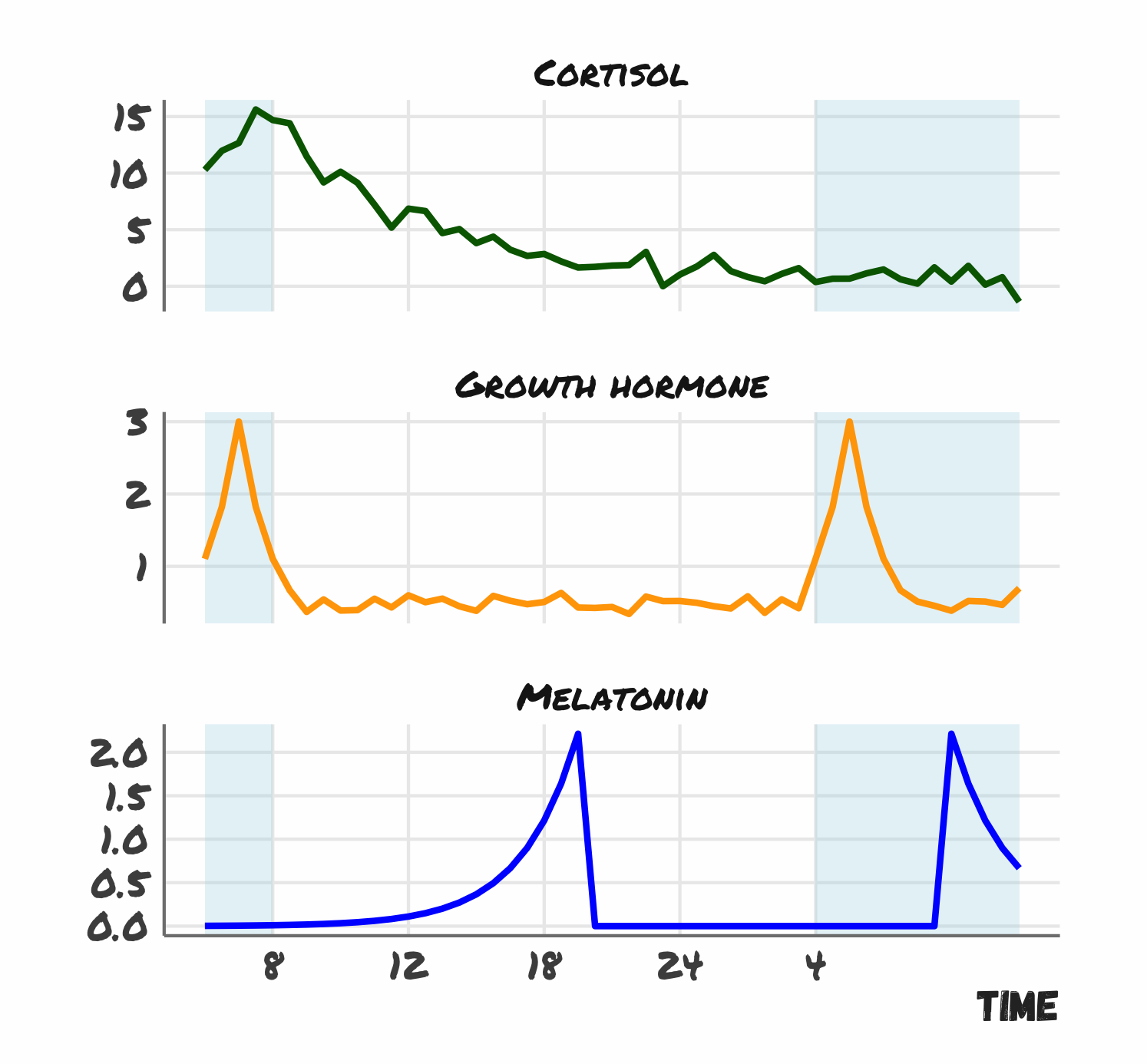
Brain Areas involved in sleep

The pineal and pituitary glands secrete a number of hormones during sleep
Why Do We Sleep?
Evolutionary Theory

