🗓️ Unit 1
What is Psychology?
PSYC 181 – Intro to Psych
Emma Marshall – Instructor
What is Psychology?
Science of Psychology
![]()

Psychology science is the study of the mind, brain, and behavior.
Psychologists Use the scientific method to study
Psychological science requires critical thinking.
What is critical thinking?
![]()
Psychological science helps us understand biased or inaccurate thinking.
Humans are naive scientists
During daily life
- People tend to:
- Notice patterns
- Draw conclusions based on those patterns
BUT they are often wrong!
Why?
Use Mental Shortcuts
Overly positive self evaluations
Ignore evidence
Patterns are seen as causal
After the fact reasoning
Psychological science helps to explains how and why people think and behave
History of Psychology as a science
Modern Origins
William Wundt

Understanding the conscious experience through introspection
William James

How mental activities contributed to survival
Structuralism
Functionalism
Modern Origins
German

Understanding the conscious experience through introspection
American

How mental activities contributed to survival
Timeline
Famous Psychologists

Sigmund Freud
Let’s talk about Freud
Historical Perspectives
Behaviorism
Focuses on observing and controlling behavior
John B. Watson

Father of behaviorism
Focused on observable behavior and ways to bring that behavior under control (not mental)
Ivon Pavlov

Classical conditioning
Conditioned reflexes to pair stimulus and response
B. F. Skinner

Operant conditioning
Modifying behavior through reinforcement and punishment
John B. Watson
Focused on observable behavior and ways to bring that behavior under control (not mental)
Ivon Pavlov

Conditioned reflexes to pair stimulus and response
B. F. Skinner

Modifying behavior through reinforcement and punishment
Gestalt psychology
Argues the whole is greater than the sum of its parts
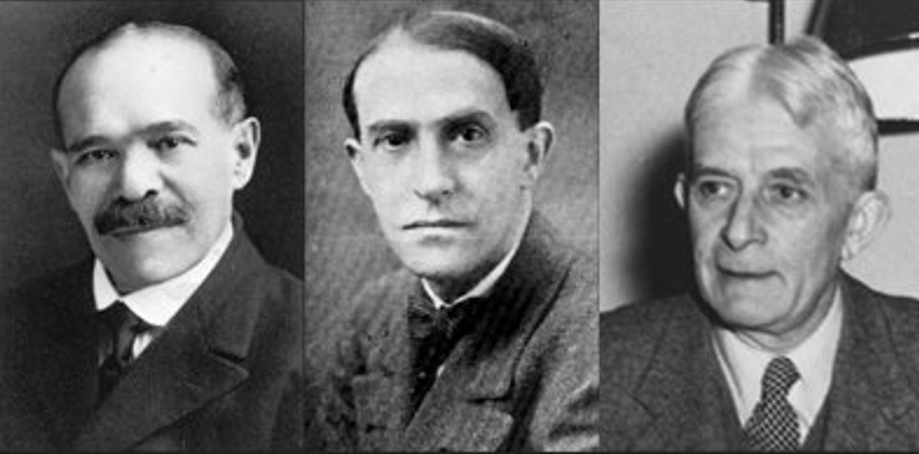

Kohler, Koffka and Wertheimer
Humanism
Emphasizes the potential for good that is innate to all humans
Carl Rogers

