🗓️Unit 03
Biopsychology
PSYC 181 – Intro to Psych
Emma Marshall – Instructor
July 19, 2024
Learning Objectives
![]()
- Describe different historical and modern approaches to understanding the nature vs. nuture debate
- Describe methods of assessing brain activity and function
- Identify basic parts of a neuron, the nervous system, and brain structures and describe their primary functions
- Explain the role of the endocrine system in regulating bodily functions
Evolution and Social Darwinism
![]()
Charles Darwin

Theory of Evolution
Proposed system of natural selection and survival of the fittest theory of evolution
Phrenology & Pseudoscience
First theory that brain regions control specific behaviors



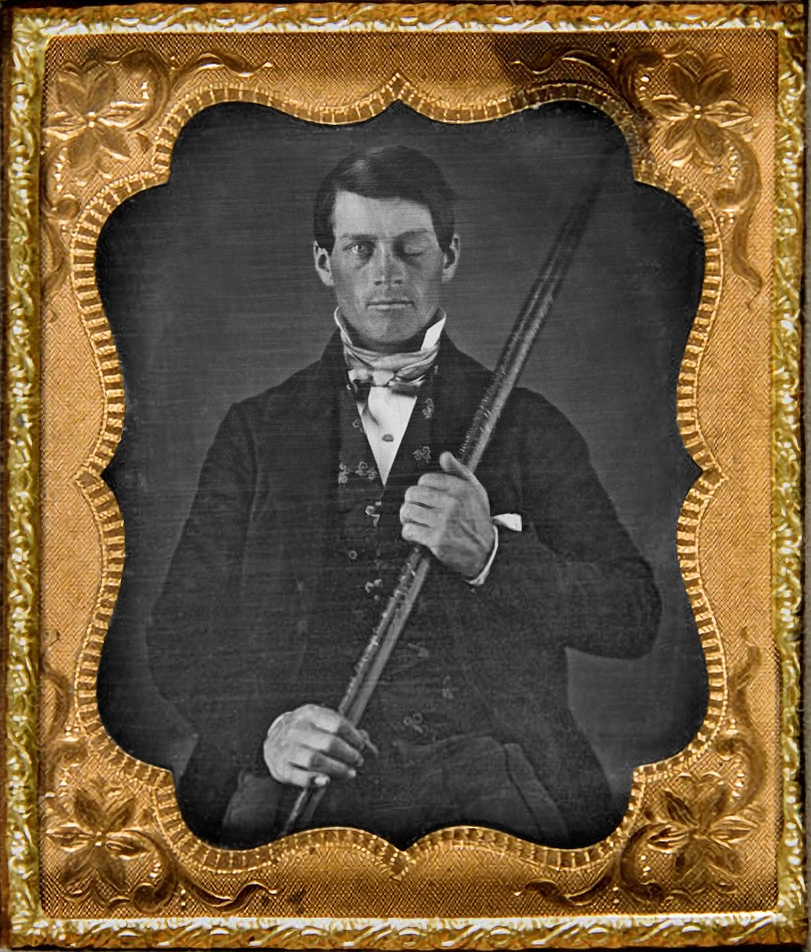
Phineas Gage

- Case study demonstrating effects of frontal lobe damage on personality
- First scientific evidence of localized brain functions

Modern Psychophysiological Assessment
Study of the relationship between mental activity and biological responses
Common methods:
- Skin conductance
- Heart rate
- Muscle movements
- Brain imaging techniques
Brain Imaging Techniques
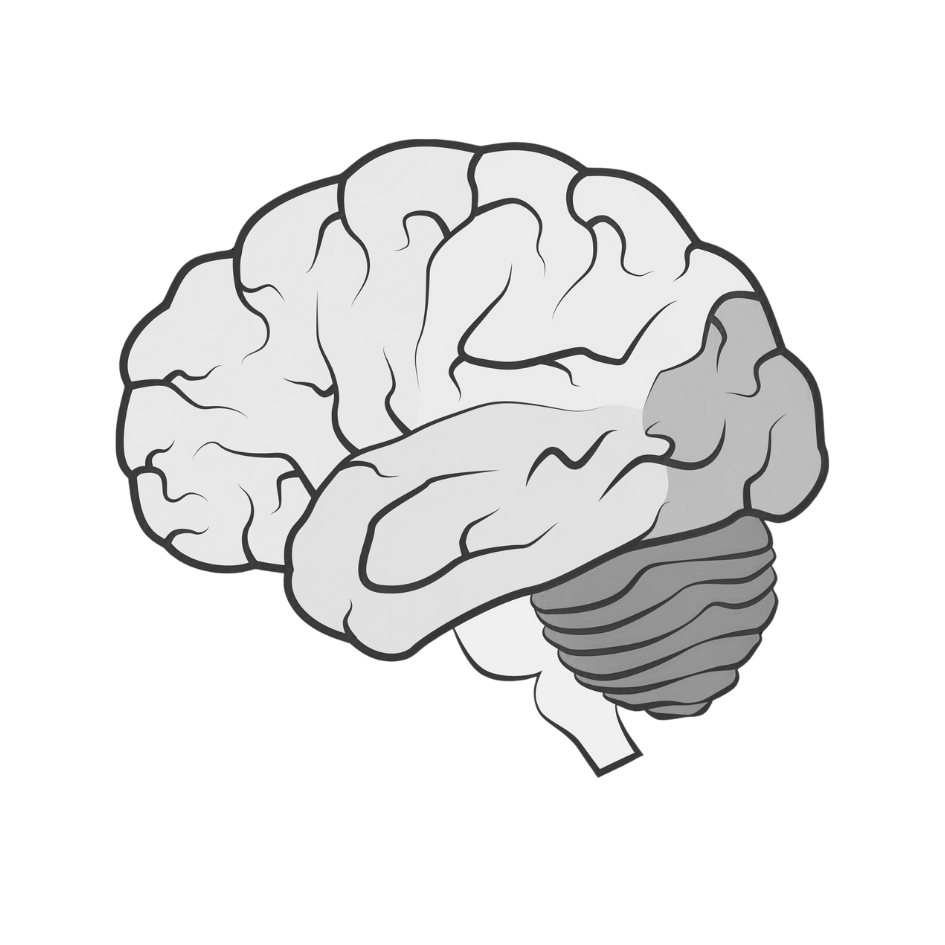
| Category | Technique | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Radiation-based | CT Scan | Uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the brain |
| PET Scan | Measures metabolic processes in the brain | |
| Magnetic field-based | MRI | Produces detailed anatomical images of the brain |
| fMRI | Shows brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow | |
| Electrical activity-based | EEG | Records electrical activity of the brain |
Radiation-based:

