| Metric | StayGames | StayWins | SwitchGames | SwitchWins | StayProbability | SwitchProbability | Age |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min. | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 18.00 |
| 1st Qu. | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 0.6333 | 19.00 |
| Median | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.5000 | 1.0000 | 20.00 |
| Mean | 3.324 | 1.378 | 2.081 | 1.486 | 0.4628 | 0.7774 | 19.86 |
| 3rd Qu. | 3.000 | 1.000 | 3.000 | 2.000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 20.00 |
| Max. | 28.000 | 13.000 | 10.000 | 7.000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 24.00 |
| NA's | NA | NA | NA | NA | 4 | 14 | NA |
🗓️Unit 2 Research Methods
PSYC 181 – Intro to Psych
July 17, 2024
What you will learn
![]()
Learning Objectives
- Explain how scientific research addresses questions about behavior
- Discuss how scientific research guides public policy
- Appreciate how scientific research can be important in making personal decisions
What is science?
Science has Four Goals
![]()
Description
Prediction
Control
Explanation
Psychology as Science
Why is research important?

#NotALLResearch
Can findings be replicated?


Psychologists are ALL scientists
BUT they all approach similar topics differently
The scientific method is circular
Research is an ongoing process…
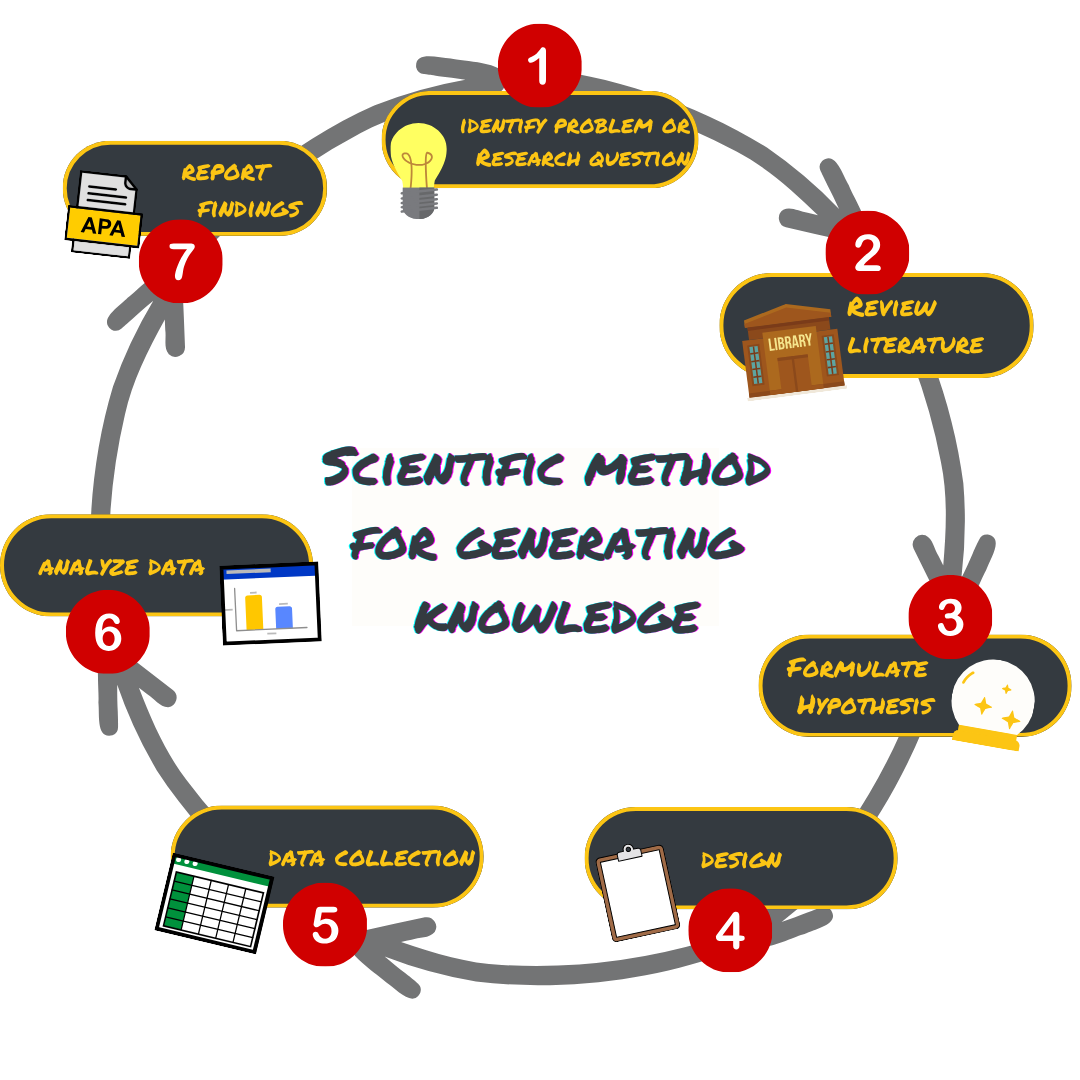
Theory ↕️ Empirical Data
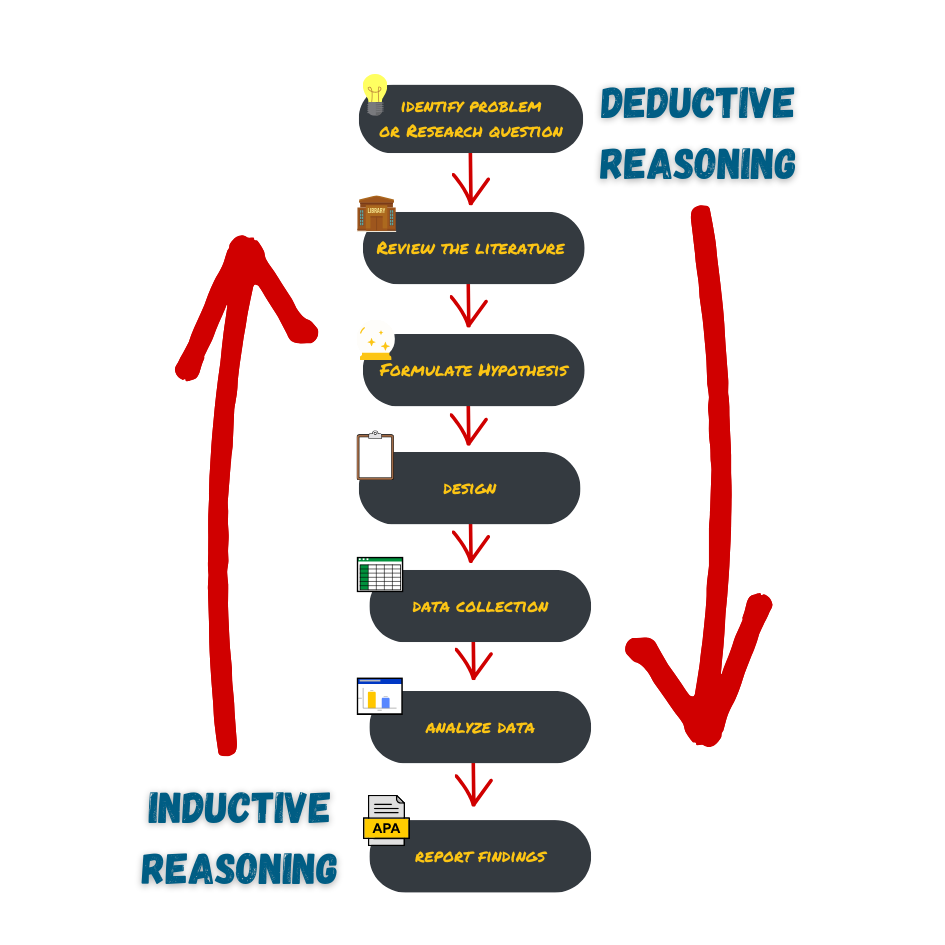
Theory vs. Hypothesis
Theory
Proposed Explanation
Relies on related concepts to Explain and Predict future events or explain how a phenomenon works
Hypothesis
If-Then Statement
A specific prediction about the relationship between two ideas
Theory or Hypothesis?
A good theory is…
- Falsifiable
- Can be shown to be incorrect
- Empirical
- Supported by data
- More supporting data = more confidence
- Parsimonious
Parisimonious = simple

Evaluating Quality of a Theory
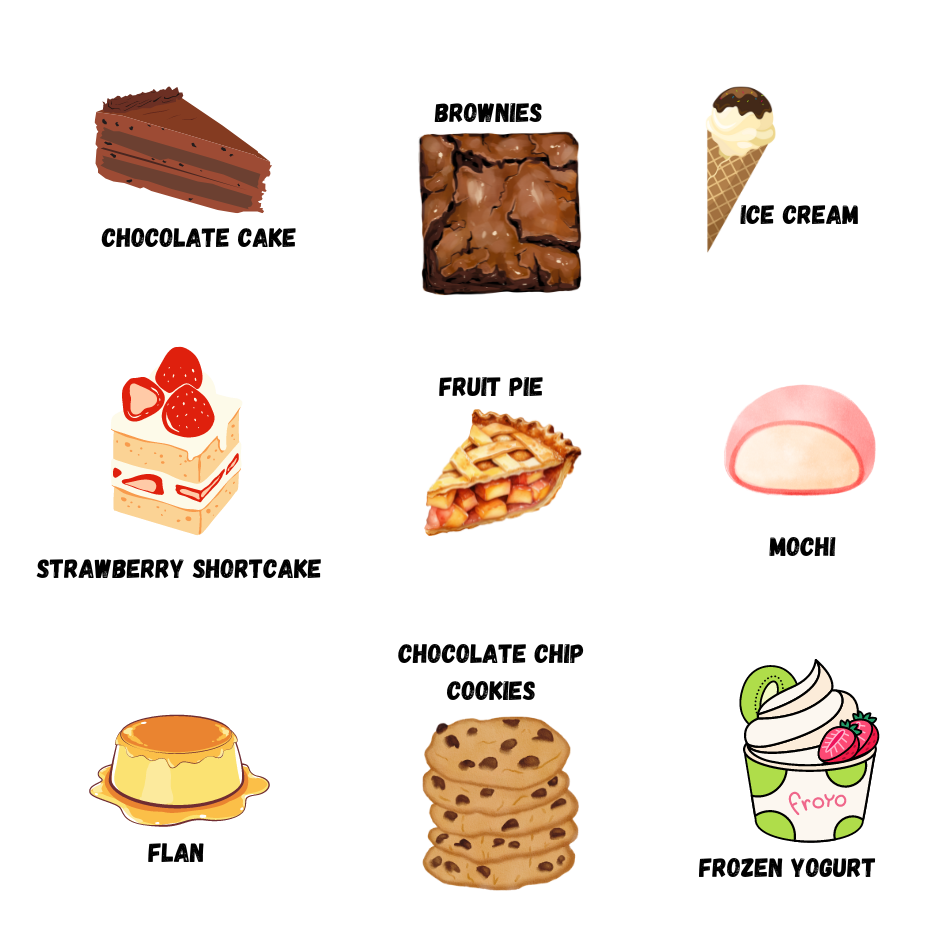
Dessert Preferences & Personality

PICK ONE
Lewandowski (2010)
Dessert Preferences & Personality
- Chocolate Cake
- Strawberry Shortcake
- Flan
- Brownies
- Fruit Pie
- Chocolate Chip Cookies
- Ice Cream
- Mochi
- Frozen Yogurt
Smooth, sexy, & articulate with your hands, you are an excellent after-dinner speaker and a good teacher. But don’t try to walk and chew gum at the same time. A bit of a diva at times, but you have many friends.