Where patient takes a lead role in the therapy session
Abraham Maslow

Proposed a hierarchy of human needs in motivating behavior
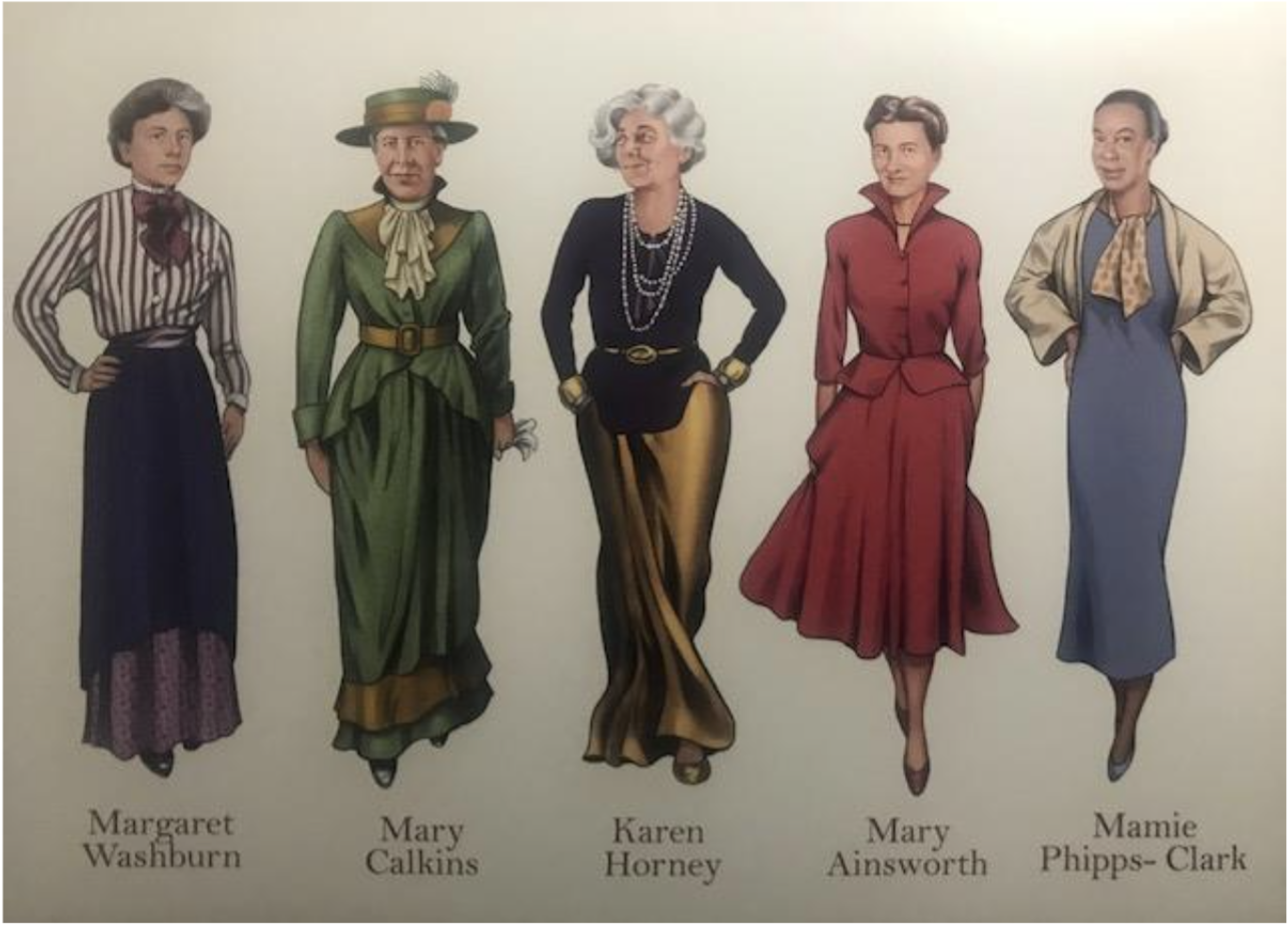
Women in Psychology

The Cognitive Revolution


Contemporary psychology
Modern Psychology
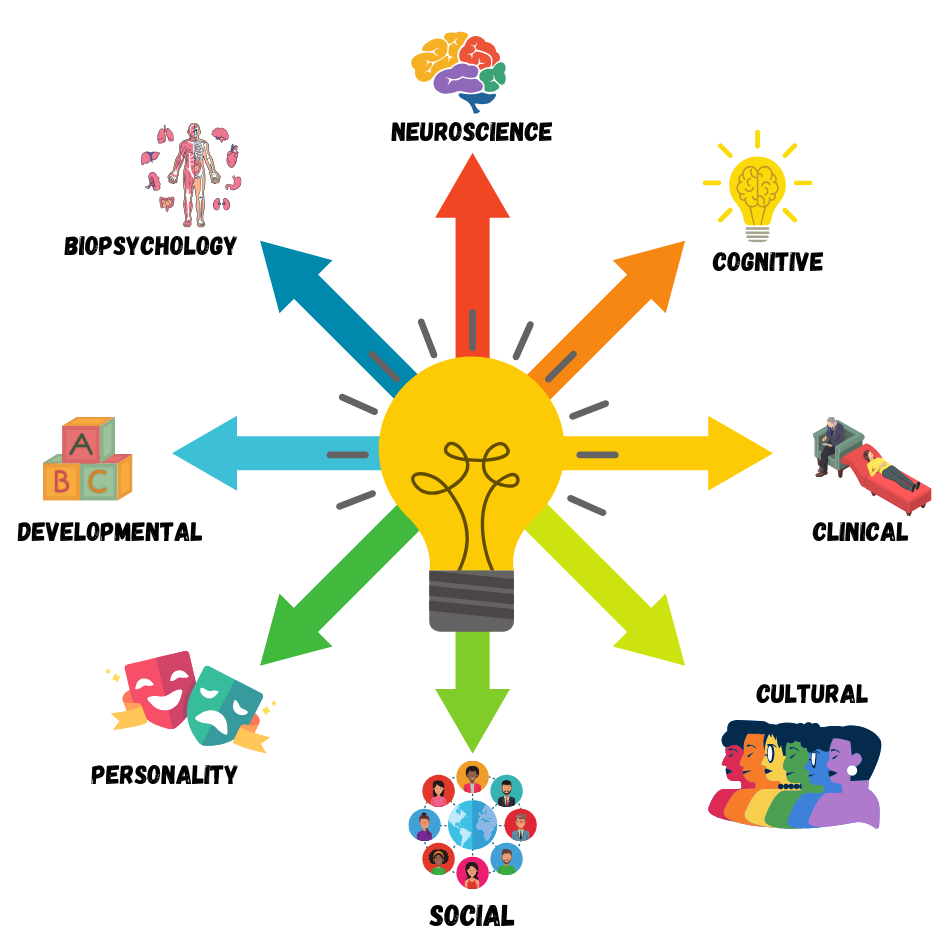
Applied Psychology