![]()
![]()
Magnetic Field-based:



Electrical activity-based:


UNL CB3

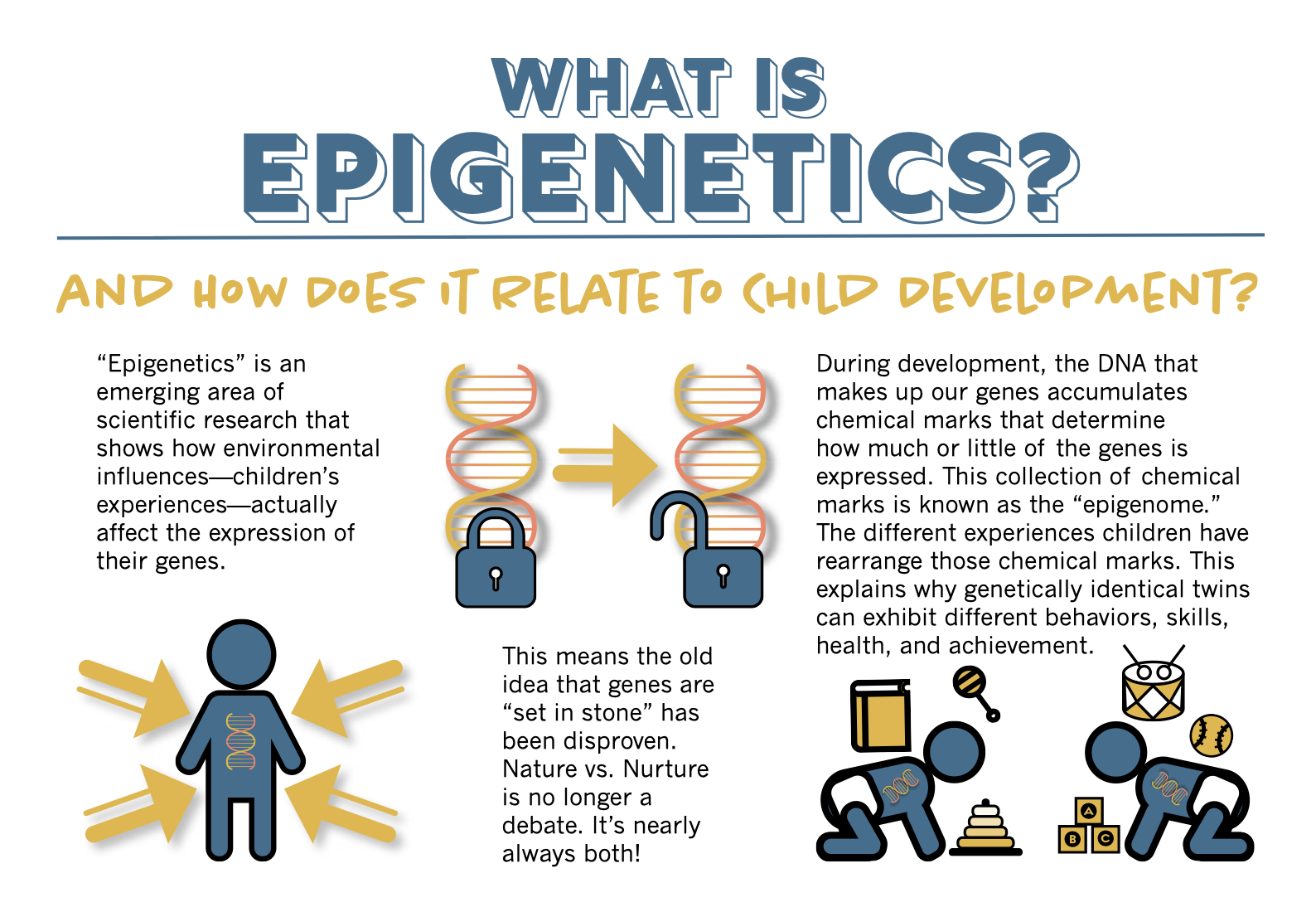
Nature vs. Nurture