Romantic, warm, loving. You care about other people, can be counted on in a pinch and expect the same in return. Intuitively keen. You can be very emotional. You are a friend for life! But look out if someone screws you over. You can hold a grudge.
You are adventurous, love new ideas, and are a champion of underdogs and a slayer of dragons. When tempers flare up you whip out your saber. You are always the oddball with a unique sense of humor and direction. You tend to be very loyal.
You like sports, whether it be baseball, football, basketball, or soccer. If you could, you would like to participate, but you enjoy watching sports. You don’t like to give up the remote control. You tend to be self-centered and high maintenance.
You are a terrible person. No one likes you. Sure, a few people act as if they like you, but they only hang out with you to make fun of you. Turns out, you aren’t that attractive either. Stay in college as long as you can because no one would hire you anyway. Your magic number is…let’s be honest….you have no magic in your life. That makes your magic number zero. Loser.
Sexy; always ready to give and receive. Very creative, adventurous, ambitious, and passionate. You can appear to have a cold exterior but are warm on the inside. Not afraid to take chances. You will not settle for anything average in life. Love to laugh.
You are a very fun loving person, who likes to laugh. You are fun to be with. People like to hang out with you. You are a very warm hearted person and a little quirky at times. You have many loyal friends.
Fun-loving, sassy, humorous, not very grounded in life; very indecisive and lack motivation.
Everyone enjoys being around you, but you are a practical joker. Others should be cautious in making you mad. However, you are a friend for life.
Sweet, loving, cuddly. You love all warm and fuzzy items. A little nutty at times. Sometimes
you need an ice cream cone at the end of the day. Others perceive you as being childlike and immature at times.
What is the problem with this Dessert Personality theory?
What types of studies are used in psychological research?
Approaches to research
Three types of studies
- Descriptive
- Correlational
- Experimental
Variables
A variable is…
- any concept or property that can be measured and changed