Careers in psychology
Top Occupations Employing Graduates with a BA in Psychology (Fogg, Harrington, Harrington, & Shatkin, 2012)
| Ranking | Occupation |
|---|---|
| 1 | Mid- and top-level management (executive, administrator) |
| 2 | Sales |
| 3 | Social work |
| 4 | Other management positions |
| 5 | Human resources (personnel, training) |
| 6 | Other administrative positions |
| 7 | Insurance, real estate, business |
| 8 | Marketing and sales |
| 9 | Healthcare (nurse, pharmacist, therapist) |
| 10 | Finance (accountant, auditor) |
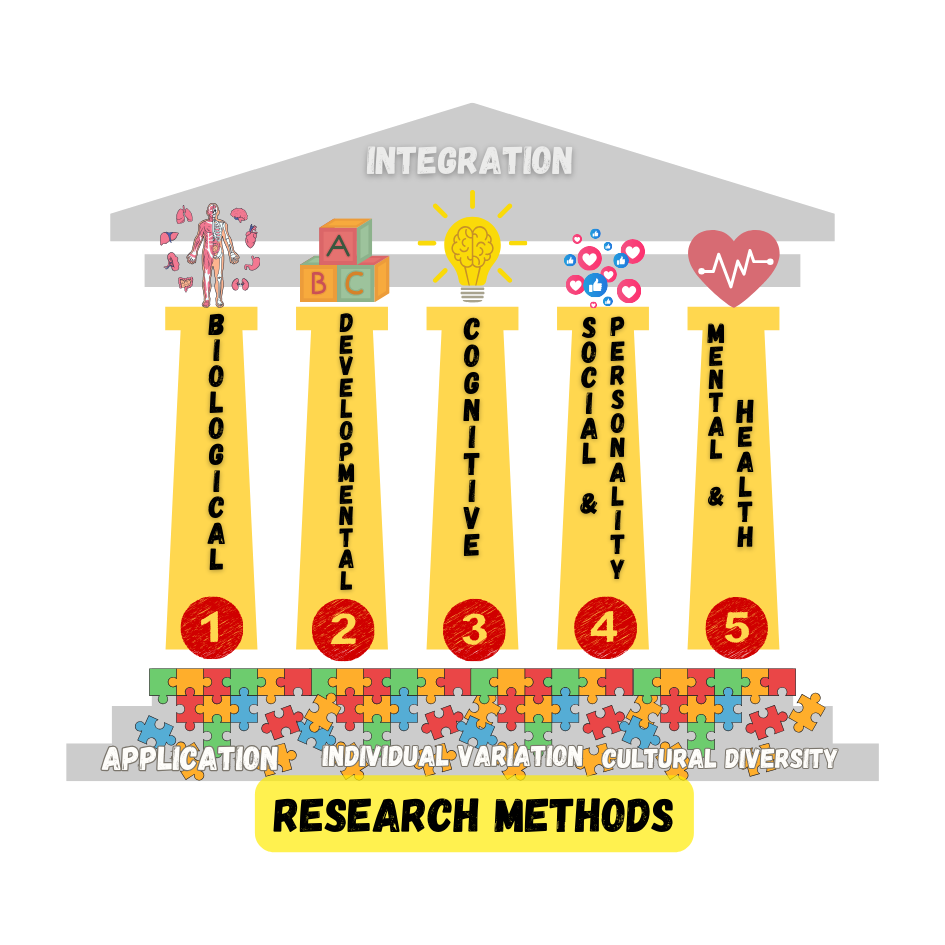
APA’s Pillars