Epigenetics
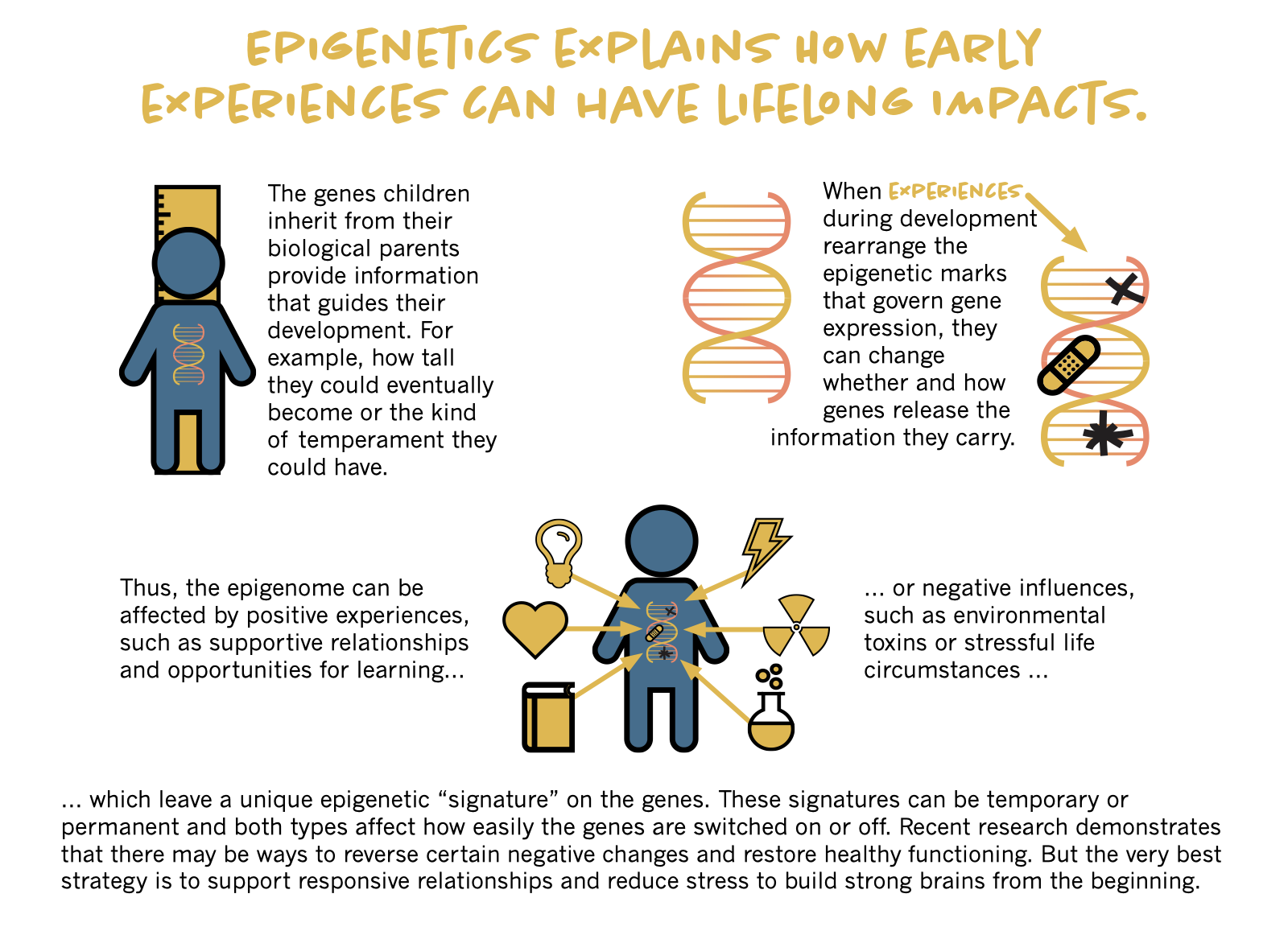
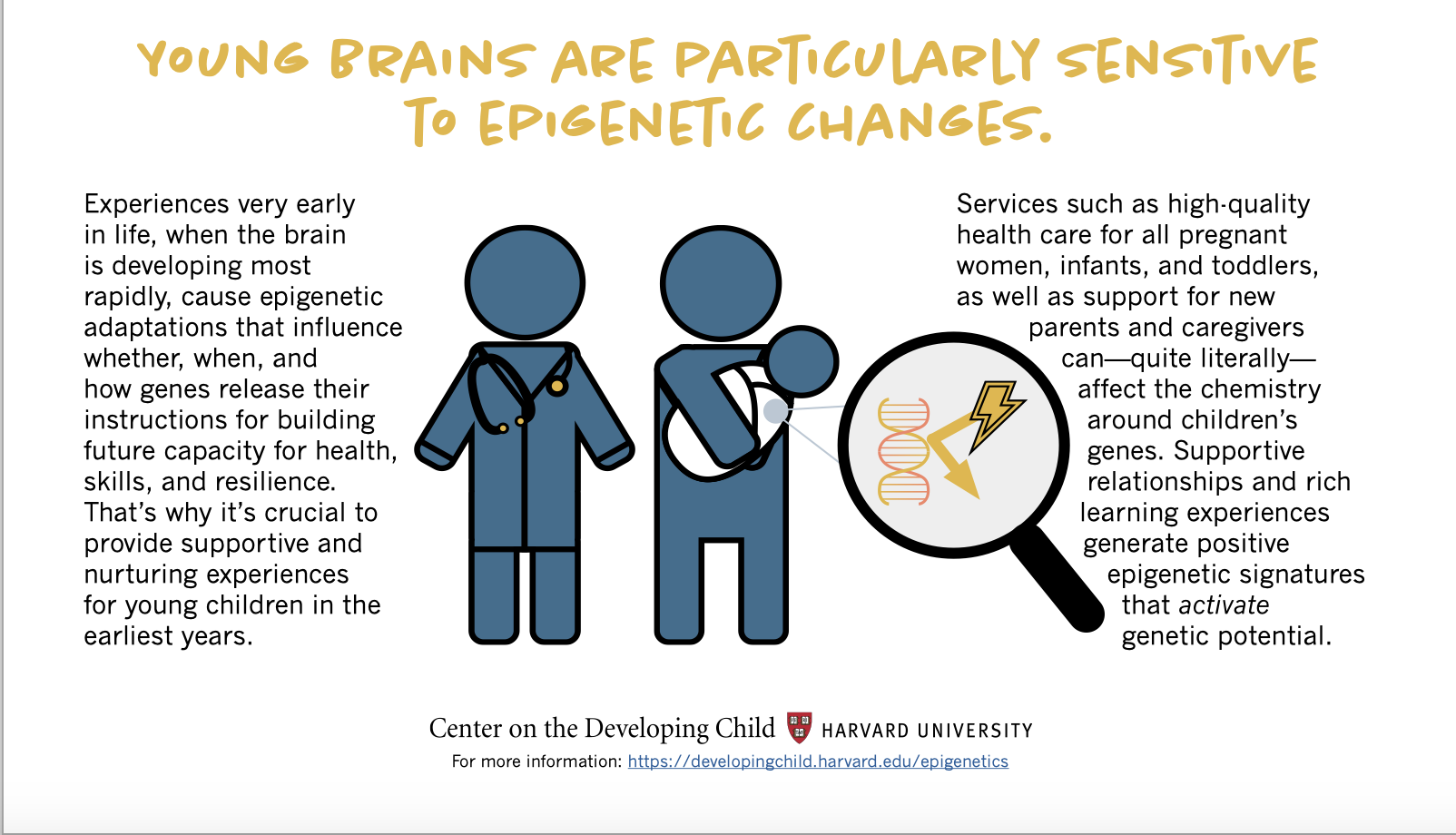
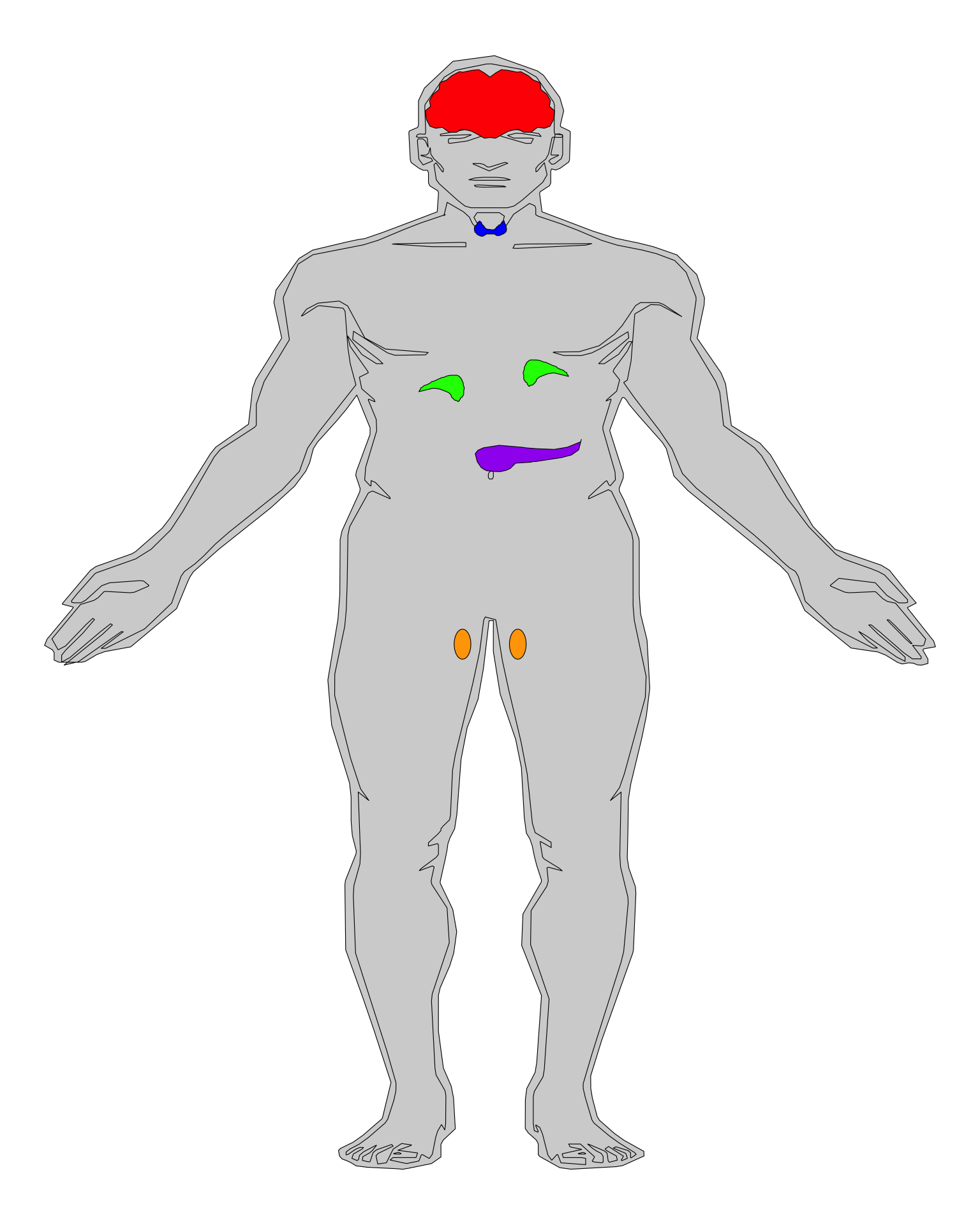