- Each type of research provides different amounts of control over variables
Changing Variables
Researchers change variables in two ways
- Manipulate: change or control within study
- Measure: evaluate or assess within study
Measuring Variables

Study Type 1: Descriptive Research
Descriptive Research
Systematically and objectively observing psychological phenomenon to describe what, when, how it occurs
Descriptive Research
Types of descriptive studies
Case Studies
- Examine one subject in detail
- Cannot apply to others
Observational Studies
- Systematic recording of behaviors
- Participant vs. Naturalistic
Self-Reports
- Surveys or Interviews
- Asking about themselves
- Can provide more specific information
Descriptive Example


Study Type 2: Correlational Research
Correlational Research
Data is from:
- Archives or records
- Observations
- Surveys or Interviews
Examine how variables are related in the world without attempts to control the variables
Correlational Research: Example
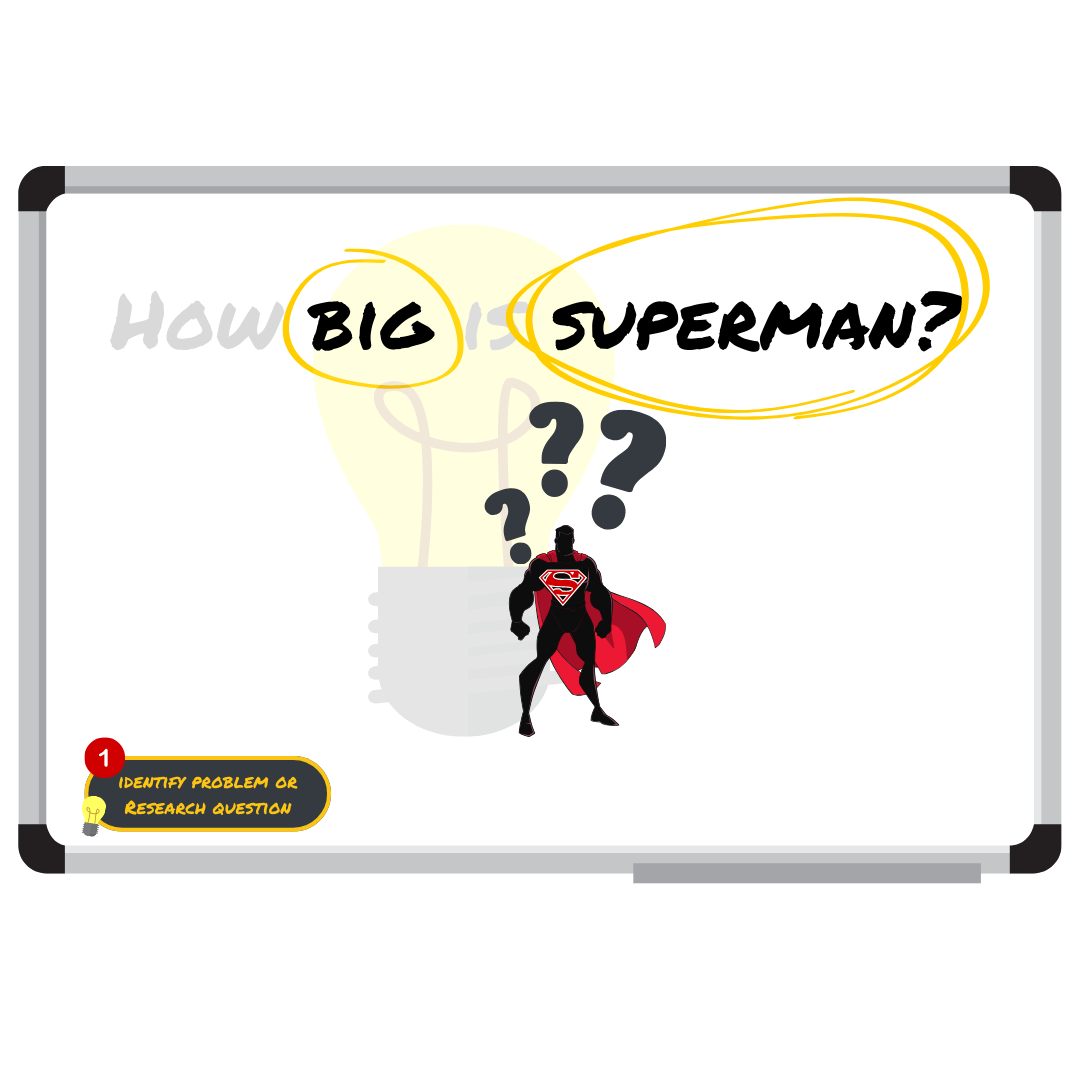
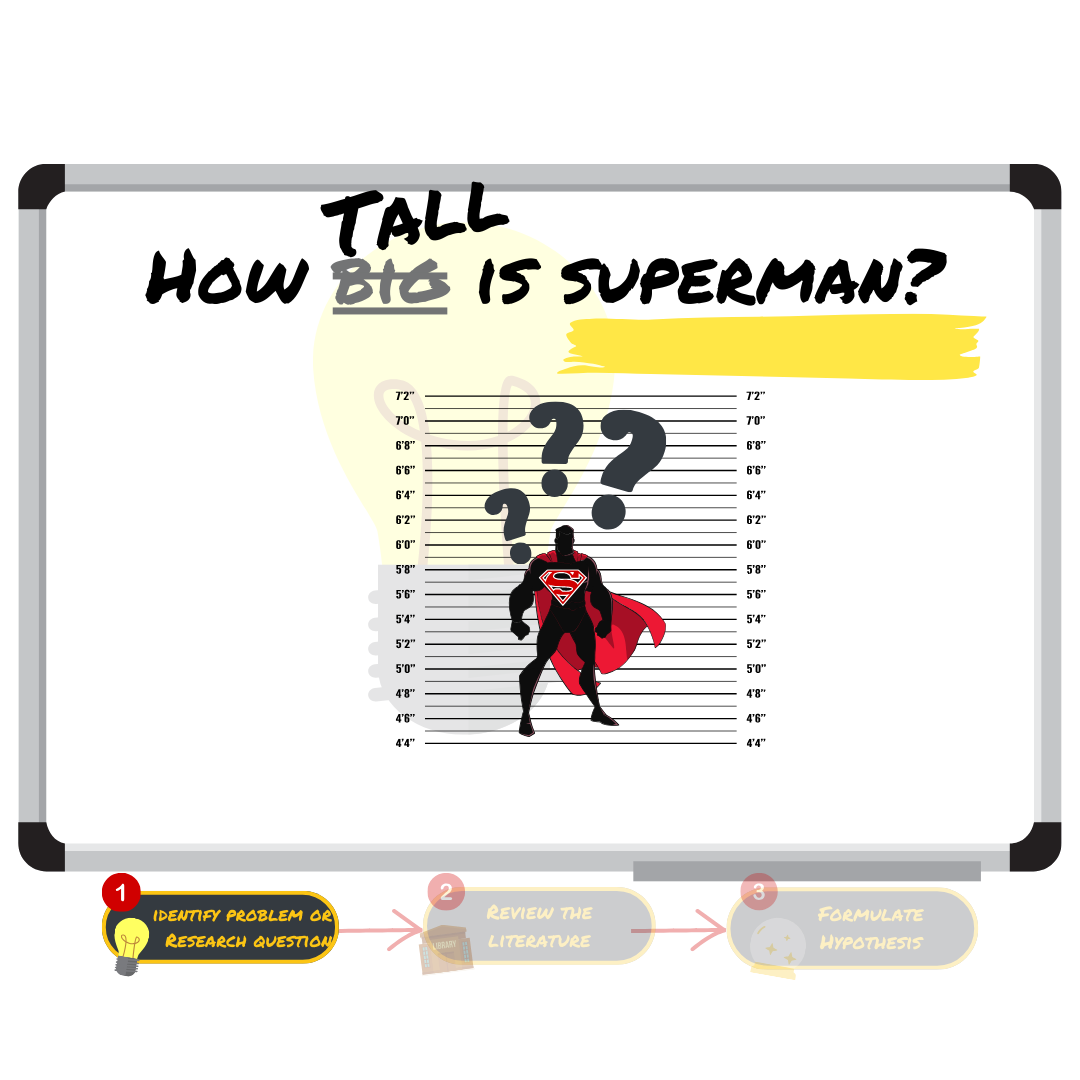
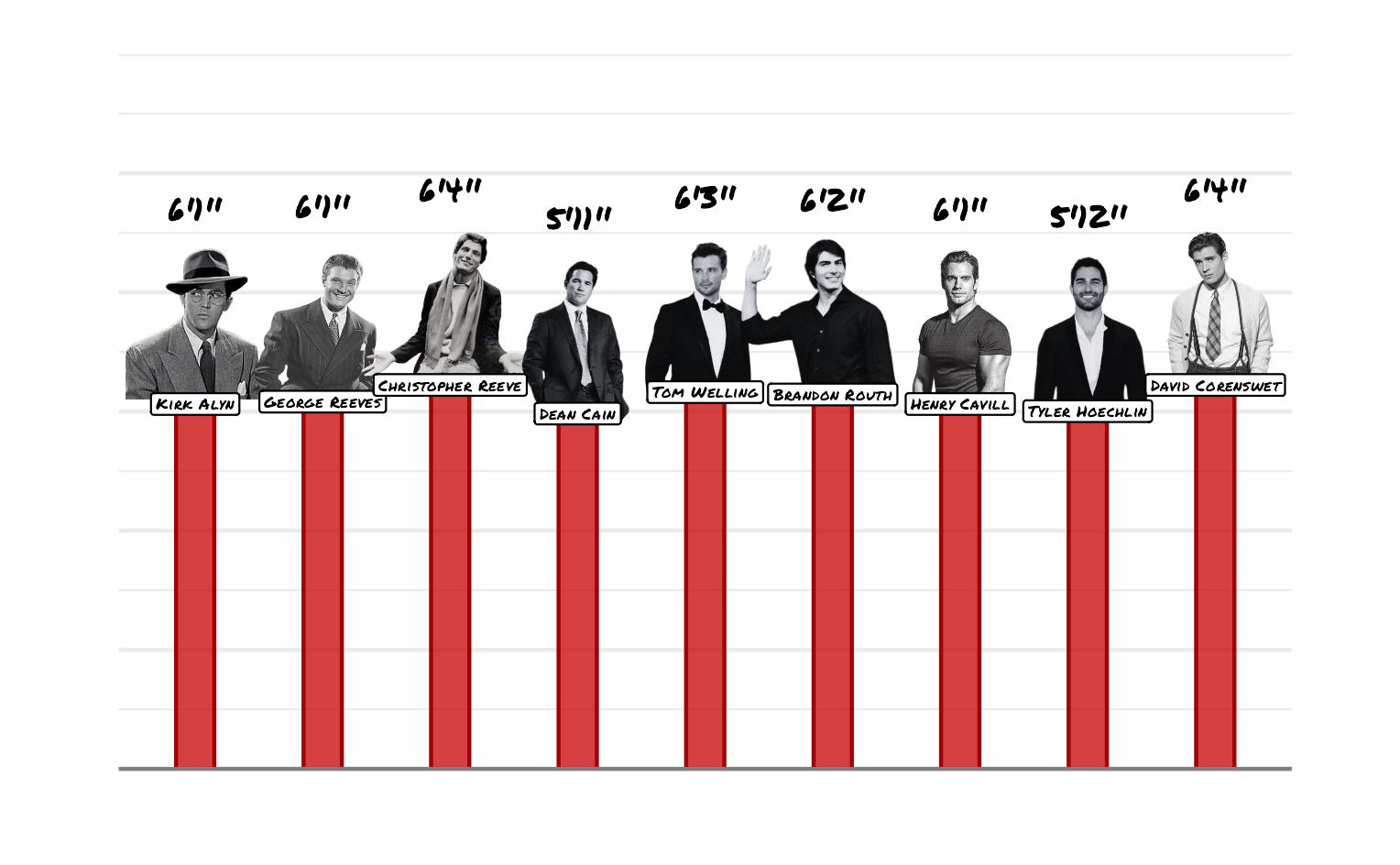
What is the relationship between Superman’s height and age?