Cognitive function

Restoration theory
Allows body to rest and repair
Waste Management System


Stages of Sleep
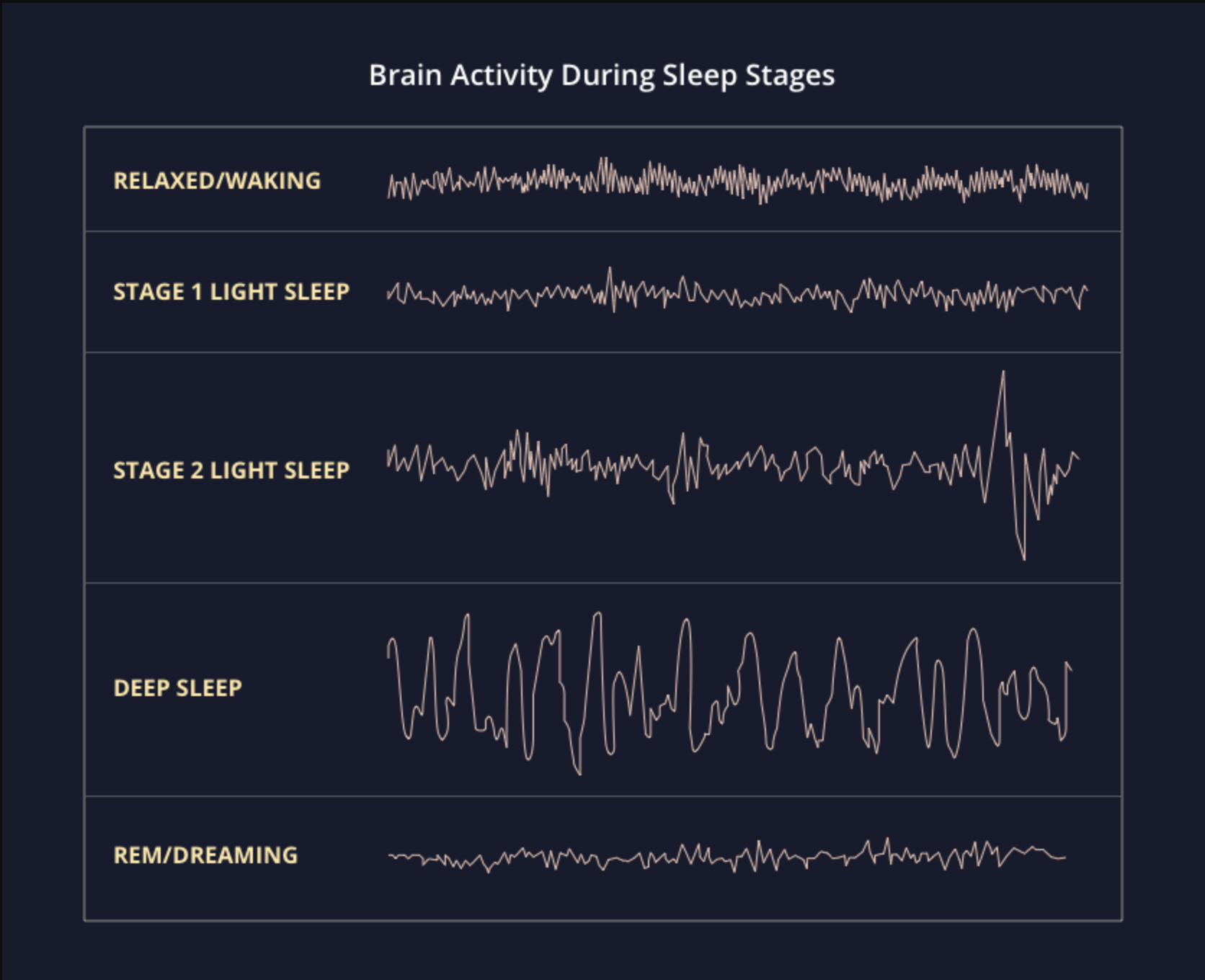
Brain Waves During Sleep
Dramatically changes in activity across stages of sleep can be visualized using EEG
- Alpha relatively low frequency, relatively high amplitude, synchronized
- Theta: low frequency, low amplitude
- Delta low frequency, high amplitude, desynchronized
Stage 1
Alpha waves
- Transitional phase between wakefulness and sleep
- Respiration and heartbeat slows
- Muscle tension and body temperature decrease
Stage 2
Theta waves
- Body enters deep relaxation
- Appearance of sleep spindles and K-complexes