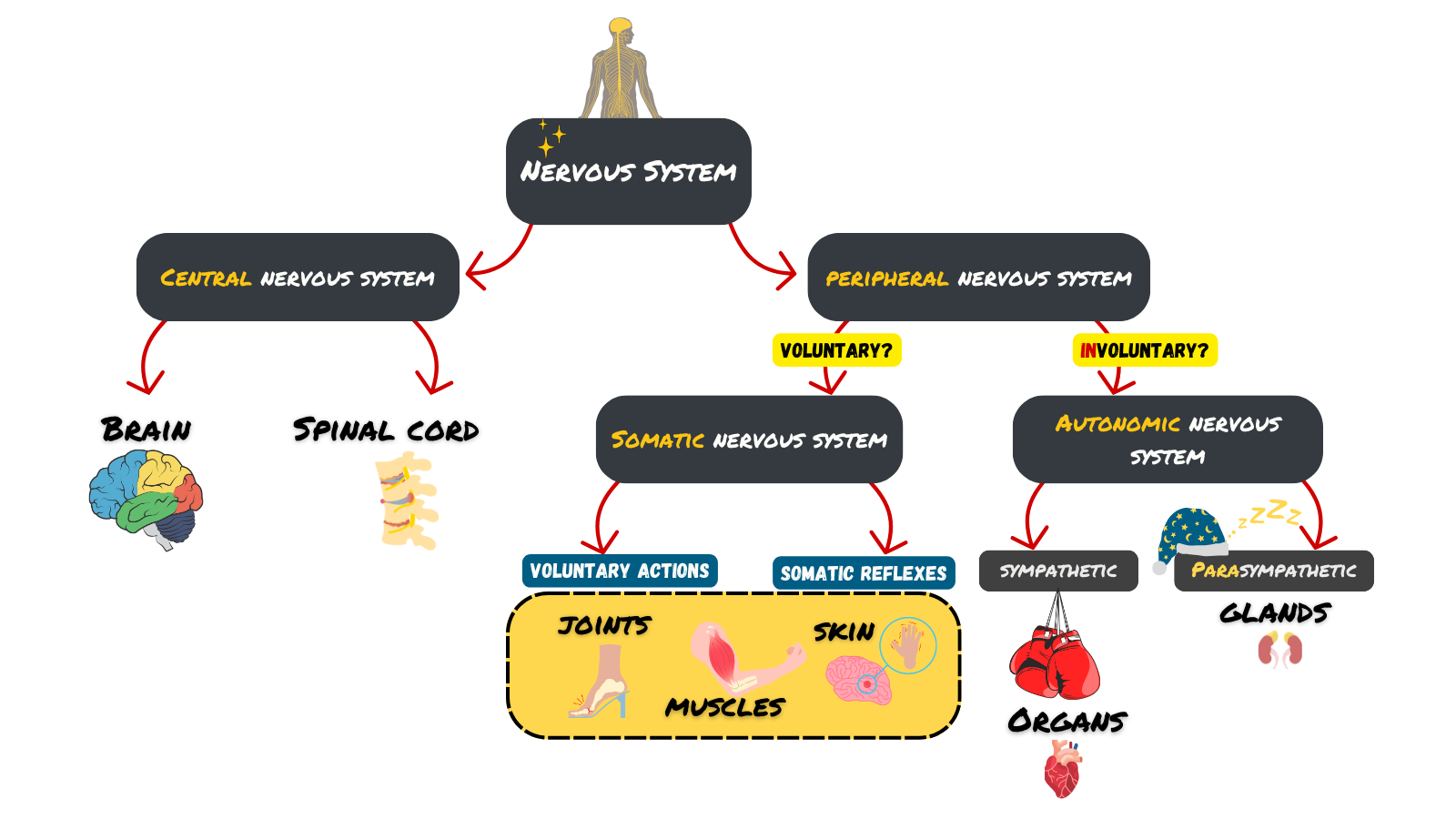
The Nervous System
Nervous System Structure
Brain Structure and Function