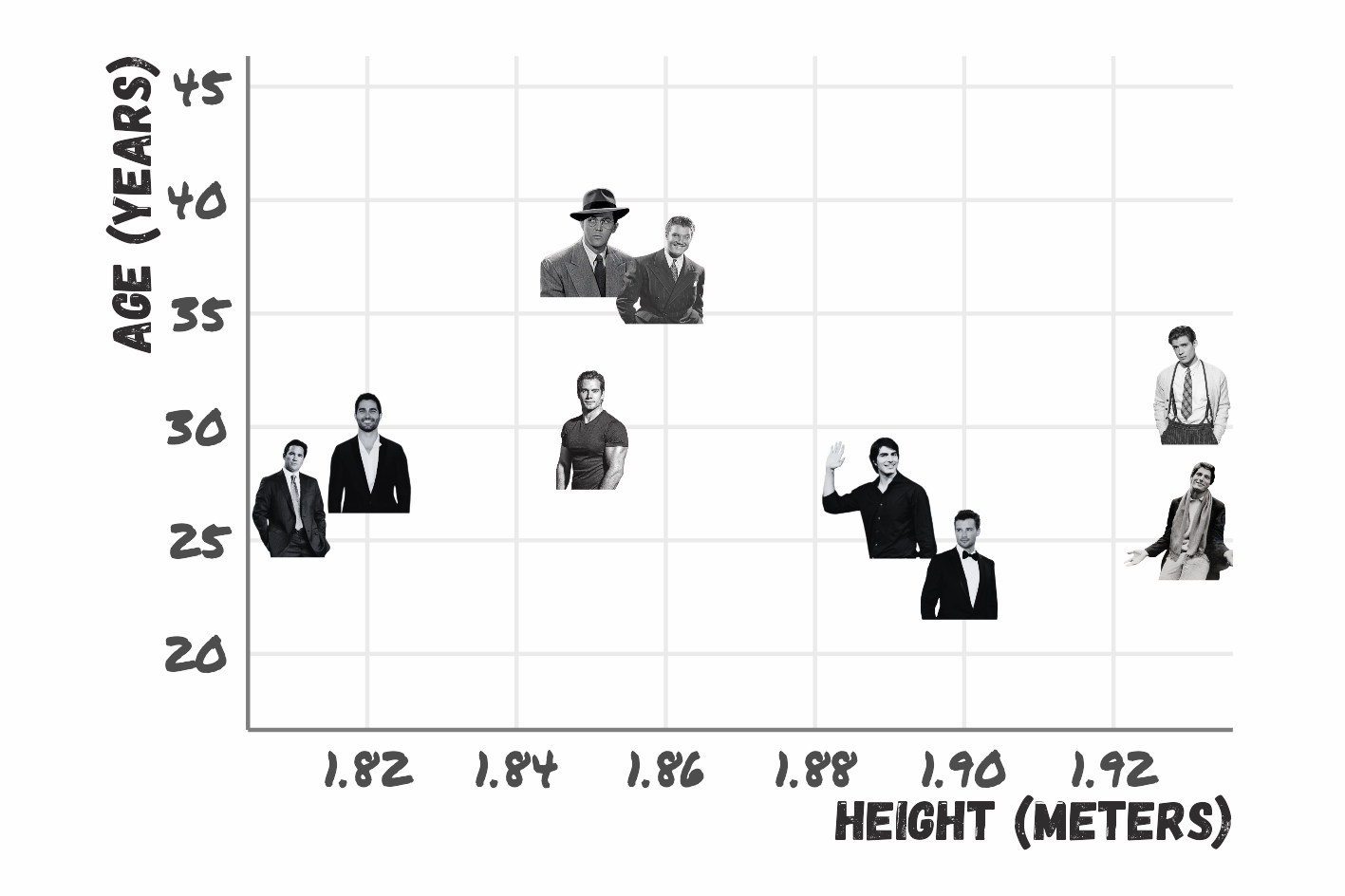

Correlation does not equal causation
Third Variable Problem
Another confounding variable might explain the relationship between the variables

Why conduct correlational research?
If cannot measure relationships otherwise…
Ethical considerations
Technological limitations
Cannot manipulate variables of interest
Research Ethics


Study Type 3: Experimental Research
Experimental methods control and explain.
Designing an experiment
- Enable scientists to have maximum control
- Independent variable (IV)
- Dependent variable (DV)
- Confounding variable(s)
- Any other variables
Independent variable is manipulated
Experimental/treatment group
- Participants who receive the treatment of interest
- Control/Comparison group