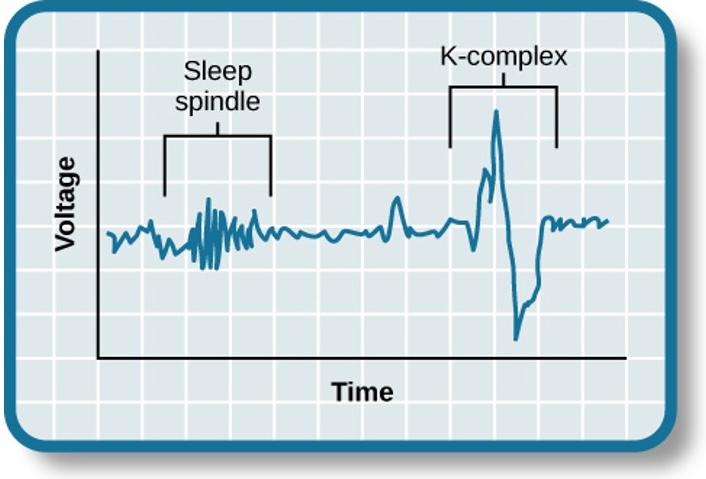
Sleep Spindles & K-complexes
- Sleep spindles: rapid burst of high frequency brainwaves
- K-complexes: very high amplitude pattern of brain activity
Stages 3 and 4
Delta waves
- Known as slow-wave sleep
- Respiration and heart rate slow down further

Rapid Eye Movement (REM)
Brain waves are similar to those seen during wakefulness
- Paralysis of voluntary muscles
- Dreams

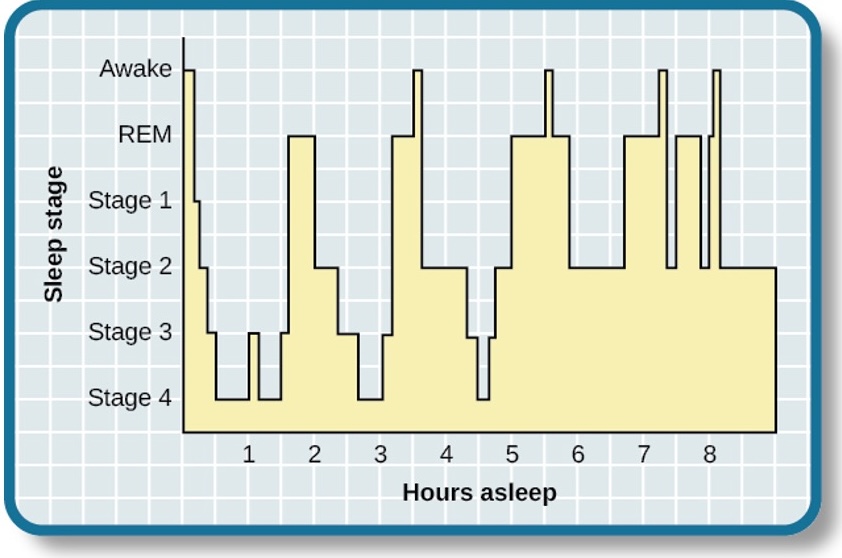
Hypnogram of sleep stages
Diagram of the stages of sleep as they occur during a period of sleep
Dreams
Unclear why we dream!
Dream Theories
Many ideas about how to interpret dreams
- Sigmund Freud: Saw dreams as a way to gain access to the unconscious.
- Manifest content: the actual dream content
- Latent content: the hidden meaning
- Carl Jung: Believed that dreams allowed us to tap into the collective unconscious.
- Collective unconscious: repository of information shared by all people across cultures
- Symbols reflect universal archetypes
Activation-Synthesis Theory
Some support in neuropsychology
- Brain tries to make sense of random activity during sleep
- Emotion centers (limbic system) active
- intense emotions
- Frontal cortices are not active
- Uncritically accept illogical events