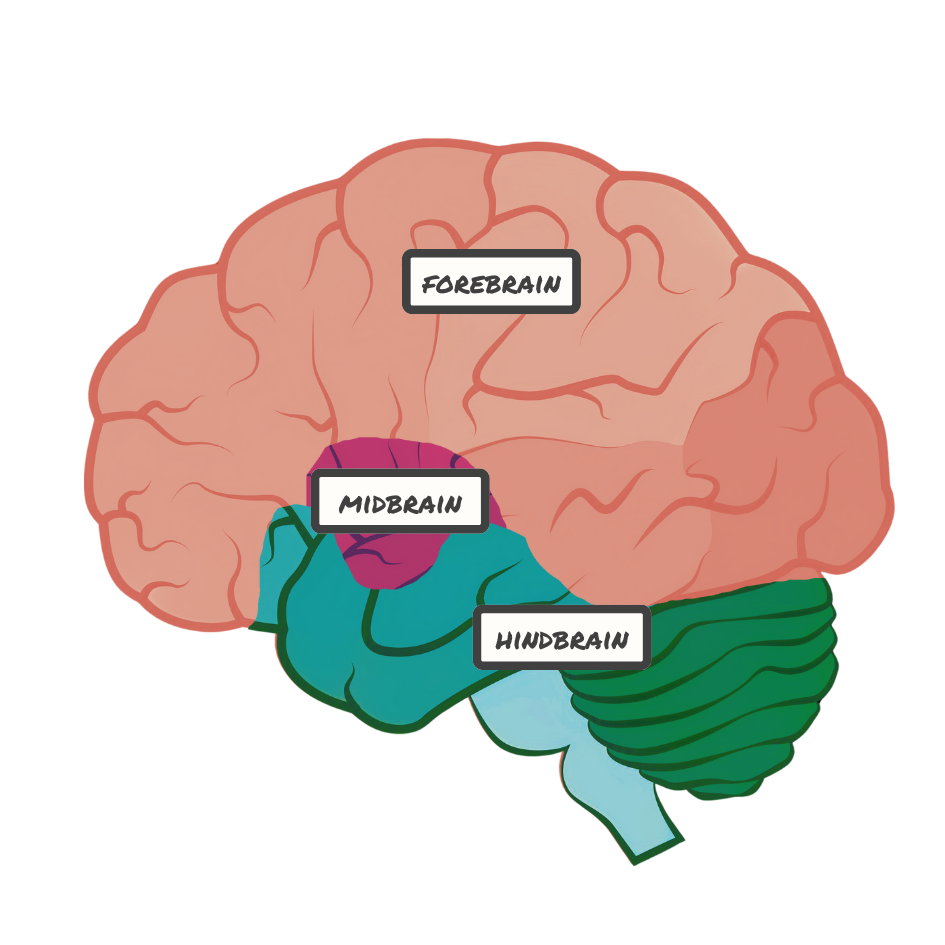
Cerebral Cortex
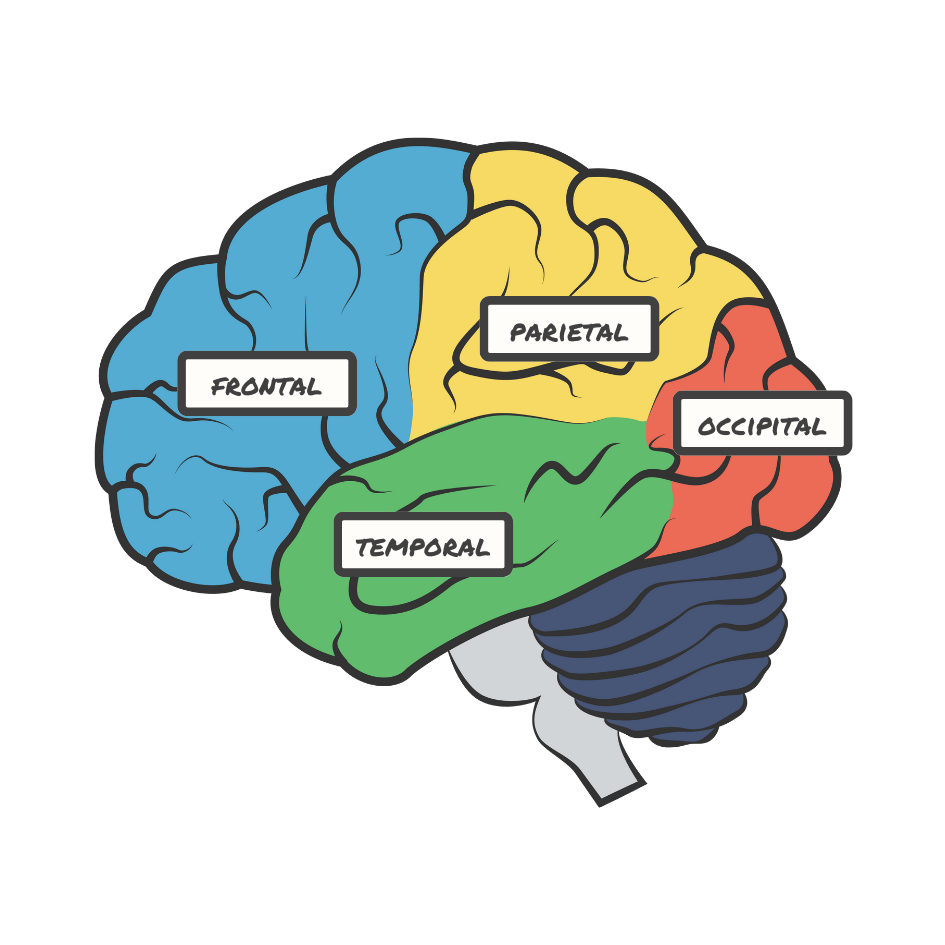
Limbic System