- Participants who DO NOT receive the treatment of interest
Participants need to be selected carefully…
Sampling is the process of selecting a group of individuals to participate in study
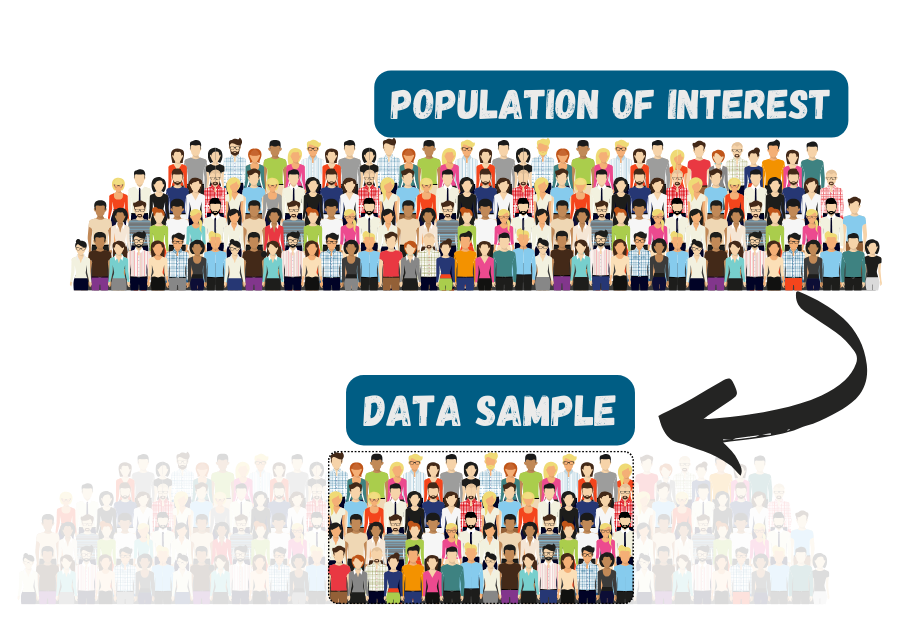
Sample should represent the population
And randomly assigned to an IV condition
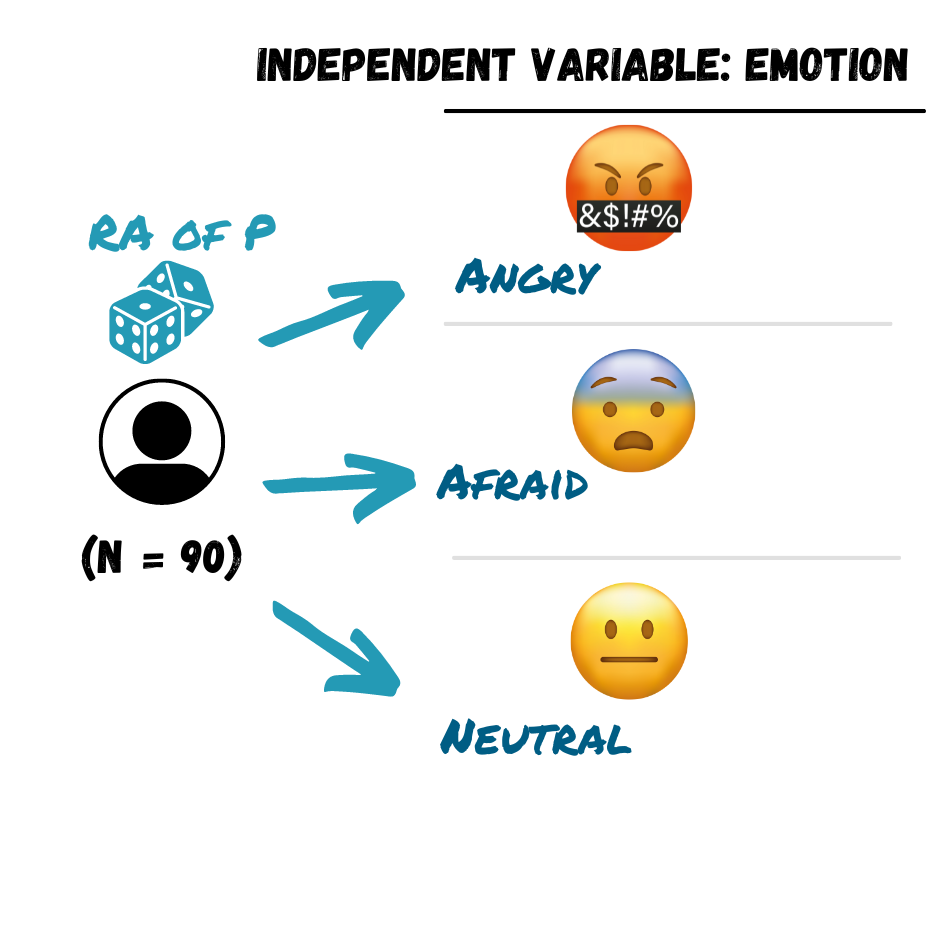
Random assignment controls for confounding variables
Random Assignment Needed for Causal Interpretation!
Allows researchers to assume
- Individual differences are evenly distributed between conditions
- All differences between the conditions are due to the treatment
Interpreting Results
Monty Hall Study

Our Class Data
N=34 out of 50 Students Responded
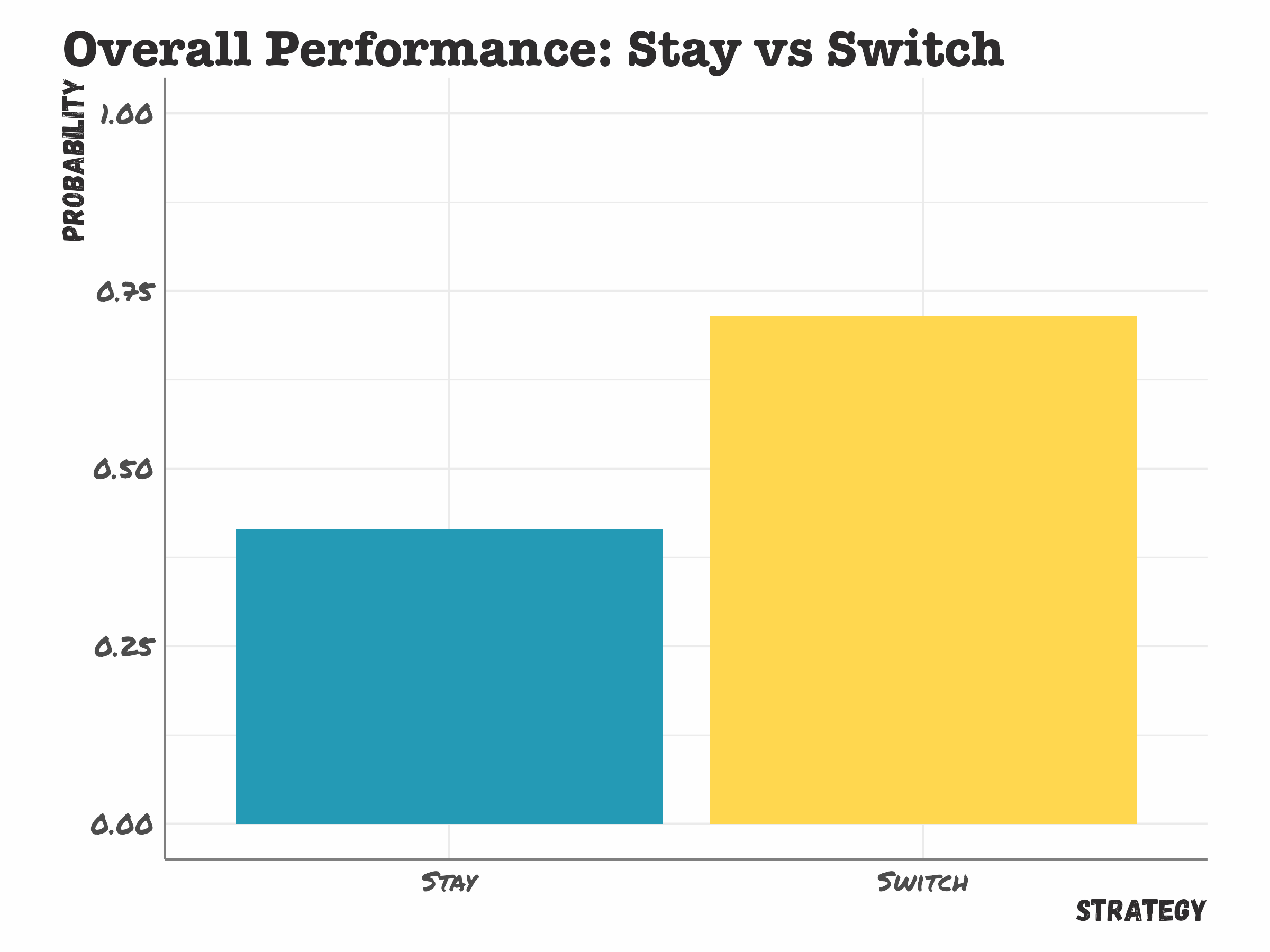
Monty Hall Performance
Relationship between Age and Performance?