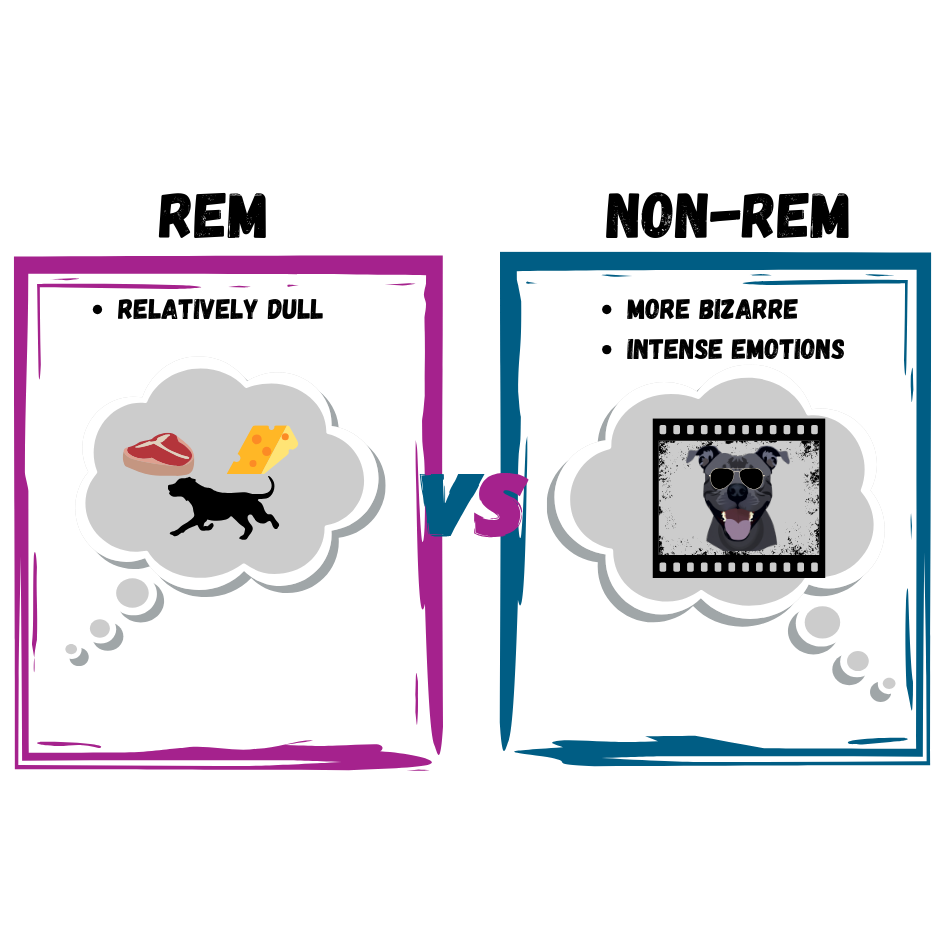
REM vs. Non-REM Dreams
Sleep Disorders
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling or staying asleep
- Parasomnias: Unwanted behaviors during sleep (e.g., sleepwalking, night terrors)
- Sleep apnea: Breathing stops during sleep
- Narcolepsy: Irresistible urge to fall asleep during waking hours
Insomnia (most common)

Defined by difficulty falling or staying asleep for at least 3 nights a week for at least one month’s time.
Contributing factors:
- Age
- Drug use
- Exercise
- Mental status
- Bedtime routines

Insomnia (treatment)

- Stress management
- Changes in problematic behaviors that could contribute to insomnia
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Parasomnia

Unwanted motor behavior/experiences throughout the sleep cycle
Sleep walking: Usually occurs during slow-wave sleep.
REM sleep behavior disorder: Occurs when the muscle paralysis associated with REM sleep does not occur.
Includes high levels of physical activity during REM sleep. Often treated with Clonazepam (an anti-anxiety medication).
Restless leg syndrome: Involves uncomfortable sensations in the legs when trying to fall asleep that are relieved by moving the legs. Can be treated with a variety of medications.
Night terrors: Sleeper experiences a sense of panic and may scream or attempt to escape. Occur during NREM sleep.
Sleep Apnea

Occurs when individuals stop breathing during their sleep, usually for 10-20 seconds or longer.
Obstructive: airway becomes blocked and air is prevented from entering the lungs.
Central: CNS fails to initiate breaths.
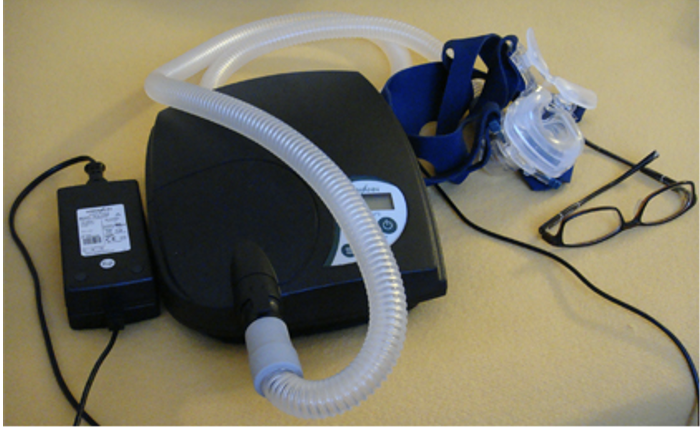
Narcolepsy

Involves an irresistible urge to fall asleep during waking hours
Cataplexy: loss of muscle tone while awake or in some cases complete paralysis of the voluntary muscles.
Hypnagogic hallucinations: vivid, dream-like hallucinations.
Treatment: psychomotor stimulant drugs.

Sleep & Dream Log