Set of structures involved in emotion and memory
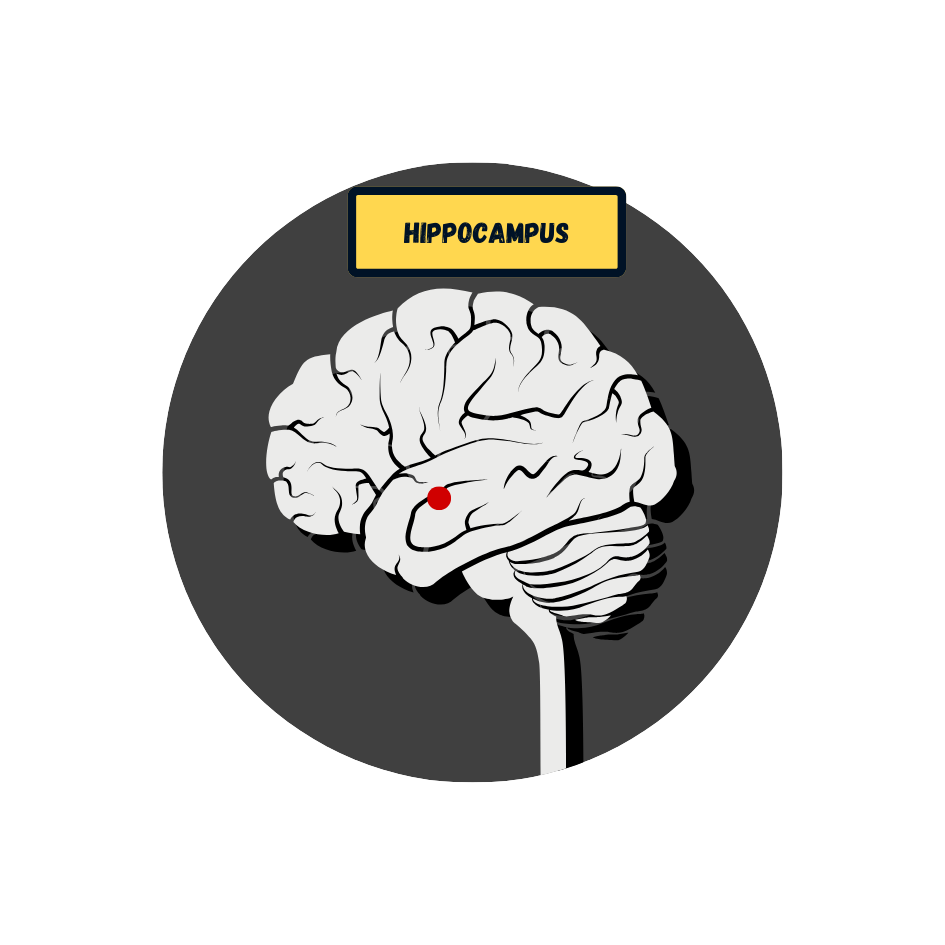
Regulates hormones
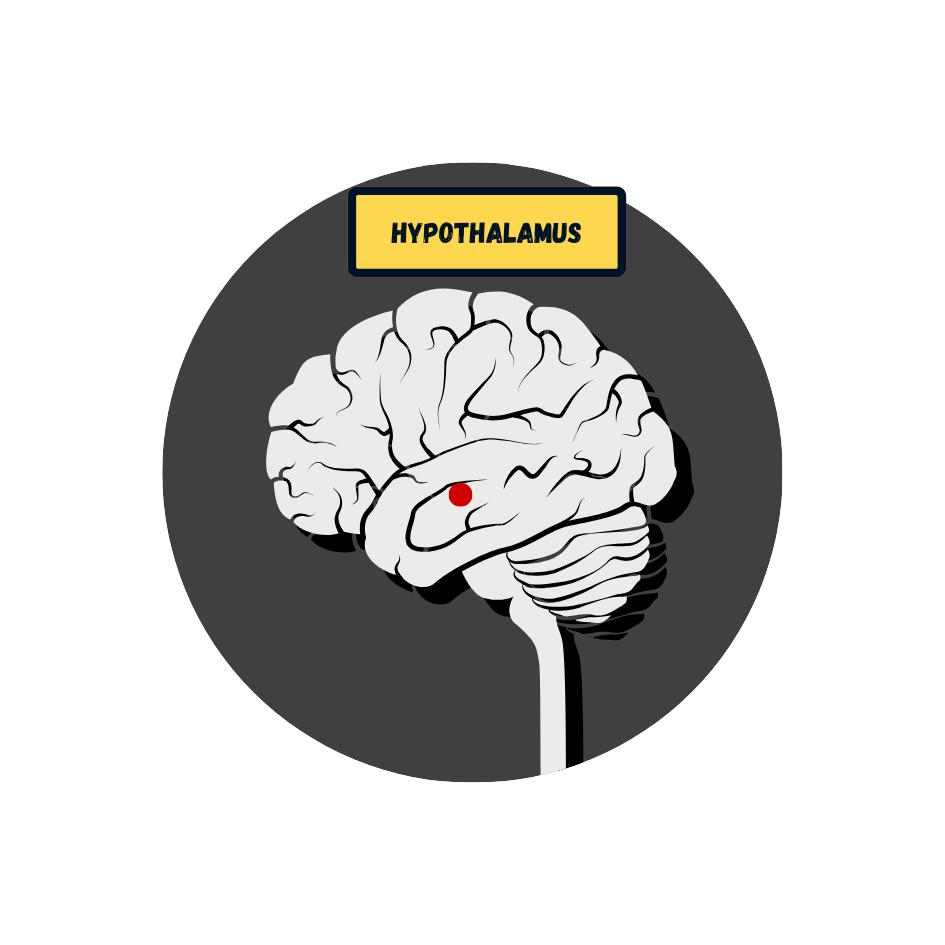