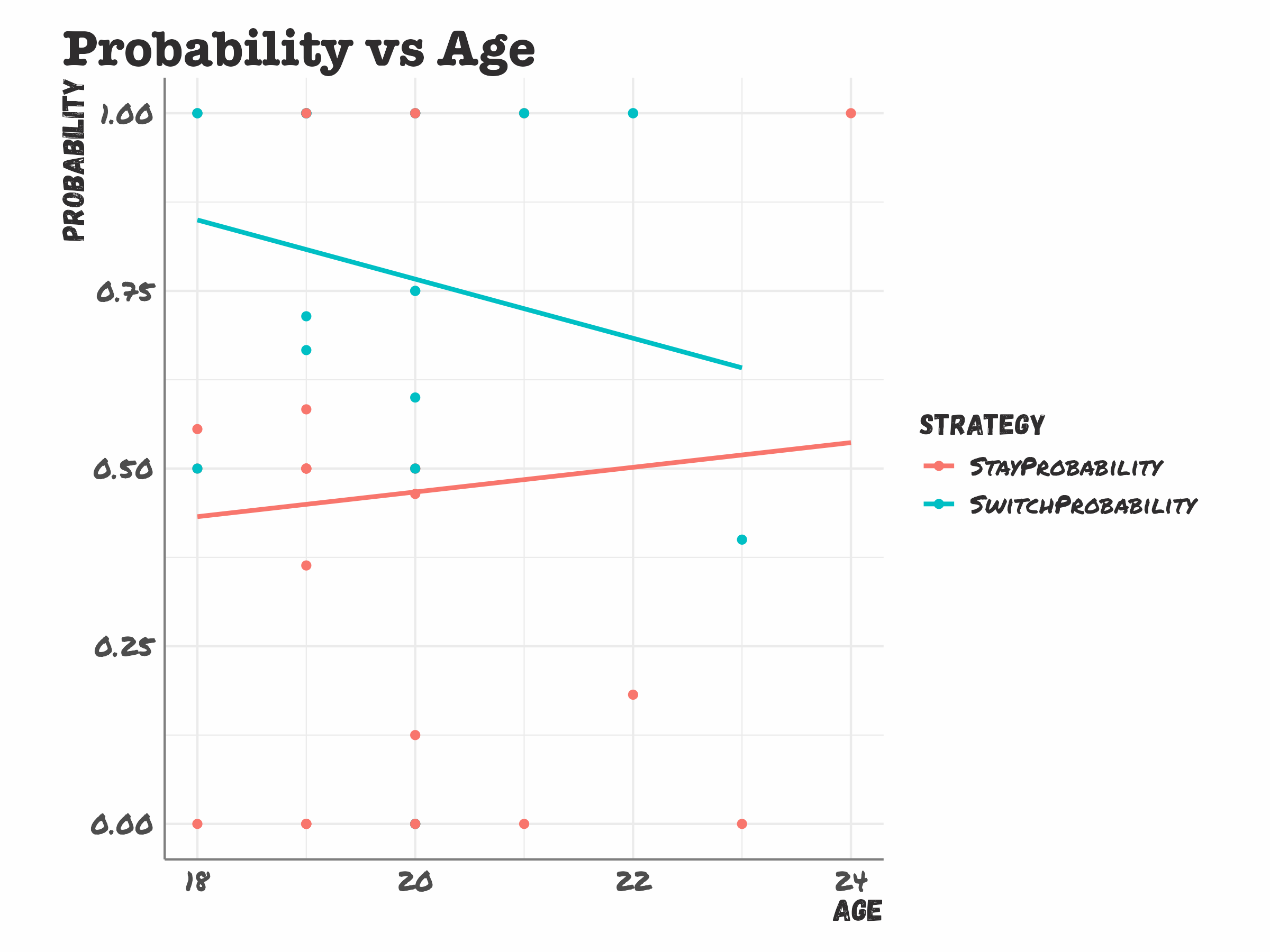
How can I interpret these findings?
Was this an experiment?
Our Class vs. Pigeons
Studies find that Pigeons outperform humans on this task

Herbranson & Schroeder (2010)