Fight or Flight
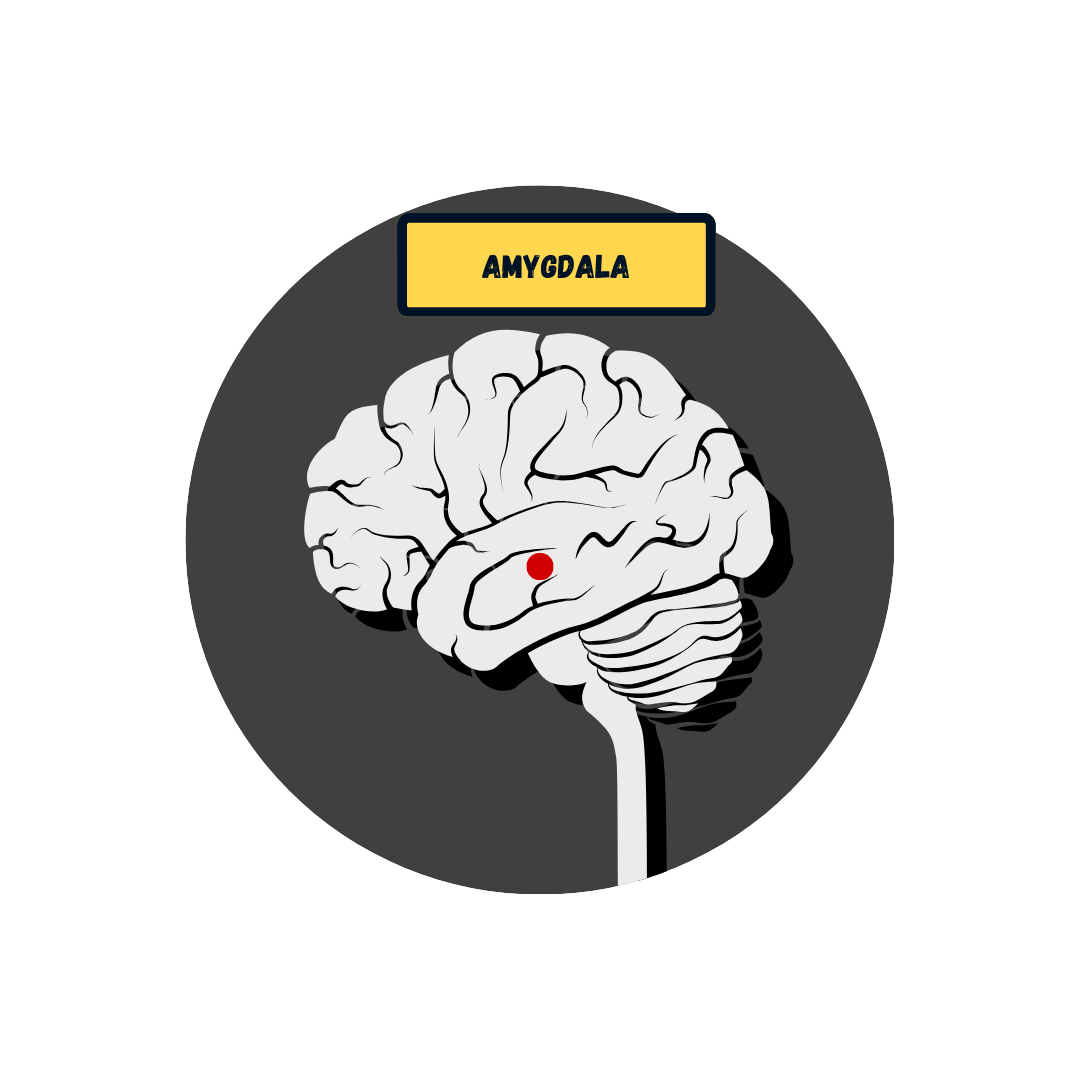

Memory processing

Nervous System Structure

Nervous System
Cells of the Nervous System
Neurons
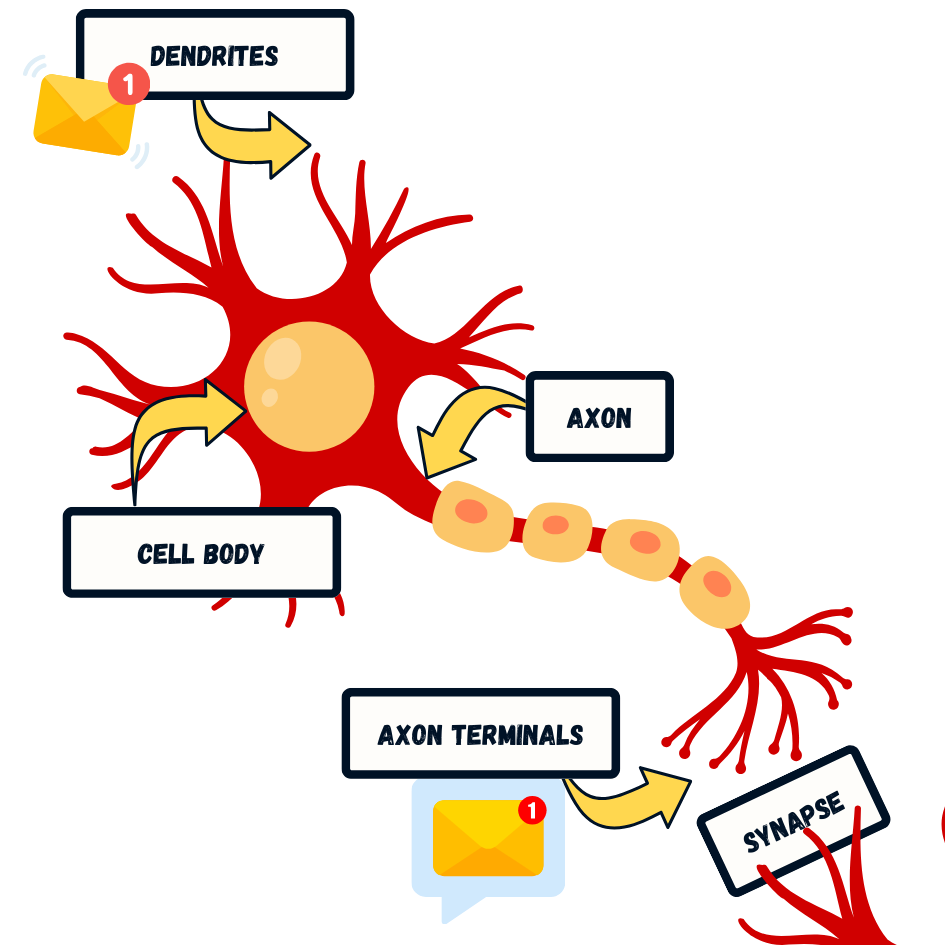
Specialized cells that transmit nerve impulses
Glial Cells

Support cells for neurons
Action Potential Process
Neuronal Communication
Neurotransmitters and Drugs
Chemical messengers released by neurons
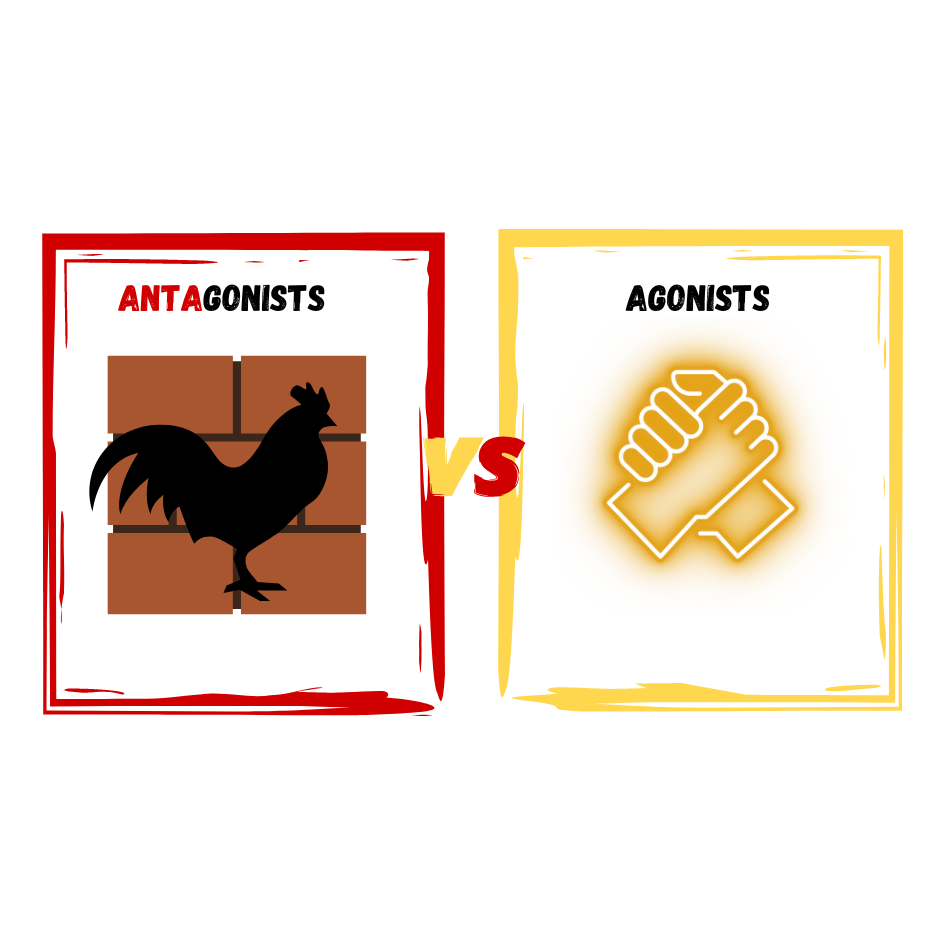
Neurotransmitters
Major Neurotransmitters and How They Affect Behavior
| Neurotransmitter | Involved in | Potential Effect on Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Acetylcholine | Muscle action, memory | Increased arousal, enhanced cognition |
| Beta-endorphin | Pain, pleasure | Decreased anxiety, decreased tension |
| Dopamine | Mood, sleep, learning | Increased pleasure, suppressed appetite |
| Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) | Brain function, sleep | Decreased anxiety, decreased tension |
| Glutamate | Memory, learning | Increased learning, enhanced memory |
| Norepinephrine | Heart, intestines, alertness | Increased arousal, suppressed appetite |
| Serotonin | Mood, sleep | Modulated mood, suppressed appetite |
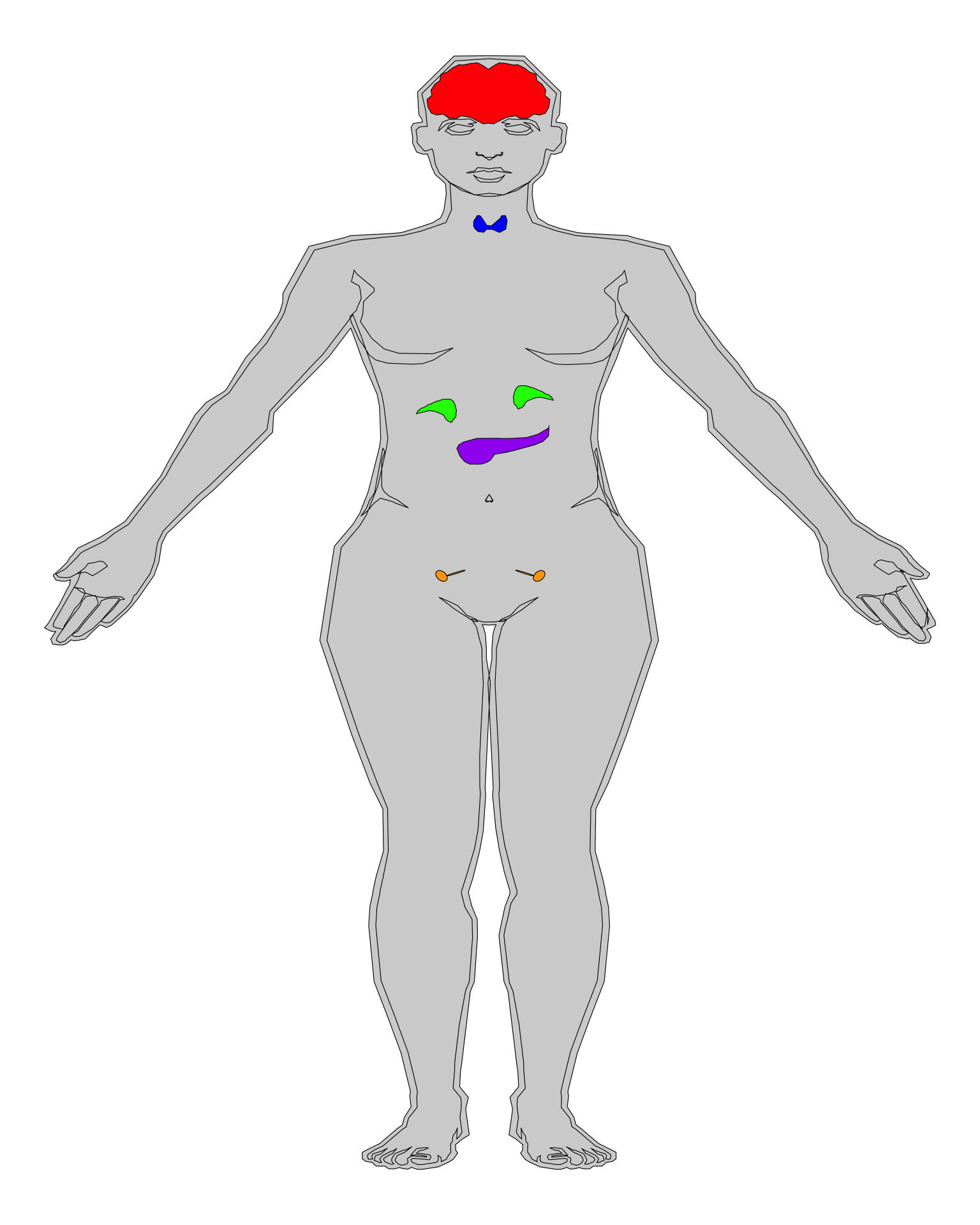
Edocrine System
Network of glands that produce and secrete hormones
Male Endocrine System
Female Endocrine System
Social Darwinism and Eugenics
Francis Galton
The Decent of Man (1871)
Helped to start Eugenics movement but also developed some basic statistics